Abstract
Rivaroxaban is an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor that targets free and clot-bound Factor Xa and Factor Xa in the prothrombinase complex. It is absorbed rapidly, with maximum plasma concentrations being reached 2–4 h after tablet intake. Oral bioavailability is high (80–100 %) for the 10 mg tablet irrespective of food intake and for the 15 mg and 20 mg tablets when taken with food. Variability in the pharmacokinetic parameters is moderate (coefficient of variation 30–40 %). The pharmacokinetic profile of rivaroxaban is consistent in healthy subjects and across a broad range of different patient populations studied. Elimination of rivaroxaban from plasma occurs with a terminal half-life of 5–9 h in healthy young subjects and 11–13 h in elderly subjects. Rivaroxaban produces a pharmacodynamic effect that is closely correlated with its plasma concentration. The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic relationship for inhibition of Factor Xa activity can be described by an E max model, and prothrombin time prolongation by a linear model. Rivaroxaban does not inhibit cytochrome P450 enzymes or known drug transporter systems and, because rivaroxaban has multiple elimination pathways, it has no clinically relevant interactions with most commonly prescribed medications. Rivaroxaban has been approved for clinical use in several thromboembolic disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) have been the only oral anticoagulants available for clinical use for many decades. Although effective, VKAs have a slow onset and offset of action, numerous food–drug and drug–drug interactions, and an unpredictable pharmacodynamic response that necessitate routine coagulation monitoring and dose adjustment [1]. Direct oral anticoagulants that specifically target a single coagulation factor (such as Factor Xa or thrombin) have been developed in recent years to overcome the limitations of established anticoagulants. Factor Xa plays a central role in blood coagulation and is activated by both the intrinsic and extrinsic coagulation pathways. Factor Xa directly converts prothrombin to thrombin via the prothrombinase complex, leading to fibrin clot formation and activation of platelets by thrombin [2]. Data from both preclinical and clinical studies have confirmed that Factor Xa and thrombin are viable targets for effective anticoagulation. Direct Factor Xa inhibitors and direct thrombin inhibitors have shown similar or improved efficacy and safety profiles compared with conventional anticoagulants, such as the VKAs (e.g. warfarin) and low molecular weight heparin, in clinical studies across several thromboembolic indications [1].
Unlike the VKAs, these direct oral anticoagulants have been shown to have predictable pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, a low potential for drug–drug interactions, and are given at fixed doses without the need for routine coagulation monitoring [1]. Several of these compounds (e.g. rivaroxaban, apixaban, and dabigatran etexilate) have been approved by the regulatory authorities for the management of specific thromboembolic disorders based on results from phase III studies. Among these, rivaroxaban (Xarelto®)—a direct Factor Xa inhibitor—was approved for clinical use in 2008 for the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in adults undergoing elective hip or knee replacement surgery. It is now also indicated for the prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in adults with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (AF) and for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), and prevention of recurrent DVT and PE in adult patients [3, 4]. In addition, rivaroxaban is now approved in the European Union for the prevention of atherothrombotic events in adult patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who have elevated cardiac biomarkers, combined with aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) with or without clopidogrel or ticlopidine [3]. The dose regimens of rivaroxaban selected for the phase III studies [5–12] that underpin these approvals were based on data from an extensive phase I and phase II clinical study program [13–16].
This article provides a summary of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic, biopharmaceutical, and drug–drug interaction profile of rivaroxaban. The population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationships of rivaroxaban, established in both healthy subjects and in the target patient populations, are reviewed and potential clinical implications are discussed.
2 Preclinical Pharmacology
2.1 Chemical and Physicochemical Properties
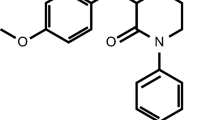
Rivaroxaban—5-chloro-N-([(5S)-2-oxo-3-[4-(3-oxomorpholin-4-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl]methyl)thiophene-2-carboxamide (Fig. 1) [17]—has a molecular weight of 435.88 and is classified under the Biopharmaceutical Classification System [18] as a low-solubility, high-permeability compound (Class 2). Rivaroxaban has limited pH-independent solubility in aqueous medium (5–7 mg/L; pH 1–9), but is, for instance, slightly soluble in polyethylene glycol 400 (2,431 mg/L). Using a validated Caco-2 cell assay, the apparent permeability values of the rivaroxaban molecule at concentrations of 1–100 μM were approximately 8 × 10−6 cm/s. With a log P value (octanol/water partition) coefficient of 1.5, rivaroxaban exhibits moderate lipophilicity, reflected in its low-to-moderate affinity to peripheral tissues.
Chemical structure of rivaroxaban [17]
2.2 Mode of Action
Rivaroxaban is a direct, specific Factor Xa inhibitor [19]. In vitro kinetic studies showed that the inhibition of human Factor Xa by rivaroxaban was competitive [inhibition constant (K i) 0.4 ± 0.02 nM] with 10,000-fold greater selectivity than for other serine proteases—it does not inhibit related serine proteases at concentrations up to 20 μM [19]. Rivaroxaban potently inhibited prothrombinase activity [inhibitory concentration 50 % (IC50) 2.1 ± 0.4 nM], and clot-associated Factor Xa activity (IC50 75 nM) [19, 20]. In human plasma, rivaroxaban inhibited endogenous Factor Xa activity in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 of 21 ± 1 nM [19]. In an ex vivo study, rivaroxaban at a single dose of 5 mg and 30 mg reduced collagen-induced endogenous thrombin potential in human plasma by approximately 80 and 90 %, respectively, and tissue factor-induced endogenous thrombin potential by approximately 40 and 65 %, respectively [21]. In contrast to indirect Factor Xa inhibitors (such as fondaparinux), rivaroxaban does not require any cofactor to exert its anticoagulant effect [22]. In human plasma, rivaroxaban concentration-dependently inhibited thrombin generation and, thus, the amplification processes of coagulation. Thrombin generation was almost completely inhibited at therapeutically relevant concentrations (80–100 nM) of rivaroxaban [23]. In addition, rivaroxaban increased the permeability and degradability of the whole blood clot, by decreasing thrombin generation [24]. However, rivaroxaban does not inhibit the activity of pre-existing thrombin molecules [25].
When given prophylactically, rivaroxaban had consistent antithrombotic effects in venous and arterial thrombotic models in mice, rats, and rabbits [19, 26]. Importantly, bleeding times were not significantly increased at antithrombotic-effective doses tested in these models [19]. When preclinical and clinical data were input into a computer-generated blood coagulation model, rivaroxaban showed favorable sensitivity for clotting induced by tissue factor concentration compared with warfarin. The model also predicted a broad therapeutic window for rivaroxaban based on a steep concentration–effect relationship that flattened rapidly at higher inhibitor concentrations [27]. No QTc prolongation effect was observed for rivaroxaban in preclinical experiments nor in a study on QT-interval in healthy volunteers [28] that was conducted according to the International Conference on Harmonisation guideline E14 [29].
