Abstract
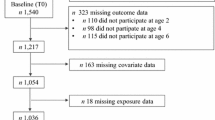
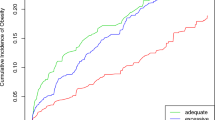
To determine how characteristics of pregnancy, birth, and early infancy are related to offspring obesity at three critical developmental periods. Mothers were followed through pregnancy and 10–15 years after. Offspring data were obtained through medical record review. Maternal and offspring characteristics were examined to predict obesity in childhood (ages 4–5 years), adolescence (ages 9–14 years), and early adulthood (ages 19–20 years). The original cohort included 802 children born to 795 women. Children who were twins, who had died, or whose mothers had died were excluded (n = 25). Medical records of 68.5% of the remaining 777 children documented a height and weight at childhood, adolescence, or early adulthood. Relative risks (RRs) to predict obesity at early adulthood were 12.3 for childhood and 45.1 at adolescence. RRs were also significant to predict obesity at early adulthood between the mother’s obesity at prepregnancy (RR = 6.4), 4–5 years postpregnancy (RR = 6.3), and 10–15 years postpregnancy (RR = 6.2). Excluding these variables from the multivariate models and adjusting by gender, birth insurance, and mother’s marital status at delivery, the best model to predict obesity at childhood included birth weight, weight gain in infancy, and delivery type. At adolescence, it included maternal pregnancy smoking status, gestational weight gain, and weight gain in infancy, and in early adulthood, included maternal pregnancy smoking status, gestational weight gain, and birth weight. Maternal pregnancy smoking status, gestational weight gain, and weight gain in infancy have long-term effects on offspring. Maternal obesity is the strongest predictor of obesity at all times studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden, C. L., Carroll, M. D., Curtin, L. R., McDowell, M. A., Tabak, C. J., & Flegal, K. M. (2006). Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 295(13), 1549–1555.
Ogden, C. L., Carroll, M. D., Curtin, L. R., Lamb, M. M., & Flegal, K. M. (2010). Prevalence of high body mass index in US children and adolescents, 2007–2008. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 303(3), 242–249.
Flegal, K. M., Carroll, M. D., Ogden, C. L., & Curtin, L. R. (2010). Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 303(3), 235–241.
Dietz, W. H. (1998). Childhood weight affects adult morbidity and mortality. The Journal of Nutrition, 128(2 Suppl), 411S–414S.
Raman, R. P. (2002). Obesity and health risks. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 21(2), 134S–139S.
He, Q., Ding, Z. Y., Fong, D. Y., & Karlberg, J. (2000). Risk factors of obesity in preschool children in China: A population-based case-control study. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity, 24(11), 1528–1536.
Hui, L. L., Nelson, E. A., Yu, L. M., Li, A. M., & Fok, T. F. (2003). Risk factors for childhood overweight in 6- to 7-y-old Hong Kong children. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity, 27(11), 1411–1418.
Li, C., Kaur, H., Choi, W. S., Huang, T. T., Lee, R. E., & Ahluwalia, J. S. (2005). Additive interactions of maternal prepregnancy BMI and breast-feeding on childhood overweight. Obesity Research, 13(2), 362–371.
Whitaker, R. C. (2004). Predicting preschooler obesity at birth: The role of maternal obesity in early pregnancy. Pediatrics, 114(1), e29–e36.
Laitinen, J., Power, C., & Jarvelin, M. R. (2001). Family social class, maternal body mass index, childhood body mass index, and age at menarche as predictors of adult obesity. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 74(3), 287–294.
Li, L., Law, C., Lo Conte, R., & Power, C. (2009). Intergenerational influences on childhood body mass index: The effect of parental body mass index trajectories. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89(2), 551–557.
Case, A., & Paxson, C. (2002). Parental behavior and child health. Health Affairs (Project Hope), 21(2), 164–178.
Dietz, W. H. (1994). Critical periods in childhood for the development of obesity. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 59(5), 955–959.
Dorosty, A. R., Emmett, P. M., Cowin, S., & Reilly, J. J. (2000). Factors associated with early adiposity rebound. ALSPAC study team. Pediatrics, 105(5), 1115–1118.
Stettler, N., Zemel, B. S., Kumanyika, S., & Stallings, V. A. (2002). Infant weight gain and childhood overweight status in a multicenter, cohort study. Pediatrics, 109(2), 194–199.
He, Q., & Karlberg, J. (2002). Probability of adult overweight and risk change during the BMI rebound period. Obesity Research, 10(3), 135–140.
Kinra, S., Baumer, J. H., & Davey Smith, G. (2005). Early growth and childhood obesity: A historical cohort study. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 90(11), 1122–1127.
Taveras, E. M., Rifas-Shiman, S. L., Belfort, M. B., Kleinman, K. P., Oken, E., & Gillman, M. W. (2009). Weight status in the first 6 months of life and obesity at 3 years of age. Pediatrics, 123(4), 1177–1183.
Gillman, M. W., Rifas-Shiman, S. L., Camargo, C. A., Jr., Berkey, C. S., Frazier, A. L., Rockett, H. R., et al. (2001). Risk of overweight among adolescents who were breastfed as infants. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 285(19), 2461–2467.
Hediger, M. L., Overpeck, M. D., Kuczmarski, R. J., & Ruan, W. J. (2001). Association between infant breastfeeding and overweight in young children. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 285(19), 2453–2460.
Armstrong, J., Reilly, J. J., & Child Health Information Team. (2002). Breastfeeding and lowering the risk of childhood obesity. Lancet, 359(9322), 2003–2004.
