Abstract
Background:
No nationally representative data from middle- and low-income countries have been analyzed to compare the prevalence of underweight and overweight, defined by using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the International Obesity TaskForce (IOTF) body mass index cut points.
Objective:
To examine the consistency in the prevalence of underweight and overweight, defined by using the CDC and IOTF cut points in Chinese, Indonesian and Vietnamese children.
Methods:
We used data from 1600 Chinese, 11 756 Indonesian and 53 826 Vietnamese children aged 2–18 years, who participated in three recent, representative surveys in China, Indonesia and Vietnam. A smaller difference between prevalence and a higher κ-statistic indicated a higher consistency level.
Results:
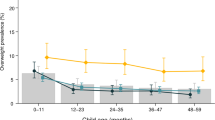
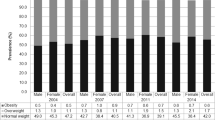
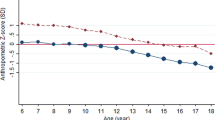
The prevalence of underweight was higher with the IOTF than the CDC cut points; absolute differences in the Chinese, Indonesian and Vietnamese were 6, 10 and 13% (boys), and 10, 13 and 19% (girls), respectively. The prevalence of overweight was more consistent (absolute differences were <2%, except for the 2–5.9-year-old Chinese and Indonesian children (from 2 to <5%)). Values of κ-statistic (from 0.55 to 0.88) varied by age, sex and ethnicity. The consistency was gradually improving from the Vietnamese to Indonesians and to Chinese boys and girls, from girls to boys, from the younger to older boys and from the older to younger girls.
Conclusions:
The age, sex and ethnic differences in the prevalence of underweight and overweight suggest a systematic evaluation of the cut points.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow SE (2007). Expert committee recommendations regarding the prevention, assessment, and treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity: summary report. Pediatrics 120, S164–S192.
Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM, Dietz WH (2000). Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ 320, 1240–1243.
Cole TJ, Flegal KM, Nicholls D, Jackson AA (2007). Body mass index cut offs to define thinness in children and adolescents: international survey. BMJ 335, 194.
Daniels SR, Khoury PR, Morrison JA (1997). The utility of body mass index as a measure of body fatness in children and adolescents: differences by race and gender. Pediatrics 99, 804–807.
Euling SY, Herman-Giddens ME, Lee PA, Selevan SG, Juul A, Sorensen TI et al. (2008a). Examination of US puberty-timing data from 1940 to 1994 for secular trends: panel findings. Pediatrics 121 (Suppl 3), S172–191.
Euling SY, Selevan SG, Pescovitz OH, Skakkebaek NE (2008b). Role of environmental factors in the timing of puberty. Pediatrics 121 (Suppl 3), S167–S171.
Guillaume M (1999). Defining obesity in childhood: current practice. Am J Clin Nutr 70, 126S–1130.
Hesketh T, Ding QJ (2000). Standard definition of child overweight and obesity worldwide. Young Chinese people in Hong Kong are not representative of those in China. BMJ 321, 1158–1159.
Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Srinivasan SR, Chen W, Malina RM, Bouchard C et al. (2005). Utility of childhood BMI in the prediction of adulthood disease: comparison of national and international references. Obesity 13, 1106–1115.
Kaplowitz P (2006). Pubertal development in girls: secular trends. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 18, 487–491.
Ko G, Ozaki R, Wong G, Kong A, So W-Y, Tong P et al. (2008). The problem of obesity among adolescents in Hong Kong: a comparison using various diagnostic criteria. BMC Pediatr 8, 10.
Kuczmarski RJ, Ogden CL, Guo SS (2002). CDC growth charts for the United States: Methods and development: National Center for Health Statistics. Vital Health Stat 11 (246): 1–190.
Ministry of Health—General Statistical Office (2003). The Report: Results of the Vietnam National Health Survey 2001-2002. Medical Publishing House: Hanoi.
Murray CJ, Lopez AD (1997). Global mortality, disability, and the contribution of risk factors: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 349, 1436–1442.
Must A, Anderson SE (2006). Body mass index in children and adolescents: considerations for population-based applications. Int J Obes 30, 590–594.
Must A, Dallal GE, Dietz WH (1991). Reference data for obesity: 85th and 95th percentiles of body mass index (wt/ht2) and triceps skinfold thickness. Am J Clin Nutr 53, 839–846.