As with other direct oral anticoagulants, there is no specific antidote available at present for rivaroxaban for use in emergency situations. The potential of hemostatic agents, such as prothrombin complex concentrate, has been investigated for reversal of the anticoagulant effect of rivaroxaban. Studies in healthy volunteers have shown that both three-factor and four-factor prothrombin complex concentrates can reverse the effect of rivaroxaban [e.g. inhibition of thrombin generation and prolongation of the prothrombin time (PT)] [30, 31].
3 Pharmacokinetic Properties
3.1 Absorption, Bioavailability, and Biopharmaceutical Profile
Rivaroxaban concentrations in human plasma were determined by use of a high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method. Using this method, a wide range of plasma concentrations (0.50–500 μg/L) could be determined with a high inter-assay accuracy (96.3–102.9 %) and precision (≤7.4 %) [32].
Rivaroxaban was absorbed rapidly with maximum plasma concentrations (C max) being reached 2–4 h after a single dose (1.25–80 mg) and multiple doses (up to 30 mg twice daily) [25, 33]. Rivaroxaban did not accumulate to a relevant extent after multiple dosing [33]. Data from other phase I studies in healthy subjects showed that absorption is almost complete (oral bioavailability approached 80–100 %) for the 10 mg tablet dose, irrespective of fasting or fed conditions. Intake with food did not affect the area under the plasma concentration–time curve (AUC) or C max after a 10 mg dose of rivaroxaban. In contrast, the bioavailability of a 20 mg tablet was 66 % under fasting conditions. The extent of absorption approached completeness when a 20 mg rivaroxaban tablet was administered with food, giving rise to an increase in the mean AUC of 39 %. Under fed conditions, dose proportionality was achieved after the administration of 10 mg, 15 mg, and 20 mg rivaroxaban tablets (Table 1). In addition, there was no influence with respect to types of food (a high-fat or high-carbohydrate meal) on the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban [34]. When administered orally with food, AUC and C max values were similar for whole and crushed rivaroxaban 20 mg tablets, whereas a crushed tablet suspended in water, administered using a nasogastric tube and followed by a liquid meal, gave similar AUC values but an 18 % reduction in C max [4].
3.2 Protein Binding and Distribution
In rats, rivaroxaban distributed heterogeneously to tissues and organs exhibited only moderate tissue affinity, and did not substantially penetrate the blood–brain barrier [35]. In studies in rats, [14C]rivaroxaban (and labeled metabolites) was found to penetrate the placental barrier to a moderate degree (AUC ratio fetus/maternal blood approximately 0.2) and its secretion into breast milk was approximately 2 % of the administered dose (Bayer HealthCare; unpublished data).
In humans, the plasma protein binding for rivaroxaban is high (approximately 92–95 % in vitro) and reversible. Serum albumin is the main plasma binding component [3, 35]. Owing to its high plasma protein binding, rivaroxaban is not expected to be dialyzable. Volume of distribution at steady state is approximately 50 L (0.62 L/kg), indicating its low-to-moderate affinity to peripheral tissues.
3.3 Metabolism and Elimination
Elimination of rivaroxaban proceeds via a dual pathway: renal elimination of unchanged drug and metabolic degradation of the drug. Approximately one-third (36 %, Fig. 2) of the dose is eliminated as unchanged active drug in the urine. Of the 36 % of the rivaroxaban dose eliminated in urine, active renal secretion accounts for 30 % and glomerular filtration for 6 % [36]. In vitro and in vivo drug interaction studies suggest that transporters involved in active renal secretion of rivaroxaban are P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein [BCRP (ABCG2)] [37, 38]. Approximately two-thirds of a dose is subject to metabolic degradation (Fig. 2). Rivaroxaban is metabolized by several cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP 3A4/5, CYP2J2) and CYP-independent mechanisms [39, 40]. The contribution of these clearance pathways has been quantified to the following average values: CYP3A4 accounts for approximately 18 % and CYP2J2 for approximately 14 % of total rivaroxaban elimination. In addition to this oxidative biotransformation, non-CYP-mediated hydrolysis of the amide bonds accounts for 14 % of total rivaroxaban elimination [38]. The resulting metabolites are eliminated both renally and via the hepatobiliary route (Fig. 2) [3, 36].
Summary of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination of rivaroxaban [3, 16, 36]. All numbers given are approximate. BCRP breast cancer resistance protein, CL sys systemic (plasma) clearance, CL R renal clearance (via active secretion CLRS and glomerular filtration CLRF), CYP3A4 cytochrome P450 3A4, CYP2J2 cytochrome P450 2J2, F abs absolute bioavailability, P-gp P-glycoprotein, V ss volume of distribution at steady-state
Unchanged rivaroxaban predominates in human plasma after administration, with no major active circulating metabolites present [3, 36]. Elimination of rivaroxaban from plasma occurs with a terminal half-life of 5–9 h in healthy young subjects [25, 33] and 11–13 h in elderly subjects [41]. The systemic clearance after intravenous administration in healthy subjects is approximately 10 L/h (0.14 L/h/kg), with a moderate inter-individual variability (coefficient of variation) ranging from 30 to 40 % (Fig. 2) [3, 16, 36].
4 Pharmacokinetic Properties in Selected Special Populations
4.1 Age
The influence of age on the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban has been investigated in phase I studies. Investigations in healthy elderly subjects aged >75 years showed that there was an increase in rivaroxaban exposure in this age group compared with younger subjects (aged 18–45 years) [42]. Although age alone had no clinically relevant effect on the C max and the time to reach C max after a 10 mg dose in this study, elderly subjects exhibited higher plasma concentrations, with mean AUC values being 41 % higher in elderly than in younger subjects. These changes were mainly attributed to the reduced rivaroxaban clearance in the elderly subjects, arising from reduced renal and non-renal clearance [42]. However, dose adjustment based on age alone is not required with rivaroxaban, as demonstrated in the subgroup analyses of several phase III clinical studies, although a dose adjustment based on renal function is recommended for stroke prevention in patients with non-valvular AF (see Sect. 5.3).
4.2 Sex and Body Weight
The potential influences of sex and body weight on the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban have also been investigated. In phase I studies, no relevant differences in pharmacokinetic parameters (such as AUC and C max) were observed between the male and female subjects within the respective treatment groups [42, 43]. Extremes in body weight (≤50 or >120 kg) had only a small influence on rivaroxaban concentrations (<25 %) compared with subjects with a body weight of 70–80 kg [43]. These findings indicated that dose adjustment for sex and/or body weight would not be necessary for rivaroxaban, which has been further supported by data from the phase III studies.
4.3 Ethnicity
Differences in rivaroxaban exposure observed between the various investigated ethnic groups—Caucasians, African-Americans, Hispanics, Chinese, and Japanese—were within the normal magnitude of inter-individual variability. The greatest difference compared with Caucasians was observed for Japanese subjects; however, this was only a minor-to-moderate increase in rivaroxaban plasma exposure (20–40 %), which can at least partially be attributed to a generally lower body weight in Japanese subjects [44]. Additional studies in healthy Chinese subjects also indicated that the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban were similar to those in healthy Caucasian subjects [45, 46]. These results suggest that fixed doses of rivaroxaban can be employed regardless of ethnicity.