Kramer, M. S., Matush, L., Bogdanovich, N., Aboud, F., Mazer, B., Fombonne, E., et al. (2009). Health and development outcomes in 6.5-y-old children breastfed exclusively for 3 or 6 mo. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 90(4), 1070–1074.
Ong, K. K., Preece, M. A., Emmett, P. M., Ahmed, M. L., Dunger, D. B., & ALSPAC Study Team. (2002). Size at birth and early childhood growth in relation to maternal smoking, parity and infant breast-feeding: Longitudinal birth cohort study and analysis. Pediatric Research, 52(6), 863–867.
Toschke, A. M., Koletzko, B., Slikker, W., Jr, Hermann, M., & von Kries, R. (2002). Childhood obesity is associated with maternal smoking in pregnancy. European Journal of Pediatrics, 161(8), 445–448.
Wideroe, M., Vik, T., Jacobsen, G., & Bakketeig, L. S. (2003). Does maternal smoking during pregnancy cause childhood overweight? Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology, 17(2), 171–179.
von Kries, R., Toschke, A. M., Koletzko, B., & Slikker, W., Jr. (2002). Maternal smoking during pregnancy and childhood obesity. American Journal of Epidemiology, 156(10), 954–961.
Salsberry, P. J., & Reagan, P. B. (2005). Dynamics of early childhood overweight. Pediatrics, 116(6), 1329–1338.
Schauberger, C. W., Rooney, B. L., & Brimer, L. M. (1992). Factors that influence weight loss in the puerperium. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 79(3), 424–429.
Rooney, B. L., & Schauberger, C. W. (2002). Excess pregnancy weight gain and long-term obesity: One decade later. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 100(2), 245–252.
Rooney, B. L., Schauberger, C. W., & Mathiason, M. A. (2005). Impact of perinatal weight change on long-term obesity and obesity-related illnesses. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 106(6), 1349–1356.
Committee on Nutritional Status During Pregnancy and Lactation, Institute of Medicine. (1990). Weight gain. Nutrition during pregnancy (p. 10). Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press.
Nader, P. R., O’Brien, M., Houts, R., Bradley, R., Belsky, J., Crosnoe, R., et al. (2006). Identifying risk for obesity in early childhood. Pediatrics, 118(3), e594–e601.
Guo, S. S., Roche, A. F., Chumlea, W. C., Gardner, J. D., & Siervogel, R. M. (1994). The predictive value of childhood body mass index values for overweight at age 35 y. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 59(4), 810–819.
Salbe, A. D., Weyer, C., Lindsay, R. S., Ravussin, E., & Tataranni, P. A. (2002). Assessing risk factors for obesity between childhood and adolescence: Part I. Birth weight, childhood adiposity, parental obesity, insulin, and leptin. Pediatrics, 110(2 Pt 1), 299–306.
Li, C., Goran, M. I., Kaur, H., Nollen, N., & Ahluwalia, J. S. (2007). Developmental trajectories of overweight during childhood: Role of early life factors. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 15(3), 760–771.
Olson, C. M., Strawderman, M. S., & Dennison, B. A. (2009). Maternal weight gain during pregnancy and child weight at age 3 years. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 13(6), 839–846.
Oken, E., & Gillman, M. W. (2003). Fetal origins of obesity. Obesity Research, 11(4), 496–506.
Sorensen, H. T., Sabroe, S., Rothman, K. J., Gillman, M., Fischer, P., & Sorensen, T. I. (1997). Relation between weight and length at birth and body mass index in young adulthood: Cohort study. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.), 315(7116), 1137.
Ong, K. K., & Dunger, D. B. (2002). Perinatal growth failure: The road to obesity, insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease in adults. Best Practice and Research. Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 16(2), 191–207.
Haas, J. S., Lee, L. B., Kaplan, C. P., Sonneborn, D., Phillips, K. A., & Liang, S. Y. (2003). The association of race, socioeconomic status, and health insurance status with the prevalence of overweight among children and adolescents. American Journal of Public Health, 93(12), 2105–2110.
Khlat, M., Jusot, F., & Ville, I. (2009). Social origins, early hardship and obesity: A strong association in women, but not in men? Social Science and Medicine(1982), 68(9), 1692–1699.
Kinnunen, T. I., Luoto, R., Gissler, M., & Hemminki, E. (2003). Pregnancy weight gain from 1960s to 2000 in Finland. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders: Journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity, 27(12), 1572–1577.
Schieve, L. A., Cogswell, M. E., & Scanlon, K. S. (1998). Trends in pregnancy weight gain within and outside ranges recommended by the Institute of Medicine in a WIC population. Maternal and Child Health Journal, 2(2), 111–116.
Institute of Medicine, National Research Council Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines. (2009). Weight gain during pregnancy: Reexamining the guidelines. Washington, D.C.: The National Academies Press.
Gidding, S. S., Dennison, B. A., Birch, L. L., Daniels, S. R., Gillman, M. W., Lichtenstein, A. H., et al. (2005). Dietary recommendations for children and adolescents: A guide for practitioners: Consensus statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation, 112(13), 2061–2075.
US Preventive Services Task Force. (2010). Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: US preventive services task force recommendation statement. Pediatrics, 125, 361–367.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by support from the Gundersen Lutheran Medical Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rooney, B.L., Mathiason, M.A. & Schauberger, C.W. Predictors of Obesity in Childhood, Adolescence, and Adulthood in a Birth Cohort. Matern Child Health J 15, 1166–1175 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-010-0689-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10995-010-0689-1