Key Points
-
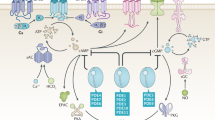
Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors are useful for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED), and a wide variety of chemotypes have shown activity as PDE5 inhibitors.
-
PDE5 inhibitors work in conjunction with sexual stimulation to induce erection, and have a low risk of priaprism.
-
Clinical studies with sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil indicate that these compounds are efficacious for the treatment of ED that is a consequence of various causes, and are safe for use in most patients.
-
Vardenafil and tadalafil have been submitted for regulatory approval in the US and European markets. Final approval and marketing of these compounds is pending the outcome of regulatory review.
-
There is substantial activity in the discovery of novel PDE5 inhibitors, some of which are more potent and selective than sildenafil in vitro.
-
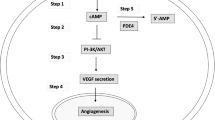
PDE5 inhibitors have also been investigated for actions on other tissues, including the gastrointestinal tract and the circulatory system. PDE5 inhibitors have been shown to reduce blood pressure in patients with pulmonary hypertension, and in animal models, have potential for use in the treatment of stroke.
Abstract
Phosphodiesterase enzymes convert cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP to the corresponding nucleotide monophosphates. Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibition is now a widely accepted and efficacious therapeutic option for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in men, as a result of extensive clinical experience with sildenafil and other new PDE5 inhibitors. Research in the field continues at a substantial level to identify new, selective PDE5 inhibitors and to investigate their usefulness and activity in other areas. This review summarizes recent clinical trials with PDE5 inhibitors, advances in medicinal chemistry, and other activities and potential applications of this class of compounds.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corbin, J. D. & Francis, S. H. Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase-5: target of sildenafil. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 13729–13732 (1999).
Fawcett, L. et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct human phosphodiesterase gene family: PDE11a. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3702–3707 (2000).
Francis, S. H., Lincoln, T. M. & Corbin, J. D. Characterization of a novel cGMP binding protein from rat lung. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 620–626 (1980).
McAllister-Lucas, L. M. et al. The structure of a bovine lung cGMP-binding, cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase deduced from a cDNA clone. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 22863–22873 (1993).
Corbin, J. D., Turko, I. V., Beasley, A. & Francis, S. H. Phosphorylation of phosphodiesterase-5 by cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase alters its catalytic and allosteric cGMP binding activities. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 2760–2767 (2000).
Lin, C.-S., Lau, A., Tu, R. & Lue, T. F. Expression of three isoforms of cGMP-binding, cGMP- specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5) in human penile tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 268, 628–635 (2000).
Yanaka, N. et al. Expression, structure and chromosomal localization of the human cGMP-binding, cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase PDE5A gene. Eur. J. Biochem. 255, 391–399 (1998).
Loughney, K. et al. Isolation and characterization of cDNAs encoding PDE5A, a human cGMP binding, cGMP specific 3′,5′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. Gene 216, 139–147 (1998).
Turko, I. V., Ballard, S. A., Francis, S. H. & Corbin, J. D. Inhibition of cyclic GMP binding, cyclic GMP specific phosphodiesterase 5 by sildenafil and related compounds. Mol. Pharmacol. 56, 124–130 (1999).
Turko, I. V., Francis, S. H. & Corbin, J. D. Hydropathic analysis and mutagenesis of the catalytic domain of the cGMP-binding and cGMP-specific phosphodiesterase 5. CGMP versus cAMP substrate selectivity. Biochemistry 37, 4200–4205 (1998).
Lue, T. F. Erectile dysfunction. N. Engl. J. Med. 324, 1802–1813 (2000).
Rotella, D. P. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors: discovery and therapeutic utility. Drugs Future 26, 153–162 (2001).
Kloner, R. A., Brown, M., Prisant, L. M. & Collins, M. Effect of sildenafil in patients with erectile dysfunction taking antihypertensive therapy. Am. J. Hypertens. 14, 70–73 (2001).An important summary of the safety and efficacy of sildenafil in a target population.
Conti, R. C., Pepine, C. J. & Sweeney, M. Efficacy and safety of sildenafil citrate in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with ischemic heart disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 83, 29C–34C (1999).
Price, D. E. et al. Sildenafil: a study of a novel oral treatment for erectile dysfunction in diabetic men. Diabetic Med. 15, 821–825 (1998).
Derry, F. A. et al. Efficacy and safety of oral sildenafil (Viagra™) in men with erectile dysfunction caused by spinal cord injury. Neurology 51, 1629–1633 (1998).