4.4 Renal Impairment
Because approximately one-third of the administered rivaroxaban dose is excreted renally as unchanged drug, renal insufficiency is expected to affect drug elimination. Data from a phase I study showed an increase in rivaroxaban exposure correlated to decreased renal function, as assessed via creatinine clearance (CLCR) measurements (calculated by the Cockcroft–Gault formula) [47]. In subjects with mild (CLCR 50–80 mL/min), moderate (CLCR 30–49 mL/min), and severe (CLCR 15–29 mL/min) renal impairment, rivaroxaban plasma concentrations (AUC) were increased 1.4-, 1.5-, and 1.6-fold, respectively, compared with subjects with normal renal function. The increase in AUC was inversely correlated with the CLCR rate, and there was a close correlation between the renal and total body clearance of rivaroxaban and the CLCR rates of the subjects. Renal clearance decreased from 2.4 L/h in healthy subjects to 0.5 L/h in subjects with severe renal impairment. Oral clearance reduced from 8.0 L/h in healthy subjects to 4.5 L/h in those with severe renal impairment [47]. There are no data available for patients with CLCR <15 mL/min, and rivaroxaban is not recommended in this patient group. No dose adjustment is required for patients with a CLCR ≥15 mL/min in the approved indications, except for stroke prevention in patients with non-valvular AF (see Table 2 and Sect. 5.3 for further details).
4.5 Hepatic Impairment
Patients with mild hepatic impairment (classified as Child–Pugh A [48, 49]) exhibited only minor changes in the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban (i.e. an average of 1.2-fold increase in AUC), compared with the healthy control group [50]. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (classified as Child–Pugh B), there was an increase in rivaroxaban plasma concentrations and a prolonged elimination phase. In these patients, the AUC and C max were increased by 2.3- and 1.3-fold, respectively, compared with healthy subjects. In addition, the elimination half-life was prolonged by approximately 2 h compared with healthy subjects. The increase in exposure was driven by both reduced hepatic and renal clearance. The renal clearance of rivaroxaban was 1.4 and 0.7 L/h in subjects with mild and moderate hepatic impairment, respectively, compared with 2.4 L/h in the healthy subjects; this decrease was independent of renal function as assessed via CLCR. There was a significant correlation between unbound rivaroxaban in plasma and serum albumin [50]. Rivaroxaban is contraindicated in patients with hepatic disease associated with coagulopathy and risk of clinically relevant bleeding, including cirrhotic patients classified as Child–Pugh B and C [3].
4.6 Pediatric Population
There are currently no clinical data on rivaroxaban in children (age <18 years). However, a formulation (oral suspension containing 1 mg/mL rivaroxaban) intended for use in the pediatric population was investigated in healthy male adults to assess the relative bioavailability compared with the standard tablet formulation. The investigated doses were 10 mg and 20 mg rivaroxaban. The data showed that the dose-normalized pharmacokinetic parameters were similar for a 10 mg tablet and a 10 mg oral suspension in the fasted state and a 20 mg rivaroxaban suspension in the fed state [34]. The first study with rivaroxaban in the pediatric population (NCT01145859) is currently ongoing in patients aged between 6 months and <18 years at the end of their VTE treatment. This phase I study will assess the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of single doses of rivaroxaban in these patients, using weight-adjusted doses of equivalent exposure to rivaroxaban 10 mg or 20 mg doses in adults.
5 Pharmacokinetics in Patient Populations
5.1 Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism after Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery
In phase II clinical trials of rivaroxaban for VTE prevention in patients undergoing total hip or knee replacement surgery, data were collected and used to construct population pharmacokinetic models to characterize the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban in typical orthopedic surgery populations [14, 51]. One model compared rivaroxaban once-daily and twice-daily doses in patients undergoing total hip replacement surgery and the other model included both hip and knee replacement patients from the phase II program. Pharmacokinetics were evaluated by non-linear mixed effects modeling using NONMEM. Inputs to the model could then be modified to simulate the effect of different dosing regimens and population demographic factors (e.g. age, renal function, and body weight) and the effect of co-medications [14, 51].
Population pharmacokinetic analyses in patients undergoing total hip surgery included 5,743 samples from 758 patients receiving either once-daily or twice-daily rivaroxaban [14]. An oral, one-compartment model with a first-order absorption rate was found to accurately describe the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban. The results confirmed that rivaroxaban exhibited a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile in total hip replacement surgery patients. The estimated values for AUC, C max, and trough plasma concentration (C trough) after 10 mg once daily are given in Table 3. The pharmacokinetic parameters were affected by body weight, study day, age, renal function, serum albumin, and hematocrit, but the average of these effects remained within the overall variability of the population [14]. In the second model, which used data from both hip and knee replacement patients from the phase II program, the only major difference in the pharmacokinetic properties was a 26 % lower rivaroxaban clearance in the knee replacement study, which resulted in an approximately 30 % greater exposure [51].
5.2 Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
Two phase II studies of rivaroxaban for the treatment of acute DVT collected pharmacokinetic data for population-based modeling of the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban in patients with acute DVT. Data based on 4,634 rivaroxaban plasma samples from 870 patients were included [15]. As with healthy subjects and patients undergoing hip or knee replacement surgery, the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban were well described by a one-compartment model, and the pharmacokinetics of all rivaroxaban doses tested (20–60 mg total daily doses) were predictable, i.e. were affected by anticipated demographic factors, whether administered once daily or twice daily [15]. Inter-individual variability in pharmacokinetics was moderate (30–40 %) and was consistent over the 12-week duration of the studies. There was a dose-dependent increase in rivaroxaban exposure and the pharmacokinetic profile was similar when given once daily or twice daily with all doses. In all once-daily and twice-daily simulations, C max was reached at 2–4 h after administration. When comparing the same total daily doses, rivaroxaban given once daily showed a higher C max and a lower C trough compared with twice-daily dosing; however, the 5th–95th percentile ranges for these parameters overlapped [15]. The estimated values for AUC, C max, and C trough at steady state after 20 mg once daily are given in Table 3.
The oral one-compartment model obtained from DVT patients was used to simulate plasma rivaroxaban concentration–time profiles for extremes in age, renal function, and body weight for patients receiving rivaroxaban 20 mg once daily (Fig. 3). Age and renal function had a moderate influence on rivaroxaban exposure, and the influence of body weight was small (Fig. 3). The C max for all simulations was within the 5th–95th percentile ranges of the population mean values, which indicated that fixed dosing would be possible for a wide patient population. In addition, simulation of the phase III VTE treatment dosing regimen (rivaroxaban 15 mg twice daily for 3 weeks followed by rivaroxaban 20 mg once daily, derived from phase II data) demonstrated that the transition from the initial intensified 15 mg twice-daily to 20 mg once-daily dosing should not expose patients to substantial fluctuation in C max [15]. Subsequently, the efficacy and safety of these dose regimens (i.e. 15 mg twice daily followed by 20 mg once daily) have been demonstrated in the phase III EINSTEIN DVT and EINSTEIN PE studies [10, 11].
