Abstract
Significance
Psoriasis, a common immune-mediated disease, affects approximately 2 % of the population worldwide. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) might be a manifestation of systemic vascular involvement in autoimmune disease. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no systematic English-language examination of the risk of SSNHL in patients with psoriasis.
Objectives
We tested the hypothesis that psoriasis is a risk factor for developing SSNHL.
Methods
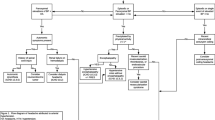
Using Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database, we conducted a retrospective cohort study to compare patients diagnosed with psoriasis from January 1, 2001 through December 31, 2006 (n = 28,817) with gender-, age-, and comorbidities-matched controls (n = 28,817). We followed each patient until the end of 2011 and evaluated the incidence of SSNHL for at least 6 years after the initial psoriasis diagnosis.
Results
The incidence of SSNHL was 1.51 times higher in the psoriasis cohort than in the control cohort (7.12 vs 4.73 per 10,000 person-years). Using Cox proportional hazard regressions, the adjusted hazard ratio (AHR) was 1.51 (95 % confidence interval [CI] 1.18–1.93). Comorbid hypertension was an independent risk factor for SSNHL (AHR 1.49; 95 % CI 1.05–2.13). However, the incidence rate ratios (IRRs) for each comorbidity subgroup in the psoriasis and control cohorts were not significantly different.
Conclusions and Relevance
Psoriasis was significantly associated with a higher risk of developing SSNHL. We suggest that physicians advise patients with psoriasis to seek medical attention if they have hearing impairments, because they may also have a higher risk of developing SSNHL.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greco A, Fusconi M, Gallo A, Marinelli C, Macri GF, De Vincentiis M. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: an autoimmune disease? Autoimmun Rev. 2011;10(12):756–61.
Giani T, Simonini G, Lunardi C, Puccetti A, De Martino M, Falcini F. Juvenile psoriatic arthritis and acquired sensorineural hearing loss in a teenager: is there an association? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2006;24(3):344–6.
Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD. Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(5):1011–21.
Lin C, Lin SW, Weng SF, Lin YS. Risk of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a population-based cohort study. Audiol Neurootol. 2013;18(2):95–100.
Liu T, Han Y, Lu L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphisms and the risk of psoriasis: a meta-analysis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2013;38(4):352–8.
Amor-Dorado JC, Barreira-Fernandez MP, Pina T, Vazquez-Rodriguez TR, Llorca J, Gonzalez-Gay MA. Investigations into audiovestibular manifestations in patients with psoriatic arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2014;41(10):2018–26.
Srikumar S, Deepak MK, Basu S, Kumar BN. Sensorineural hearing loss associated with psoriatic arthritis. J Laryngol Otol. 2004;118(11):909–11.
Brauchli YB, Jick SS, Meier CR. Psoriasis and the risk of incident diabetes mellitus: a population-based study. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159(6):1331–7.
Ni C, Chiu MW. Psoriasis and comorbidities: links and risks. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2014;7:119–32.
McCabe BF. Autoimmune sensorineural hearing loss. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2007;116(12):875–9.
Harris JP, Sharp PA. Inner ear autoantibodies in patients with rapidly progressive sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 1990;100(5):516–24.
Hisashi K, Komune S, Taira T, Uemura T, Sadoshima S, Tsuda H. Anticardiolipin antibody-induced sudden profound sensorineural hearing loss. Am J Otolaryngol. 1993;14(4):275–7.
Rubin DB. Estimating causal effects from large data sets using propensity scores. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127(8 Pt 2):757–63.
Cutolo M, Sulli A, Straub RH. Estrogen metabolism and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev. 2012;11(6–7):A460–4.
Olsen NJ, Kovacs WJ. Hormones, pregnancy, and rheumatoid arthritis. J Gend Specif Med. 2002;5(4):28–37.
O’Brien SM, Fitzgerald P, Scully P, Landers A, Scott LV, Dinan TG. Impact of gender and menstrual cycle phase on plasma cytokine concentrations. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2007;14(2):84–90.
Hochberg MC. Mortality from systemic lupus erythematosus in England and Wales, 1974–1983. Br J Rheumatol. 1987;26(6):437–41.
Kaslow RA, Masi AT. Age, sex, and race effects on mortality from systemic lupus erythematosus in the United States. Arthritis Rheum. 1978;21(4):473–9.
Onumah N, Kircik LH. Psoriasis and its comorbidities. J Drugs Dermatol. 2012;11(5 Suppl):s5–10.
Balta I, Balta S, Demirkol S, Celik T, Ekiz O, Cakar M, et al. Aortic arterial stiffness is a moderate predictor of cardiovascular disease in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Angiology. 2014;65(1):74–8.
Ena P, Madeddu P, Glorioso N, Cerimele D, Rappelli A. High prevalence of cardiovascular diseases and enhanced activity of the renin–angiotensin system in psoriatic patients. Acta Cardiol. 1985;40(2):199–205.