Fava, M., Rankin, M. A., Alpert, J. F., Nierenberg, A. A. & Worthington, J. J. An open trial of oral sildenafil in antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction. Psychother. Pyschosom. 67, 328–331 (1998).
Hanning, H. et al. Imidazo[5,1-f][1,2,4]triazin-4(3H)-ones: a new class of potent PDE5 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 12, 865–868 (2002).This paper describes the discovery of vardenafil.
Terret, N. K., Bell, A. S., Brown, D. & Ellis, P. Sildenafil (Viagra™) a potent and selective inhibitor of type 5 cGMP phosphodiesterase with utility for the treatment of male erectile dysfunction. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 6, 1819–1824 (1996).
Klotz, T. et al. Vardenafil increases penile rigidity and tumescence in erectile dysfunction patients: a RigiScan and pharmacokinetic study. World J. Urol. 19, 32–39 (2001).
Porst, H. et al. The efficacy and tolerability of vardenafil, a new oral selective phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor in patients with erectile dysfunction: the first at home clinical trial. Int. J. Impotence Res. 13, 192–199 (2001).This paper describes data obtained using a novel clinical-trial design.
Vardenafil effective and safe as ED therapy in men with prostatectomy, CAD and hypertension. Prous Daily Essentials (February 27, 2002).
US delay for Lilly Icos's Cialis. Scrip World Pharmaceutical News (May 1, 2002).
Porst, H. IC351 (tadalafil, Cialis™): update on clinical experience. Int. J. Impotence Res. 14 (Suppl. 1), S57–S64 (2002).A useful summary of the activity of tadalafil in clinical trials.
Porst, H. et al. Tadalafil allows men with erectile dysfunction to have successful intercourse up to 36 hours postdose. J. Urol. 167 (Suppl.), 177 (2002).
Padma-Nathan, H., Rosen, R. C., Shobsigh, R., Watkins, V. S. & Pullman, B. Cialis (IC351) provides prompt response and extended responsiveness for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. J. Urol. 165 (Suppl.), 224 (2001).
Hutter, A. M. et al. Blood pressure and cardiovascular effects of tadalafil, a new PDE5 inhibitor. Am. J. Hypertens. 15 (Part 2), 140A (2002).
Padma-Nathan, H. et al. Efficacy and safety of tadalafil in men with erectile dysfunction with and without hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 15 (Part 2), 143A (2002).This abstract describes the safety and efficacy profile of tadalafil in an important target population.
Vivus cleared to proceed with TA-1790 trial in erectile dysfunction. Prous Daily Essentials (January 22, 2002).
Oh, T. Y., Kang, K. K., Ahn, B. O., Yoo, M. & Kim, W. B. Erectogenic effect of the selective phosphodiesterase inhibitor DA-8159. Arch. Pharm. Res. 23, 471–476 (2000).
Hosogai, N. et al. FR226807: a potent and selective phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor. Eur. J. Pharmcol. 428, 295–302 (2001).
Kotera, J. et al. Characterization and effects of methyl-2-(4-aminophenyl)-1,2-dihydro-1-oxo-7-(2-pyridylmethoxy)-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3-isoquinoline carboxylate sulfate (T-1032) a novel potent inhibitor of cGMP-binding, cBMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE5). Biochem. Pharmacol. 60, 1333–1341 (2000).
Takagi, M. et al. Pharmacologic profile of T-1032, a novel, specific phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor in isolated rat aorta and rabbit corpus cavernosum. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 411, 161–168 (2001).
Inoue, H., Yano, K., Ikeo, T., Noto, T. & Kikkawa, K. T-1032 a novel specific phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor increases venous compliance in anesthetized rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 422, 109–114 (2001).
Ukita, T. et al. Novel potent and selective PDE5 inhibitors: synthesis and biological activities of a series of 4-aryl-1-isoquinolinone derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 44, 2204–2218 (2001).
Hirose, R. et al. KF31327 a new potent and selective inhibitor of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 5. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 431, 17–24 (2001).
Kim, D.-K. et al. Synthesis and phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitory activity of novel phenyl ring modified sildenafil analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 1609–1616 (2001).
Kim, D.-K. et al. Synthesis and phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitory activity of new 5-phenyl-1,6-dihydro-7H-pyrazolo-[4,3d]pyrimidin-7-one derivatives containing an N-acylamido group on a phenyl ring. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 1895–1899 (2001).
Rotella, D. P. et al. N-3-substituted imidazoquinazolinones: potent and selective PDE5 inhibitors as potential agents for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. J. Med. Chem. 43, 1257–1263 (2001).
Kim, D.-K. et al. Synthesis and phosphodiesterase inhibitory activity of new sildenafil analogs containing a carboxylic acid group in the 5′-sulfonamide moiety of a phenyl ring. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 9, 3013–3021 (2001).