Predicted steady-state rivaroxaban plasma concentration–time profiles for typical patients with extremes in age, renal function (expressed as calculated CLCR), and body weight, according to the relationships established in the pharmacokinetic model, for patients receiving rivaroxaban 20 mg once daily compared with the post hoc estimated rivaroxaban plasma concentration range [geometric mean, 5th–95th percentiles] of the 20 mg once-daily treatment group in the phase II EINSTEIN DVT study [15]. Reproduced from Mueck et al. [15] with permission from Springer International Publishing AG (© Adis Data Information BV 2011. All rights reserved.). CL CR creatinine clearance
5.3 Stroke Prevention in Patients with Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation
No dose-finding study has been conducted in patients with non-valvular AF; doses for this patient population were derived from the phase II studies for the treatment of DVT. However, compared with patients with DVT, patients with AF are generally older and likely to have decreased renal function. A population pharmacokinetic model for rivaroxaban in patients with AF was constructed based on data from the DVT treatment studies, taking into account the fact that AF populations are typically older than those receiving rivaroxaban for the treatment of DVT [15]. A virtual population of 1,000 elderly patients with AF was simulated. In this virtual AF population receiving rivaroxaban 20 mg once daily, the average AUC was 3,310 μg/h/L, and the average C max and C trough were 290 and 32 μg/L, respectively. In addition, data from these simulations demonstrated that moderate renal impairment (i.e. CLCR 30–49 mL/min) and, to a lesser extent, increased age (≥75 years) led to a slight increase in rivaroxaban exposure because of reduced clearance, a prolonged elimination half-life, and increased C trough values [15]. This is expected because approximately one-third of the rivaroxaban dose is excreted as unchanged drug by the kidneys [35, 36], and elderly patients are likely to have decreased renal function [52], which would affect the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban. Additional simulations in virtual patient populations with AF showed that a rivaroxaban dose of 15 mg once daily in patients with a CLCR of 30–49 mL/min would achieve AUC and C max values similar to those observed with rivaroxaban 20 mg once daily in patients with normal renal function [15].
Based on these data, patients with moderate renal impairment (CLCR 30–49 mL/min) were given a reduced dose of rivaroxaban 15 mg once daily (as opposed to rivaroxaban 20 mg for patients without renal impairment or with mild renal impairment) in the phase III ROCKET AF study in patients with non-valvular AF. The exposure predictions [15] were subsequently confirmed in a population pharmacokinetic analysis of the ROCKET AF study (Table 3) (Girgis et al. unpublished data). Subgroup analyses of data from the ROCKET AF study demonstrated that the clinical outcomes were consistent between patients receiving rivaroxaban 20 mg once daily (CLCR ≥50 mL/min) and those receiving 15 mg once daily (CLCR 30–49 mL/min) [9, 53].
5.4 Secondary Prevention in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome
Using data from the phase II ATLAS ACS TIMI 46 study [54], a population pharmacokinetic model was constructed to characterize the parameters of rivaroxaban in this population. Data from 2,290 patients were used for the population pharmacokinetic modeling [55], which showed that the pharmacokinetics of this patient population were adequately described by an oral one-compartment model. Total clearance and apparent volume of distribution for the ACS patient population were similar to those in the populations for VTE prevention, DVT treatment, and stroke prevention in patients with AF. Simulations of individual steady-state drug exposures following oral administration of a 2.5 mg twice-daily dosing regimen indicated that the influence of renal function, age, and body weight on exposure were consistent with previous findings in other patient populations. The estimated values for AUC, C max, and C trough at steady state are given in Table 3 [55]. In the subsequent phase III ATLAS ACS 2 TIMI 51 study, rivaroxaban (2.5 mg or 5 mg twice daily) in combination with mono or dual antiplatelet therapy was shown to reduce the risk of death from cardiovascular causes, myocardial infarction, or stroke, without increasing the rate of fatal bleeding events, in patients with ACS [12]. The 2.5 mg twice-daily dose has been approved for this indication in Europe [3].
5.5 Use in Patients with Chronic Heart Failure
The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban have been investigated in a small study of patients with chronic heart failure [56]. Patients with acute decompensated heart failure or stable, severe, New York Heart Association Class III/IV heart failure received rivaroxaban 10 mg once daily for 6 days. Rivaroxaban exhibited similar, predictable pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in patients with acute and stable chronic heart failure. Compared with healthy young and healthy elderly subjects (aged 65–80 years), rivaroxaban exposure (AUC) was increased by 1.8- and 1.2-fold, respectively, in patients with chronic heart failure [56].
5.6 Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Acutely Ill, Hospitalized Patients
Rivaroxaban was compared with enoxaparin for the prevention of VTE in patients hospitalized for medical illnesses in the randomized, phase III MAGELLAN study [57]. Compared with short-duration enoxaparin, extended-duration rivaroxaban at a dose of 10 mg once daily further reduced the incidence of VTE but was associated with a significant increase in the incidence of major or clinically relevant non-major bleeding. Values for drug exposure at steady state were in the range of those previously obtained with rivaroxaban 10 mg once daily both in healthy adults and in patients undergoing major orthopedic surgery (Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals and Janssen Research & Development, LLC: data on file).
6 Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Relationships
6.1 Healthy Volunteers
Because of its mode of action, several specific and global clotting tests are affected by rivaroxaban. In phase I studies, Factor Xa activity was inhibited in a dose-dependent fashion by rivaroxaban, which provided the ‘proof of mechanism’ in humans (Fig. 4) [25, 33]. After single rivaroxaban doses of 1.25–80 mg, maximal Factor Xa inhibition was seen 1–4 h after tablet intake, and the inhibition effect was still evident 24 h after the administration of doses >5 mg. Rivaroxaban was selective for Factor Xa inhibition and had no direct effect on the activity of thrombin and antithrombin [25]. After multiple rivaroxaban doses up to 30 mg twice daily, Factor Xa activity was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner, reaching a maximum after approximately 3 h, and the inhibition continued until the end of the dosing interval [33]. The inhibition of Factor Xa activity and plasma concentrations of rivaroxaban were closely correlated according to a maximum effect (E max) model [16]. Prolongation of the PT (using Neoplastin) was correlated with the rivaroxaban plasma concentrations in a linear relationship (Fig. 4). The models described the observed pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship with high accuracy (mean percentage error was 4.8 % for Factor Xa activity and 0.1 % for PT prolongation), and high precision (root mean square percentage error was 17.9 % for Factor Xa activity and 7.3 % for PT prolongation). Rivaroxaban also prolonged activated partial thromboplastin time and HepTest, and the profiles were similar in shape to those for PT prolongation and inhibition of Factor Xa activity, although the sensitivity was different [25, 33]. In healthy male subjects, rivaroxaban (a single 5 mg or 30 mg dose) also dose-dependently inhibited thrombin generation in response to tissue factor or collagen stimulation. Some parameters of thrombin generation remained inhibited for 24 h after administration of a 30 mg dose [21].
