Abstract
Background
Mammographic screening and increased awareness has led to an increase in the detection of T1 breast tumors that are generally estimated as having low risk of recurrence after locoregional treatment. However, even small tumors can metastasize, which leaves us with the question for the necessity of adjuvant treatment. Therefore, additional prognostic markers are needed to tailor adjuvant systemic treatment for these relatively low-risk patients. The aim of our study was to evaluate the accuracy of the 70-gene MammaPrint signature in T1 breast cancer.
Materials and Methods
We selected 964 patients from previously reported studies with pT1 tumors (≤2 cm). Frozen tumor samples were hybridized on the 70-gene signature array at the time of the initial study and classified as having good prognosis or poor prognosis.
Results
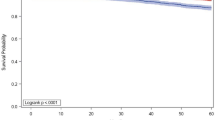
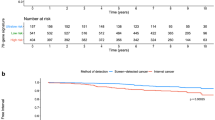
The median follow-up was 7.1 years (range 0.2–25.2). The 10-year distant metastasis-free (DMFS) and breast cancer specific survival (BCSS) probabilities were 87% (SE 2%) and 91% (SE 2%), respectively, for the good prognosis-signature group (n = 525), and 72% (SE 3%) and 72% (SE 3%), respectively, for the poor prognosis-signature group (n = 439). The signature was an independent prognostic factor for BCSS at 10 years (multivariate hazard ratio [HR] 3.25 [95% confidence interval, CI, 1.92–5.51; P < .001]). Moreover, the 70-gene MammaPrint signature predicted DMFS at 10 years for 139 patients with pT1ab cancers (HR 3.45 [95% CI 1.04–11.50, P = .04]).
Conclusions
The 70-gene MammaPrint signature is an independent prognostic factor in patients with pT1 tumors and can help to individualize adjuvant treatment recommendation in this increasing breast cancer population.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter CL, Allen C, Henson DE. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. 1989;63:181–7.
Fitzgibbons PL, Page DL, Weaver D, Thor AD, Allred DC, Clark GM, et al. Prognostic factors in breast cancer. College of American Pathologists Consensus Statement 1999. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000;124:966–78.
Koscielny S, Tubiana M, Le MG, Valleron AJ, Mouriesse H, Contesso G, et al. Breast cancer: relationship between the size of the primary tumour and the probability of metastatic dissemination. Br J Cancer. 1984;49:709–15.
Page DL. Prognosis and breast cancer. Recognition of lethal and favorable prognostic types. Am J Surg Pathol. 1991;15:334–49.
Rosen PP, Groshen S, Saigo PE, Kinne DW, Hellman S. Pathological prognostic factors in stage I (T1N0M0) and stage II (T1N1M0) breast carcinoma: a study of 644 patients with median follow-up of 18 years. J Clin Oncol. 1989;7:1239–51.
Bernards R, Weinberg RA. A progression puzzle. Nature. 2002;418:823.
Van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 2002;415:530–6.
Hanrahan EO, Valero V, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hortobagyi GN. Prognosis and management of patients with node-negative invasive breast carcinoma that is 1 cm or smaller in size (stage 1; T1a,bN0M0): a review of the literature. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2113–22.
Hanrahan EO, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Giordano SH, Rouzier R, Broglio KR, Hortobagyi GN, et al. Overall survival and cause-specific mortality of patients with stage T1a,bN0M0 breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:4952–60.
Eifel P, Axelson JA, Costa J, Crowley J, Curran WJ Jr, Deshler A, et al. National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Conference Statement: Adjuvant Therapy for Breast Cancer, November 1–3, 2000. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:979–89.
NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Breast Cancer V.I.2009. www.nccn.org. 2009.
Goldhirsch A, Ingle JN, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ, et al. Thresholds for therapies: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2009. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:1319–29.
Fracheboud J, Otto SJ, van Dijck JA, Broeders MJ, Verbeek AL, de Koning HJ. Decreased rates of advanced breast cancer due to mammography screening in The Netherlands. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:861–7.
Connor RJ, Chu KC, Smart CR. Stage-shift cancer screening model. J Clin Epidemiol. 1989;42:1083–95.