Neovius M, Linne Y, Barkeling B, Rossner S (2004). Discrepancies between classification systems of childhood obesity. Obes Rev 5, 105–114.
O'Neill JL, McCarthy SN, Burke SJ, Hannon EM, Kiely M, Flynn A et al. (2006). Prevalence of overweight and obesity in Irish school children, using four different definitions. Eur J Clin Nutr 61, 743–751.
Pan H, Cole TJ (2008). lmsGrowth, a Microsoft Excel add-in to access growth references based on the LMS method. Version 2.64.
Parent AS, Teilmann G, Juul A, Skakkebaek NE, Toppari J, Bourguignon JP (2003). The timing of normal puberty and the age limits of sexual precocity: variations around the world, secular trends, and changes after migration. Endocr Rev 24, 668–693.
Popkin BM (2006). Global nutrition dynamics: the world is shifting rapidly toward a diet linked with noncommunicable diseases. Am J Clin Nutr 84, 289–298.
Popkin BM, Paeratakul S, Zhai F, Ge K (1995). Dietary and environmental correlates of obesity in a population study in China. Obes Res 3 (Suppl 2), 135s–143s.
Reichenheim ME (2004). Confidence intervals for the kappa statistic. Stata J 4, 421–428.
Rosner B (2006). Hypothesis testing: categorical data. In: Rosner B (ed). Fundamentals of Biostatistics. Thomson-Brooks/Cole: Belmont, CA. pp. 385–463.
Strauss J, Beegle K, Sikoki B, Dwiyanto A, Herawati Y, Witoelar F (2004). The third wave of the Indonesia Family Life Survey (IFLS3): overview and field report: RAND Labor and Population WR-144/1-NIA/NICHD.
Tuan NT, Tuong PD, Popkin BM (2008). Body mass index (BMI) dynamics in Vietnam. Eur J Clin Nutr 62, 78–86.
Vidal E, Carlin E, Driul D, Tomat M, Tenore A (2006). A comparison study of the prevalence of overweight and obese Italian preschool children using different reference standards. Eur J Pediatr 165, 696–700.
Voss LD, Metcalf BS, Jeffery AN, Wilkin TJ (2006). IOTF thresholds for overweight and obesity and their relation to metabolic risk in children (EarlyBird 20). Int J Obes (Lond) 30, 606–609.
Wang Y, Adair L (2001). How does maturity adjustment influence the estimates of overweight prevalence in adolescents from different countries using an international reference? Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25, 550–558.
Wehkalampi K, Silventoinen K, Kaprio J, Dick DM, Rose RJ, Pulkkinen L et al. (2008). Genetic and environmental influences on pubertal timing assessed by height growth. Am J Hum Biol 20, 417–423.
WHO (2005). Preventing Chronic Diseases: A Vital Investment: WHO Global Report. WHO: Geneva.
WHO Expert Committee (1995). Physical Status: The Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry. WHO: Geneva.
World Bank (2008). World Development Indicators 2008. World Bank Publications: Washington, DC.
Wyshak G, Frisch RE (1982). Evidence for a secular trend in age of menarche. N Engl J Med 306, 1033–1035.
Zimmermann MB, Gubeli C, Puntener C, Molinari L (2004). Detection of overweight and obesity in a national sample of 6-12-y-old Swiss children: accuracy and validity of reference values for body mass index from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the International Obesity Task Force. Am J Clin Nutr 79, 838–843.
Acknowledgements
The study was finally supported by the Vietnam Educational Foundation (VEF) and the USDA ARS CRIS 6250-51000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on European Journal of Clinical Nutrition website (http://www.nature.com/ejcn)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuan, N., Nicklas, T. Age, sex and ethnic differences in the prevalence of underweight and overweight, defined by using the CDC and IOTF cut points in Asian children. Eur J Clin Nutr 63, 1305–1312 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.90
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2009.90
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Prevalence of thinness and its effect on height velocity in schoolchildren
BMC Research Notes (2021)
-
Eating behaviour and weight status at 2 years of age: data from the Cork BASELINE Birth Cohort Study
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2015)
-
Weight Perception and Dietary Intake among Chinese Youth, 2004–2009
International Journal of Behavioral Medicine (2014)
-
Childhood obesity in developing countries
World Journal of Pediatrics (2010)