The pharmacodynamic parameters of rivaroxaban were affected by variations in demographic characteristics to differing degrees. In elderly subjects, values for the inhibition of Factor Xa activity and the prolongation of PT were higher compared with those in younger patients after a single 10 mg dose of rivaroxaban, but returned close to baseline levels within 24 h [42]. Variations in body weight, sex, and ethnicity did not affect rivaroxaban pharmacodynamics to a relevant extent (as with the pharmacokinetics) [42, 43, 45, 46]. In subjects with mild (CLCR 50–80 mL/min), moderate (CLCR 30–49 mL/min), and severe (CLCR 15–29 mL/min) renal impairment, the overall inhibition of Factor Xa activity was increased by 1.5-, 1.9-, and 2.0-fold, respectively, compared with healthy subjects. The AUC for prolongation of PT was 1.3-, 2.2-, and 2.4-fold higher in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively, than that in healthy subjects [47]. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment, pharmacodynamic responses were significantly enhanced compared with those in healthy subjects, as measured by the inhibition of Factor Xa activity (P < 0.05 for the maximum effect) and prolongation of PT (P < 0.0001 for the maximum prolongation) [50]. The prolonged PT was in part caused by the increases in plasma levels; however, the underlying hepatic disease that impairs the synthesis of coagulation factors had additional effects on the PT. This influence of the underlying disease results in higher PT values at baseline as well as a steeper linear regression between PT and rivaroxaban plasma concentrations. There are no data in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child–Pugh C) and rivaroxaban is contraindicated in patients with hepatic disease associated with coagulopathy and clinically relevant bleeding risk, including cirrhotic patients classified as Child–Pugh B and C [3].
In the early stage of clinical development it was believed that PT might be a useful laboratory test platform for measuring rivaroxaban, if required in certain clinical situations. Existing data suggest that PT can provide a quantitative measurement of rivaroxaban when using one central laboratory with a reagent sensitive to rivaroxaban. However, the assay is not optimal under field conditions when different laboratories and assays are used. Likewise, corrections using the international normalized ratio (INR) [58, 59] do not address this limitation. In contrast, a number of studies have confirmed the clinical utility of anti-Factor Xa chromogenic assays for the quantitative measurements of rivaroxaban plasma levels, when used in conjunction with rivaroxaban calibrators. These assay kits and rivaroxaban calibrators are now commercially available and are suitable for detecting a wide range of rivaroxaban plasma levels covering the therapeutic doses [59–62].
6.2 Patient Populations
In accordance with the data established in healthy subjects in the phase I studies, rivaroxaban exhibited dose-dependent pharmacodynamics. The relationships between rivaroxaban plasma concentration and pharmacodynamic parameters could also be established in all patient populations studied (e.g. in VTE prevention after total hip or knee surgery, DVT treatment, stroke prevention in patients with AF, and in the ACS patient population) [15, 51, 55].
Pharmacodynamic modeling using data from the phase II studies in patients undergoing total hip or knee replacement surgery showed that inhibition of Factor Xa activity was closely correlated with rivaroxaban plasma concentrations following an inhibitory E max model [51]. The concentration of rivaroxaban producing 50 % of the maximum inhibition of Factor Xa activity was 296 μg/L in the hip study. In both once-daily and twice-daily dosing hip replacement studies, PT correlated with rivaroxaban plasma concentrations according to a simple, linear intercept model [51]. In phase II studies in patients receiving rivaroxaban for the treatment of acute DVT, the concentration–effect relationships for all pharmacodynamic parameters were broadly consistent with those found in healthy subjects and patients undergoing total hip or knee replacement surgery. Maximum PT prolongation was seen 1–4 h after tablet intake, and PT prolongation correlated with plasma rivaroxaban concentrations (up to 500 μg/L) in an almost linear fashion [15]. The pharmacodynamic estimates in the AF and ACS patient populations were similar to those for VTE prevention and DVT treatment [15, 55].
7 Drug Interactions
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Rivaroxaban
Unlike the VKAs, rivaroxaban has a low potential for drug–drug interactions. In phase I studies in healthy subjects, the absorption and pharmacokinetic parameters of rivaroxaban were not affected by changes in gastric pH induced by the H2-receptor antagonist ranitidine (150 mg twice daily) or antacid [63]. There was also no clinically meaningful effect on the pharmacokinetic parameters when a single 20 mg dose of rivaroxaban was given to healthy subjects who had received omeprazole 40 mg once daily for 5 days [64]. The potential influence of other commonly prescribed drugs on the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban has also been investigated in a number of phase I studies. Data from these studies showed that co-administration of rivaroxaban with naproxen (500 mg) [65], aspirin (500 mg followed by 100 mg) [66], clopidogrel (300 mg followed by 75 mg) [67], enoxaparin (40 mg) [68], and warfarin (titrated to an INR of 2.0–3.0) [69] did not affect the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban [3].
The high bioavailability of rivaroxaban indicates a lack of presystemic extraction (i.e. intestinal P-gp and CYP3A4 do not play a relevant role in absorption). However, because of the involvement of CYP3A4 and CYP2J2 in the oxidative metabolism of rivaroxaban and P-gp/BCRP in its active renal secretion, it was anticipated that co-administration with drugs that interfere with these pathways could affect rivaroxaban exposure. Data from phase I studies showed that there was no clinically relevant pharmacokinetic interaction between rivaroxaban and the CYP3A4 substrate midazolam, the P-gp substrate digoxin, or with the CYP3A4/P-gp substrate atorvastatin [38, 70], confirming that rivaroxaban is not an inducer or inhibitor of any major CYP isoforms. Concomitant administration of rivaroxaban with strong inhibitors of both CYP3A4 and P-gp/BCRP (e.g. ketoconazole and ritonavir), however, significantly increased rivaroxaban exposure [38]. When a single dose of rivaroxaban (10 mg) and steady-state ketoconazole 200 mg once daily were co-administered, the AUC and C max of rivaroxaban were increased by 1.8- and 1.5-fold, respectively. Using multiple doses of rivaroxaban (10 mg once daily) and a higher dose of ketoconazole (400 mg once daily), concomitant administration led to a 2.6-fold increase in the AUC and a 1.7-fold increase in the C max of rivaroxaban [38]. Similarly, steady-state ritonavir (600 mg twice daily) also significantly increased rivaroxaban exposure after a single 10 mg dose; the AUC and C max of rivaroxaban increased by 2.5- and 1.6-fold, respectively, in a phase I study in healthy subjects [38]. These data support the recommendation that co-administration of rivaroxaban with strong inhibitors of both CYP3A4 and P-gp should be avoided because of increased rivaroxaban exposure, and consequently, increased risk of bleeding complications [3]. However, strong inhibitors of either CYP3A4 or P-gp, or moderate inhibitors of both of these pathways, produced less marked effects [38]. The following drugs moderately affected rivaroxaban exposure, but not to a clinically relevant extent: erythromycin (moderate CYP3A4/P-gp inhibitor; 34 % increase), clarithromycin (strong CYP3A4/moderate P-gp inhibitor; 54 % increase), and fluconazole (moderate CYP3A4/possible BCRP inhibitor; 42 % increase) [38]. In contrast, co-administration of rivaroxaban and erythromycin (and, by extension, other moderate CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitors) in patients with renal impairment may increase rivaroxaban exposure [38]. Concomitant administration of rivaroxaban and strong CYP3A4 and P-gp inducers, such as the antibiotic rifampicin, led to decreases in rivaroxaban exposure; therefore, such a combination should be used with caution [3] (Table 4).