Bi, Y. et al. The discovery of novel potent and selective PDE5 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem Lett. 11, 2461–2464 (2001).
Yu, G. et al. Substituted pyrazolopyridines as potent and selective PDE5 inhibitors: potential agents for treatment of erectile dysfunction. J. Med. Chem. 44, 1025–1027 (2001).
Kumar, V. & Dority, J. A. Jr. Preparation of N-cycloalkylmethyl-1H-pyrazolo[3,4b]quinoline-4-amines as cGMP phosphodiesterase inhibitors. US patent 5,488,055 (1996).
Vemulapalli, S. & Kuroski, S. Sildenafil relaxes rabbit clitoral corpus cavernosum. Life Sci. 67, 23–29 (2000).
Min, K. et al. Sildenafil augments pelvic nerve mediated female genital sexual arousal in the anesthetized rabbit. Int. J. Impotence Res. 12 (Suppl. 3), S32–S39 (2000).
Reis, R. B. et al. Safety and efficacy of sildenafil in postmenopausal women with sexual dysfunction. Urology 53, 481–486 (1999).
Caruso, S., Intelisano, G., Lupo, L. & Agnello, C. Premenopausal women affected by sexual arousal disorder treated with sildenafil: a double-blind, cross-over, placebo-controlled study. Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 108, 623–628 (2001).
McPherson, M. A., Pereira, M. M. C., Mills, C. L., Murray, K. J. & Dormer, R. L. A cyclic nucleotide PDE5 inhibitor corrects defective mucin secretion in submandibular cells containing antibody directed against the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein. FEBS Lett. 464, 48–52 (1999).
Bortolotti, M., Mari, C., Lopilato, C., Porrazzo, G. & Miglioli, M. Effects of sildenafil on esophageal motility of patients with idiopathic achalasia. Gastroenterology 118, 253–257 (2000).
Bortolotti, M., Mari, C., Lopilato, C., La Rovere, L. & Miglioli, M. Sildenafil inhibits gastroduodenal motility. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 15, 157–161 (2001).
Wilkens, H. et al. Effect of inhaled iloprost plus oral sildenafil in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 104, 1218–1222 (2001).
Sobey, C. G. Cerebrovascular dysfunction after subarachnoid hemorrhage: novel mechanisms and directions for therapy. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 28, 926–929 (2001).
Sildenafil demonstrates beneficial activity in rat model of cerebral ischemia. Prous Daily Essentials (February 7, 2002).
Berkels, R., Klotz, T., Sticht, G., Englemann, U. & Klaus, W. Modulation of human platelet aggregation by the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor sildenafil. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 37, 413–421 (2001).
Soderling, S. H. & Beavo, J. A. Regulation of cAMP and cGMP signalling: new phosphodiesterases and new functions. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 12, 174–179 (2000).
Acknowledgements
The assistance of V. Florio and K. Fowler in the preparation of this review is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Related links
Related links
DATABASES
LocusLink
Medscape DrugInfo
OMIM
FURTHER INFORMATION
Investigational Drugs Database
LINKS
Glossary
- CORPUS CAVERNOSUM
-
The vascular space in erectile tissue.
- PENDANT
-
A functional group that is attached to another in a molecule.
- HYDROPATHY
-
The analysis of the hydrophobic and hydrophilic characteristics of molecules.
- HAEMODYNAMIC
-
Relating to physical aspects of blood circulation.
- PRIAPRISM
-
A persistent erection of the penis resulting from causes other than sexual stimulation.
- PLETHYSMOGRAPHY
-
The measurement and recording of changes in volume of an organ or structure.
- TUMESCENCE
-
Becoming swollen.
- ISOSTERE
-
Isosteres are atoms or functional groups of similar size and molecular orientation relative to each other.
- HETEROATOMS
-
Atoms other than carbon or hydrogen in a molecule.
- TORSIONAL
-
The freedom or ability to rotate along a defined angle.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rotella, D. Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors: current status and potential applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1, 674–682 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd893
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd893
This article is cited by
-
Capillary leak and endothelial permeability in critically ill patients: a current overview
Intensive Care Medicine Experimental (2023)
-
Neutrophils as potential therapeutic targets in hepatocellular carcinoma
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (2022)
-
Current and emerging drug targets in heart failure treatment
Heart Failure Reviews (2022)
-
Selectivity mechanism of phosphodiesterase isoform inhibitor through in silico investigations
Journal of Molecular Modeling (2022)
-
Maternal tadalafil therapy for fetal growth restriction prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and adipocyte hypertrophy in the offspring
Scientific Reports (2021)