Chu KC, Smart CR, Tarone RE. Analysis of breast cancer mortality and stage distribution by age for the Health Insurance Plan clinical trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988;80:1125–32.
van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van ‘t Veer LJ, Dai H, Hart AA, Voskuil DW, et al. A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1999–2009.
Buyse M, Loi S, van’t Veer L, Viale G, Delorenzi M, Glas AM, et al. Validation and clinical utility of a 70-gene prognostic signature for women with node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:1183–92.
Bueno-de-Mesquita JM, Linn SC, Keijzer R, Wesseling J, Nuyten DS, van Krimpen C, et al. Validation of 70-gene prognosis signature in node-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;117:483–95.
Wittner BS, Sgroi DC, Ryan PD, Bruinsma TJ, Glas AM, Male A, et al. Analysis of the MammaPrint breast cancer assay in a predominantly postmenopausal cohort. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:2988–93.
Mook S, Schmidt MK, Viale G, Pruneri G, Eekhout I, Floore A, et al. The 70-gene prognosis-signature predicts disease outcome in breast cancer patients with 1–3 positive lymph nodes in an independent validation study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;116:295–302.
Mook S, Schmidt MK, Weigelt B, Kreike B, Eekhout I, van de Vijver MJ, et al. The 70-gene prognosis-signature predicts early metastasis in breast cancer patients between 55 and 70 years of age. Ann Oncol. 2009; Oct 13 (Epub ahead of print).
Bueno-de-Mesquita JM, van Harten WH, Retel VP, van’t Veer LJ, van Dam FS, Karsenberg K, et al. Use of 70-gene signature to predict prognosis of patients with node-negative breast cancer: a prospective community-based feasibility study (RASTER). Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:1079–87.
Kok M, Koornstra RH, Mook S, et al. Additional value of the 70-gene signature and levels of ER and PR for the prediction of outcome in tamoxifen-treated ER-positive breast cancer. 2009 (submitted).
CBO Richtlijn Mammacarcinoom 2008. http://www.cbo.nl/product/richtlijnen/folder20021023121843/rl_mamma_08.pdf.
Glas AM, Floore A, Delahaye LJ, Witteveen AT, Pover RC, Bkx N, et al. Converting a breast cancer microarray signature into a high-throughput diagnostic test. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:278–87.
Mook S, Bonnefoi H, Pruneri G, Larsimont D, Jaskiewicz J, Sabadell MD, et al. Daily clinical practice of fresh tumour tissue freezing and gene expression profiling; logistics pilot study preceding the MINDACT trial. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:1201–8.
West M, Blanchette C, Dressman H, Huang E, Ishida S, Spang R, et al. Predicting the clinical status of human breast cancer by using gene expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:11462–7.
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10869–74.
Huang E, Cheng SH, Dressman H, Pittman J, Tsou MH, Horng CF, et al. Gene expression predictors of breast cancer outcomes. Lancet. 2003;361:1590–6.
Andre F, Michiels S, Dessen P, Scott V, Suciu V, Uzan C, et al. Exonic expression profiling of breast cancer and benign lesions: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:381–90.
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005; 365:1687–1717.
Bender RA, Knauer M, Rutgers EJ, Glas AM, de Snoo FA, Linn SC, et al. The 70-gene profile and chemotherapy benefit in 1,600 breast cancer patients. ASCO Annual Meeting Proceedings 2009; J Clin Oncol. 2009;27 (Supplement; abstract No. 512).
Acknowledgment
We are indebted to Marleen Kok and Rutger Koornstra for providing part of the data used for our analyses and to Annuska M. Glas and Arno Floore of Agendia BV for hybridization of all tumor samples. We thank Marjanka K. Schmidt for helpful discussions. Laura J van’t Veer is named inventor on a 70 gene prognosis-signature patent. Laura J van’t Veer reports holding equity in Agendia BV.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Mook and M. Knauer contributed equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mook, S., Knauer, M., Bueno-de-Mesquita, J.M. et al. Metastatic Potential of T1 Breast Cancer can be Predicted by the 70-gene MammaPrint Signature. Ann Surg Oncol 17, 1406–1413 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0902-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-009-0902-x