Costa L, Caso F, D’Elia L, Atteno M, Peluso R, Del Puente A, et al. Psoriatic arthritis is associated with increased arterial stiffness in the absence of known cardiovascular risk factors: a case control study. Clin Rheumatol. 2012;31(4):711–5.
Ma C, Harskamp CT, Armstrong EJ, Armstrong AW. The association between psoriasis and dyslipidaemia: a systematic review. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168(3):486–95.
Ribatti D, Levi-Schaffer F, Kovanen PT. Inflammatory angiogenesis in atherogenesis—a double-edged sword. Ann Med. 2008;40(8):606–21.
Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420(6917):868–74.
Tekin NS, Tekin IO, Barut F, Sipahi EY. Accumulation of oxidized low-density lipoprotein in psoriatic skin and changes of plasma lipid levels in psoriatic patients. Mediators Inflamm. 2007;2007:78454.
Capaccio P, Ottaviani F, Cuccarini V, Bottero A, Schindler A, Cesana BM, et al. Genetic and acquired prothrombotic risk factors and sudden hearing loss. Laryngoscope. 2007;117(3):547–51.
Weiss D, Neuner B, Gorzelniak K, Bremer A, Rudack C, Walter M. Platelet glycoproteins and fibrinogen in recovery from idiopathic sudden hearing loss. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e86898.
Scheibe F, Haupt H, Baumgartl H. Effects of experimental cochlear thrombosis on oxygenation and auditory function of the inner ear. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 1997;254(2):91–4.
Mierzwa K, Schneider G, Muller A. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss during oral anticoagulant therapy. J Laryngol Otol. 2004;118(11):872–6.
Tripodi A, Capaccio P, Pignataro L, Chantarangkul V, Menegatti M, Bamonti F, et al. Thrombin generation in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Thromb Res. 2014;133(6):1130–4.
Al-Mutairi N, Al-Farag S, Al-Mutairi A, Al-Shiltawy M. Comorbidities associated with psoriasis: an experience from the Middle East. J Dermatol. 2010;37(2):146–55.
Azfar RS, Seminara NM, Shin DB, Troxel AB, Margolis DJ, Gelfand JM. Increased risk of diabetes mellitus and likelihood of receiving diabetes mellitus treatment in patients with psoriasis. Arch Dermatol. 2012;148(9):995–1000.
Qureshi AA, Choi HK, Setty AR, Curhan GC. Psoriasis and the risk of diabetes and hypertension: a prospective study of US female nurses. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145(4):379–82.
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(5):1111–9.
Kariya S, Cureoglu S, Fukushima H, Morita N, Baylan MY, Maeda Y, et al. Comparing the cochlear spiral modiolar artery in type-1 and type-2 diabetes mellitus: a human temporal bone study. Acta Med Okayama. 2010;64(6):375–83.
Wackym PA, Linthicum FH Jr. Diabetes mellitus and hearing loss: clinical and histopathologic relationships. Am J Otol. 1986;7(3):176–82.
Lin SW, Lin YS, Weng SF, Chou CW. Risk of developing sudden sensorineural hearing loss in diabetic patients: a population-based cohort study. Otol Neurotol. 2012;33(9):1482–8.
Le H, Tfelt-Hansen P, Russell MB, Skytthe A, Kyvik KO, Olesen J. Co-morbidity of migraine with somatic disease in a large population-based study. Cephalalgia. 2011;31(1):43–64.
Chu CH, Liu CJ, Fuh JL, Shiao AS, Chen TJ, Wang SJ. Migraine is a risk factor for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a nationwide population-based study. Cephalalgia. 2013;33(2):80–6.
Espinosa-Sanchez JM, Lopez-Escamez JA. Migraine, sudden sensorineural hearing loss and autoimmune ear disease. Cephalalgia. 2013;33(14):1206–7.
Sacco S, Kurth T. Migraine and the risk for stroke and cardiovascular disease. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2014;16(9):524.
Lin HC, Chao PZ, Lee HC. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss increases the risk of stroke: a 5-year follow-up study. Stroke. 2008;39(10):2744–8.
Harandi SA, Togha M, Sadatnaseri A, Hosseini SH, Jahromi SR. Cardiovascular risk factors and migraine without aura: a case–control study. Iran J Neurol. 2013;12(3):98–101.
Mosnier I, Stepanian A, Baron G, Bodenez C, Robier A, Meyer B, et al. Cardiovascular and thromboembolic risk factors in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a case–control study. Audiol Neurootol. 2011;16(1):55–66.
Acknowledgments
The study was designed and conducted by Y. S. Lin and Y. C. Yen. Y. C. Yen, F. J. Lai, and Y. S. Lin recorded the clinical data and supervised the writing of the manuscript. S. F. Wang did the epidemiological and statistical analyses. Y. S. Lin wrote the paper and was primarily responsible for its final content. Y. C. Yen, Y. S. Lin, S. F. Weng, and F. J. Lai have nothing to disclose and declare no conflicts of interest. This study was supported by a Grant from the Taipei Medical University–Chi Mei Medical Center Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yen, YC., Lin, YS., Weng, SF. et al. Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Patients with Psoriasis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Am J Clin Dermatol 16, 213–220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-015-0117-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-015-0117-9