7.2 Effect of Rivaroxaban on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs
In a number of phase I studies, the potential influence of rivaroxaban on the pharmacokinetic profiles of other co-administered agents was also investigated, as well as their influence on the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban. In all these studies, no clinically relevant effect of rivaroxaban was found on the pharmacokinetic parameters of the drugs tested, including digoxin [70], atorvastatin [70], midazolam [38], enoxaparin [68], and warfarin [69].
7.3 Pharmacodynamic Drug Interactions
As an anticoagulant, rivaroxaban has the potential to interact with other drugs that influence the coagulation system. In phase I studies, co-administration of rivaroxaban (a single 15 mg dose) and naproxen (representative of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) showed that naproxen (500 mg) had no influence on the inhibition of Factor Xa activity and prolongation of PT induced by rivaroxaban. The combination of rivaroxaban and naproxen did not affect platelet aggregation, but co-administration of both drugs significantly increased bleeding time compared with rivaroxaban or naproxen alone. Increases in bleeding times from baseline were 1.46-, 1.20-, and 2.17-fold after naproxen alone, rivaroxaban alone, and the combination of rivaroxaban and naproxen, respectively [65]. Aspirin (500 mg followed by 100 mg) did not alter the effects of rivaroxaban (a single 15 mg dose) on Factor Xa activity or clotting tests, and rivaroxaban did not influence the effects of aspirin on platelet aggregation. Bleeding time was significantly prolonged with aspirin alone and the combination of both drugs, compared with rivaroxaban alone. The combination of rivaroxaban and aspirin prolonged bleeding time slightly more than aspirin alone [66]. The potential pharmacodynamic interaction of rivaroxaban (a single 15 mg dose) with clopidogrel (300 mg followed by 75 mg) has also been studied in healthy subjects. The data showed that clopidogrel had no influence on the inhibition of Factor Xa activity or prolongation of the PT induced by rivaroxaban when co-administered. Inhibition of adenosine diphosphate-stimulated platelet aggregation by clopidogrel was not affected by rivaroxaban. Bleeding time was increased by clopidogrel, and co-administration of rivaroxaban and clopidogrel further increased bleeding time in a subset of subjects (least squares means of 3.8 times baseline compared with 1.1 times baseline with rivaroxaban alone and 2.0 times baseline with clopidogrel alone) [67]. In healthy subjects, single doses of rivaroxaban (10 mg) and enoxaparin (40 mg) showed similar anti-Factor Xa activities, and co-administration of rivaroxaban with enoxaparin resulted in an enhanced anti-Factor Xa activity compared with each drug alone [68]. Furthermore, it was anticipated that in daily clinical practice, some patients may require switching between anticoagulants in certain situations, including from warfarin to rivaroxaban or vice versa. The pharmacodynamic profiles during transition from steady-state warfarin (INR 2.0–3.0) to rivaroxaban 20 mg once daily was, therefore, investigated in healthy subjects. Data from this study demonstrated an additive effect on the prolongation of PT/INR during the initial transitioning period from warfarin to rivaroxaban, but the effects of rivaroxaban on anti-Factor Xa activity, HepTest, and prothrombinase-induced clotting time were not affected by pretreatment with warfarin [3, 69] (see Table 4 for a summary of the drug–drug interaction profile of rivaroxaban).
8 Discussion and Conclusions
Data from the extensive phase I and phase II dose-ranging studies and the subsequent population modeling demonstrate that the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban are predictable and were affected by anticipated demographic factors, as expected, and that the pharmacodynamic parameters correlate closely with rivaroxaban plasma concentrations in both healthy subjects and in patients receiving rivaroxaban for several thromboembolic indications, including VTE prevention after total hip or knee replacement surgery, treatment of DVT, and secondary prevention in patients with ACS [14, 15, 55]. Together, these data have supported the dose selections for the phase III studies conducted with rivaroxaban.
Oral absorption of rivaroxaban is almost complete for the 10 mg tablet, and intake with food does not affect its AUC or C max; therefore, rivaroxaban 10 mg tablets can be taken with or without food. Higher doses of rivaroxaban (15 mg and 20 mg) should be taken with food to achieve a high bioavailability. Variability in the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban is moderate, with inter-individual variability (coefficient variation) of 30–40 %. The most important covariates determining the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban were found to be age and renal function, the latter occurring either as a co-linear factor owing to age-related decrease in renal function or through age-independent renal impairment. In all patient populations studied, the pharmacokinetic properties of rivaroxaban were similar to those found in healthy subjects. The influence of demographic factors on the pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban was moderate, as anticipated, and, on average, within the variability of the overall patient population. Simulations of typical patients with extreme demographics (such as elderly with a low body weight and impaired renal function) showed that the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of rivaroxaban in these patients remain within the variability range confidence interval of an average patient [14, 15], supporting fixed dosing without the need for routine coagulation monitoring. Nevertheless, to optimize therapy, a reduced dose of 15 mg rivaroxaban is recommended for patients with AF with impaired renal function (i.e. elderly patients with CLCR 30–49 mL/min) who receive long-term anticoagulation for stroke prevention.
Similarly, the direct Factor Xa inhibitor apixaban and the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran have also been shown to exhibit predictable pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. However, there are some important, clinically relevant differences in the pharmacokinetic properties of these direct oral anticoagulants. For example, renal elimination is markedly lower with apixaban (approximately 27 %) [71] and rivaroxaban (approximately 36 %) [38], compared with dabigatran, which is largely eliminated via the kidneys (>80 %) [72]. Therefore, dose reductions with dabigatran are mandated or suggested in patients with moderate renal impairment (CLCR 30–50 mL/min) [73]. In Europe, dabigatran is contraindicated in patients with CLCR <30 mL/min [73], whereas apixaban and rivaroxaban may be given to patients with CLCR ≥15 mL/min [3, 71].
Data from the phase I drug-interaction studies indicate that the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters of rivaroxaban are not influenced by many commonly prescribed medications. However, strong inhibitors of both CYP3A4 and P-gp should not be co-administered, as outlined in the Summary of Product Characteristics [3]. Neither dabigatran nor its prodrug dabigatran etexilate are metabolized by CYP-dependent mechanisms [73], which contrasts with the metabolism of rivaroxaban [3] and apixaban [71]. However, because dabigatran etexilate is a P-gp substrate, the effect of P-gp inhibitors and inducers on the bioavailability of dabigatran is stronger than with rivaroxaban, and co-administration with such agents may necessitate dose adjustments [73, 74]. It should also be noted that P-gp transporters play a role in the absorption of apixaban, but not rivaroxaban [3, 71, 73, 75].
