Abstract
Background:
We have previously shown that by term age, preterm infants have elevated intrahepatocellular lipid (IHCL) content and altered regional adiposity, both of which are risk factors for cardiometabolic illness in adult life. Preterm nutritional intake is a plausible determinant of these aberrant trajectories of development.
Objective:
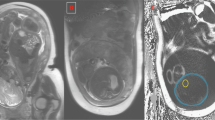
We aimed to establish if macronutritional components of the preterm diet were determinants of IHCL deposition measured at term equivalent age, using 1H Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy (MRS).
Methods:
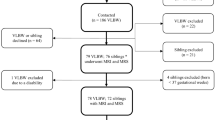
Prospective observational case–control study in a single UK neonatal unit. 1H MR spectra were acquired from 18 preterm infants (<32 weeks gestational age at birth) at term age and 31 healthy term infants, who acted as a control group. Neonatal nutritional information was collected from birth to 34+6 weeks postmenstrual age.
Results:
IHCL (median, interquartile range) was significantly higher in preterm-at-term infants compared with term-born infants: 0.735, 0–1.46 versus 0.138, 0–0.58; P=0.003. In preterm infants, IHCL was positively correlated with lipid intake in the first week of life (r=0.52, P=0.04).
Conclusions:
This study confirms our previous observation of elevated IHCL in preterm infants at term and suggests that early lipid intake may be a determinant. Future work is warranted to establish the clinical relevance and the role of nutritional intervention in attenuating or exacerbating this effect in preterm infants.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Doyle LW, Faber B, Callanan C, Morley R . Blood pressure in late adolescence and very low birth weight. Pediatrics 2003; 111: 252–257.
Julka D, Karatza A, Hartnoll G, Gardiner H, Modi N . The influence of preterm birth on cardiovascular development at term. Neonatal Society Spring Meeting (Abstract) 2009.
Hofman PL, Regan F, Jackson WE, Jefferies C, Knight DB, Robinson EM et al. Premature birth and later insulin resistance. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 2229–2231.
Kajantie E, Osmond C, Barker DJP, Eriksson JG . Preterm birth-a risk factor for type 2 diabetes?: the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2010; 33: 2623–2625.
Uthaya S, Thomas EL, Hamilton G, Dore CJ, Bell J, Modi N . Altered adiposity after extremely preterm birth. Pediatr Res 2005; 57: 211–215.
Thomas EL, Parkinson JR, Hyde MJ, Yap IKS, Holmes E, Doré C et al. Aberrant adiposity and ectopic lipid deposition characterize the adult phenotype of the preterm infant. Ped Res 2011; 70: 507–512.
Thomas EL, Uthaya S, Vasu V, McCarthy JP, McEwan P, Hamilton G et al. Neonatal intrahepatocellular lipid. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008; 93: F382–F383.
Georgoff P, Thomasson D, Louie A, Fleischman E, Dutcher L, Mani H et al. Hydrogen-1 MR spectroscopy for measurement and diagnosis of hepatic steatosis. Am J Roentgenol 2012; 199: 2–7.
Thomas EL, Hamilton G, Patel N, O’Dwyer R, Doré CJ, Goldin RD et al. Hepatic triglyceride content and its relation to body adiposity: a magnetic resonance imaging and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Gut 2005; 54: 122–127.
Vasu V, Modi N . Assessing the impact of preterm nutrition. Early Hum Dev 2007; 83: 813–818.
Bottomley PA . Spatial localization in NMR spectroscopy in vivo. Ann NY Acad Sci 1987; 508: 333–348.
Vanhamme L, van den Boogaart A, Van Huffel S . Improved method for accurate and efficient quantification of MRS data with use of prior knowledge. J Magn Reson 1997; 129: 35–43.
Naressi A, Couturier C, Devos JM, Janssen M, Mangeat C, de Beer R et al. Java-based graphical user interface for the MRUI quantitation package. MAGMA 2001; 12: 141–152.
Emery JL, Finch E . The fat and water content of the left and right liver before and after birth. Arch Dis Child 1954; 29: 242–247.
Tsang RC . Appendix 3-summary of reasonable nutrient intakes (mass units) for preterm infants. In: Tsang R, Uauy R, Koletzko B, Zlotkin SH, (eds). Nutrition of the Preterm Infant: Scientific Basis and Practical Guidelines 2nd edn. Digital Education Publishing, Inc.: Cincinnati, OH, 2005. pp 415–416.
Hyde MJ, Amusquivar E, Laws J, Corson AM, Geering RR, Lean IJ et al. Effects of lipid-supplemented total parenteral nutrition on fatty liver disease in a premature neonatal piglet model. Neonatology 2008; 93: 77–86.
Rodekamp E, Harder T, Kohlhoff R, Franke K, Dudenhausen JW, Plagemann A . Long-term impact of breast-feeding on body weight and glucose tolerance in children of diabetic mothers: role of the late neonatal period and early infancy. Diabetes Care 2005; 28: 1457–1462.
Bortolotti M, Kreis R, Debard C, Cariou B, Faeh D, Chetiveaux M et al. High protein intake reduces intrahepatocellular lipid deposition in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 2009; 90: 1002–1010.
Regan FM, Cutfield WS, Jefferies C, Robinson E, Hofman PL . Theimpact of early nutrition in premature infants on later childhood insulin sensitivity and growth. Pediatrics 2006; 118: 1943–1949.
Modi N, Murgasova D, Ruager-Martin R, Thomas EL, Hyde MJ, Gale C et al. The influence of maternal body mass index on infant adiposity and hepatic lipid content. Pediatr Res 2011; 70: 287–291.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the parents and patients for agreeing to participate in this study, support by grants from Medical Research Council UK and Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and the infrastructure support from the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre funding scheme at Imperial College London. This work was supported by grants from Medical Research Council UK and Chelsea and Westminster Hospital NHS Foundation Trust.
Author contributions
VV, NM, JDB designed the study, VV conducted research, collected and analysed nutritional data, GD provided MR imaging support, ELT analysed IHCL data, VV performed statistical analysis, VV, ELT, GD, MJH, JDB, NM wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vasu, V., Thomas, E., Durighel, G. et al. Early nutritional determinants of intrahepatocellular lipid deposition in preterm infants at term age. Int J Obes 37, 500–504 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.213
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.213