In all relevant studies conducted with rivaroxaban to date, inhibition of Factor Xa and prolongation of the PT (when using Neoplastin) are closely correlated with rivaroxaban plasma concentrations. It is now well recognized that anti-Factor Xa chromogenic assays are best suited for the quantitative measurement of rivaroxaban plasma levels, instead of PT [76]; this is also the case for apixaban [58]. Anti-Factor Xa assay kits and rivaroxaban calibrators are commercially available for clinical use [such as Neoplastin® CI Plus (Diagnostica Stago, Asnières-sur-Seine, France) or RecombiPlasTin (Instrumentation Laboratory, Bedford, MA, USA)] and provide sensitive measurements of rivaroxaban exposure, if required in certain clinical circumstances such as overdose, prior to emergency surgery, or when drug accumulation is suspected (e.g. if patients develop acute renal failure) [76, 77]. However, there are currently no data showing a direct correlation between bleeding events and rivaroxaban plasma levels in patients receiving therapeutic doses of rivaroxaban. The anti-Factor Xa method is also suitable for measurement of apixaban concentrations. The Hemoclot® Thrombin Inhibitor assay (HYPHEN BioMed, Neuville-sur-Oise, France) can be used for measuring the anticoagulant activity of dabigatran using dabigatran calibrators [78].
In conclusion, the oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban has a fast onset of action, well-established pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in all patient populations studied, and limited drug–drug interactions. With the fixed-dose regimens tailored for specific indications without routine coagulation monitoring, rivaroxaban has the potential to simplify and improve the management of thromboembolic disorders.
References
Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, et al. Oral anticoagulant therapy: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141:e44S–88S.
Weitz JI, Bates SM. New anticoagulants. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:1843–53.
Bayer Pharma AG. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban) Summary of Product Characteristics; 2013. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/000944/WC500057108.pdf (Accessed 23 Jul 2013).
Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban) Prescribing Information; 2013. http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/022406s004lbl.pdf (Accessed 23 Jul 2013).
Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ, et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2765–75.
Kakkar AK, Brenner B, Dahl OE, et al. Extended duration rivaroxaban versus short-term enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2008;372:31–9.
Lassen MR, Ageno W, Borris LC, et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2776–86.
Turpie AGG, Lassen MR, Davidson BL, et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty (RECORD4): a randomised trial. Lancet. 2009;373:1673–80.
Patel MR, Mahaffey KW, Garg J, et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:883–91.
The EINSTEIN Investigators. Oral rivaroxaban for symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:2499–510.
The EINSTEIN–PE Investigators. Oral rivaroxaban for the treatment of symptomatic pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1287–97.
Mega JL, Braunwald E, Wiviott SD, et al. Rivaroxaban in patients with a recent acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:9–19.
Perzborn E, Roehrig S, Straub A, et al. The discovery and development of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:61–75.
Mueck W, Borris LC, Dahl OE, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of once- and twice-daily rivaroxaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Thromb Haemost. 2008;100:453–61.
Mueck W, Lensing AW, Agnelli G, et al. Rivaroxaban: population pharmacokinetic analyses in patients treated for acute deep-vein thrombosis and exposure simulations in patients with atrial fibrillation treated for stroke prevention. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2011;50:675–86.
Mueck W, Becka M, Kubitza D, et al. Population model of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—in healthy subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2007;45:335–44.
Roehrig S, Straub A, Pohlmann J, et al. Discovery of the novel antithrombotic agent 5-chloro-N-([(5S)-2-oxo-3-[4-(3-oxomorpholin-4-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-5-yl]methyl)thiophene-2-carboxamide (BAY 59-7939): an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. J Med Chem. 2005;48:5900–8.
US Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Guidance for industry: waiver of in vivo bioavailability and bioequivalence studies for immediate-release solid oral dosage forms based on a biopharmaceutics classification system; 2000. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm070246.pdf (Accessed 23 Jul 2013).
Perzborn E, Strassburger J, Wilmen A, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies of the novel antithrombotic agent BAY 59-7939—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3:514–21.
Depasse F, Busson J, Mnich J, et al. Effect of BAY 59-7939—a novel, oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—on clot-bound Factor Xa activity in vitro [abstract no. P1104]. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(Suppl 1).
Graff J, von Hentig N, Misselwitz F, et al. Effects of the oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban on platelet-induced thrombin generation and prothrombinase activity. J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;47:1398–407.
Samama MM. The mechanism of action of rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—compared with other anticoagulants. Thromb Res. 2011;127:497–504.
Gerotziafas GT, Elalamy I, Depasse F, et al. In vitro inhibition of thrombin generation, after tissue factor pathway activation, by the oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:886–8.
Varin R, Mirshahi S, Mirshahi P, et al. Effect of rivaroxaban, an oral direct Factor Xa inhibitor, on whole blood clot permeation and thrombolysis: critical role of red blood cells [abstract no. 1064]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts). 2009;114.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Voith B, et al. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of single doses of BAY 59-7939, an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005;78:412–21.
Biemond BJ, Perzborn E, Friederich PW, et al. Prevention and treatment of experimental thrombosis in rabbits with rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939)—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97:471–7.
Burghaus R, Coboeken K, Gaub T, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of rivaroxaban using a computer model for blood coagulation. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e17626.
Kubitza D, Mueck W, Becka M. Randomized, double-blind, crossover study to investigate the effect of rivaroxaban on QT-interval prolongation. Drug Saf. 2008;31:67–77.
International Conference on Harmonisation. ICH E14 The clinical evaluation of QT/QTc interval prolongation and proarrhythmic potential for non-antiarrhythmic drugs (CHMP/ICH/2/04); 2005. http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Efficacy/E14/E14_Guideline.pdf (Accessed 23 Jul 2013).
Eerenberg ES, Kamphuisen PW, Sijpkens MK, et al. Reversal of rivaroxaban and dabigatran by prothrombin complex concentrate: a randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study in healthy subjects. Circulation. 2011;124:1573–9.
Levi M, Moore T, Castillejos C, et al. Effects of three-factor and four-factor prothrombin complex concentrates on the pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11:167:Abstract OC 36.5.
Rohde G. Determination of rivaroxaban—a novel, oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2008;872:43–50.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Wensing G, et al. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of BAY 59-7939—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—after multiple dosing in healthy male subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2005;61:873–80.
Stampfuss J, Kubitza D, Becka M, et al. The effect of food on the absorption and pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2013;51:549–61.
Weinz C, Buetehorn U, Daehler HP, et al. Pharmacokinetics of BAY 59-7939—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—in rats and dogs. Xenobiotica. 2005;35:891–910.
Weinz C, Schwarz T, Kubitza D, et al. Metabolism and excretion of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor, in rats, dogs and humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009;37:1056–64.
Gnoth MJ, Buetehorn U, Muenster U, et al. In vitro and in vivo P-glycoprotein transport characteristics of rivaroxaban. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;338:372–80.
Mueck W, Kubitza D, Becka M. Co-administration of rivaroxaban with drugs that share its elimination pathways: pharmacokinetic effects in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;76:455–66.
Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee. FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document; 2009. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/AdvisoryCommittees/CommitteesMeetingMaterials/Drugs/CardiovascularandRenalDrugsAdvisoryCommittee/UCM181524.pdf (Accessed 23 Jul 2013).
European Medicines Agency. CHMP assessment report for Xarelto; 2008. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Public_assessment_report/human/000944/WC500057122.pdf (Accessed 23 Jul 2013).
Kubitza D, Becka M, Roth A, et al. Dose-escalation study of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban in healthy elderly subjects. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24:2757–65.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Roth A, et al. The influence of age and gender on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53:249–55.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Zuehlsdorf M, et al. Body weight has limited influence on the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, or pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939) in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;47:218–26.
Tanigawa T, Kaneko M, Hashizume K, et al. Model-based dose selection for phase III rivaroxaban study in Japanese patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2013;28:59–70.
Jiang J, Hu Y, Zhang J, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single doses of rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—in elderly Chinese subjects. Thromb Haemost. 2010;103:234–41.
Zhao X, Sun P, Zhou Y, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of single/multiple doses of the oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban in healthy Chinese subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2009;68:77–88.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. Effects of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of rivaroxaban, an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;70:703–12.
European Medicines Agency. Guideline on the evaluation of the pharmacokinetics of medicinal products in patients with impaired hepatic function; 2005. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2009/09/WC500003122.pdf (Accessed 24 Jul 2013).
US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), et al. Guidance for industry. Pharmacokinetics in patients with impaired hepatic function—study design, data analysis, and impact on dosing and labeling; 2003. http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm072123.pdf (Accessed 18 Jul 2013).
Kubitza D, Roth A, Becka M, et al. Effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a single dose of rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;76:89–98.
Mueck W, Eriksson BI, Bauer KA, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—in patients undergoing major orthopaedic surgery. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47:203–16.
Clark B. Biology of renal aging in humans. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2000;7:11–21.
Fox KAA, Piccini JP, Wojdyla D, et al. Prevention of stroke and systemic embolism with rivaroxaban compared with warfarin in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and moderate renal impairment. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:2387–94.
Mega JL, Braunwald E, Mohanavelu S, et al. Rivaroxaban versus placebo in patients with acute coronary syndromes (ATLAS ACS-TIMI 46): a randomised, double-blind, phase II trial. Lancet. 2009;374:29–38.
Xu XS, Moore K, Burton P, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;74:86–97.
Gheorghiade M, Thyssen A, Zolynas R, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban and its effect on biomarkers of hypercoagulability in patients with chronic heart failure. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2011;30:218–26.
Cohen AT, Spiro TE, Büller HR, et al. Rivaroxaban for thromboprophylaxis in acutely ill medical patients. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:513–23.
Barrett YC, Wang Z, Frost C, et al. Clinical laboratory measurement of direct Factor Xa inhibitors: Anti-Xa assay is preferable to prothrombin time assay. Thromb Haemost. 2010;104:1263–71.
Samama MM, Martinoli JL, Le Flem L, et al. Assessment of laboratory assays to measure rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 2010;103:815–25.
Lindhoff-Last E, Samama MM, Ortel TL, et al. Assays for measuring rivaroxaban: their suitability and limitations. Ther Drug Monit. 2010;32:673–9.
Mani H, Rohde G, Stratmann G, et al. Accurate determination of rivaroxaban levels requires different calibrator sets but not addition of antithrombin. Thromb Haemost. 2012;108:191–8.
Samama MM, Contant G, Spiro TE, et al. Evaluation of the anti-Factor Xa chromogenic assay for the measurement of rivaroxaban plasma concentrations using calibrators and controls. Thromb Haemost. 2012;107:379–87.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Zuehlsdorf M, et al. Effect of food, an antacid, and the H2 antagonist ranitidine on the absorption of BAY 59-7939 (rivaroxaban), an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2006;46:549–58.
Moore KT, Plotnikov AN, Thyssen A, et al. Effect of multiple doses of omeprazole on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of a single dose of rivaroxaban. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2011;58:581–8.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. Rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939)—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—has no clinically relevant interaction with naproxen. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63:469–76.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—are not affected by aspirin. J Clin Pharmacol. 2006;46:981–90.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. Effect of co-administration of rivaroxaban and clopidogrel on bleeding time, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics: a phase I study. Pharmaceuticals. 2012;5:279–96.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Schwers S, et al. Investigation of pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic interactions between rivaroxaban and enoxaparin in healthy male subjects. Clinical Pharm Drug Dev. 2013;2:270–7.
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mück W, et al. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics during the transition from warfarin to rivaroxaban in healthy subjects: a multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11:820 (Abstract PB 3.46-1).
Kubitza D, Becka M, Roth A, et al. Absence of clinically relevant interactions between rivaroxaban—an oral, direct Factor Xa inhibitor—and digoxin or atorvastatin in healthy subjects. J Int Med Res. 2012;40:1688–707.
Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer EEIG. Eliquis® (apixaban) Summary of Product Characteristics; 2013. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/002148/WC500107728.pdf (Accessed 3 Jul 2013).
Blech S, Ebner T, Ludwig-Schwellinger E, et al. The metabolism and disposition of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor, dabigatran, in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 2008;36:386–99.
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Pradaxa® (dabigatran etexilate) Summary of Product Characteristics; 2013. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Information/human/000829/WC500041059.pdf (Accessed 11 Jul 2013).
Härtter S, Koenen-Bergmann M, Sharma A, et al. Decrease in the oral bioavailability of dabigatran etexilate after co-medication with rifampicin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;74:490–500.
Zhang D, Frost CE, He K, et al. Investigating the enteroenteric recirculation of apixaban, a Factor Xa inhibitor: administration of activated charcoal to bile duct-cannulated rats and dogs receiving an intravenous dose and use of drug transporter knockout rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41:906–15.
Samama MM. Which test to measure the anticoagulant effect of rivaroxaban: the anti-Factor Xa assay. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11:579–80.
Lindhoff-Last E, Ansell J, Spiro T, et al. Laboratory testing of rivaroxaban in routine clinical practice: when, how, and which assays. Ann Med. 2013;45:423–9.
Stangier J, Feuring M. Using the HEMOCLOT direct thrombin inhibitor assay to determine plasma concentrations of dabigatran. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2012;23:138–43.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by research funding from Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals and Janssen Research & Development, LLC. We wish to acknowledge Yong-Ling Liu and Stephen Purver, who provided editorial support with funding from Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals and Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC.
Conflict of interest
Wolfgang Mueck, Jan Stampfuss, Dagmar Kubitza, and Michael Becka are employees of Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial License which permits any noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and the source are credited.
About this article
Cite this article
Mueck, W., Stampfuss, J., Kubitza, D. et al. Clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profile of Rivaroxaban. Clin Pharmacokinet 53, 1–16 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-013-0100-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40262-013-0100-7