Abstract
Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) is successful in ∼70–80 % after repeated procedures. This suggests a subgroup of PAF patients where electrical abnormalities outside the pulmonary veins are important. Prolonged P-wave duration (PWD), a marker of atrial remodelling, may identify this subgroup. This study’s aim was to assess the association of PWD on standard 12 lead ECG with AF recurrence post PVI.
Methods
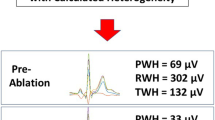
Retrospectively, ECGs were blindly analysed on PVI patients from August 2007–August 2011; patients with persistent AF, mitral valve disease, undergoing redo procedures or no sinus rhythm (SR) ECG within 1 year of PVI were excluded. ECGs were directly uploaded at 300 dpi, amplified ×10, and then PWD measured in all leads. Prolonged PWD was as priori defined as maximum PWD ≥ 140 ms.
Results
The selective cohort consisted of 100 patients out of a total of 170 PVI: age 58 ± 11 years, 72 % male, LVEF 62 ± 9 %, 18 % ischaemic heart disease and 13 % diabetic. Thirty-five had prolonged PWD, which was associated with greater AF recurrence rates compared to those without prolonged PWD (63 vs. 38 %, p < 0.05). Similarly, AF recurrence was associated with greater maximum PWD (139 ± 17 vs. 129 ± 14, p < 0.01), P-wave dispersion (58 ± 21 vs. 49 ± 15, p < 0.01), left atrium (LA) dimension (41 ± 6 vs. 38 ± 5, p < 0.05) and LA volumes (40 ± 14 vs. 34 ± 11, p < 0.05) compared to those who remained in SR. None of these variables were independent predictors of AF recurrence by multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
The presence of pre-existent prolonged PWD is associated with a higher risk of AF recurrence post PVI for paroxysmal AF.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calkins, H., Kuck, K. H., Cappato, R., Brugada, J., Camm, A. J., Chen, S. A., et al. (2012). HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation: Recommendations for patient selection, procedural techniques, patient management and follow-up, definitions, endpoints, and research trial design: A report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation. Developed in partnership with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA), a registered branch of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society (ECAS); and in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS), and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS). Endorsed by the governing bodies of the American College of Cardiology Foundation, the American Heart Association, the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society, the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society, and the Heart Rhythm Society. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 33, 171–257.
Medi, C., Sparks, P. B., Morton, J. B., Kistler, P. M., Halloran, K., Rosso, R., et al. (2011). Pulmonary vein antral isolation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: results from long-term follow-up. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(2), 137–141.
Callans, D. J., Gerstenfeld, E. P., Dixit, S., Zado, E., Vanaderhoff, M., et al. (2004). Efficacy of repeat pulmonary vein isolation procedures in patients with recurrent atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 15(9), 1050–1055.
Gerstenfeld, E. P., Callans, D. J., Dixit, S., Zado, E., & Marchlinski, F. E. (2003). Incidence and location of focal atrial fibrillation triggers in patients undergoing repeat pulmonary vein isolation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 14(7), 685–690.
Brooks, A. G., Stiles, M. K., Laborderie, J., Lau, D. H., Kuklik, P., Shipp, N. J., et al. (2010). Outcomes of long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: a systematic review. Heart Rhythm, 7(6), 835–846.
Redfearn, D. P., Lane, J., Ward, K., & Stafford, P. J. (2006). High-resolution analysis of the surface P wave as a measure of atrial electrophysiological substrate. Annals of Noninvasive Electrocardiology, 11(1), 12–19.
de Luna, B., Cladellas, M., Oter, R., Torner, P., Guindo, J., Marti, V., et al. (1988). Interatrial conduction block and retrograde activation of the left atrium and paroxysmal supraventricular tachyarrhythmia. European Heart Journal, 9(10), 1112–1118.
Agarwal, Y. K., Aronow, W. S., Levy, J. A., & Spodick, D. H. (2003). Association of interatrial block with development of atrial fibrillation. American Journal of Cardiology, 91(7), 882.
Ariyarajah, V., Apiyasawat, S., Fernandes, J., Kranis, M., & Spodick, D. H. (2007). Association of atrial fibrillation in patients with interatrial block over prospectively followed controls with comparable echocardiographic parameters. American Journal of Cardiology, 99(3), 390–392.
Magnani, J. W., Johnson, V. M., Sullivan, L. M., Gorodeski, E. Z., Schnabel, R. B., Lubitz, S. A., et al. (2011). P wave duration and risk of longitudinal atrial fibrillation in persons >60 years old (from the Framingham Heart Study). The American Journal of Cardiology, 107(6), 917–921.
Budeus, M., Hennersdorf, M., Perings, C., Wieneke, H., Erbel, R., & Sack, S. (2005). Prediction of the recurrence of atrial fibrillation after successful cardioversion with P wave signal-averaged ECG. Annals of Noninvasive Electrocardiology, 10(4), 414–419.
Koide, Y., Yotsukura, M., Ando, H., Aoki, S., Suzuki, T., Sakata, K., et al. (2008). Usefulness of P-wave dispersion in standard twelve-lead electrocardiography to predict transition from paroxysmal to persistent atrial fibrillation. The American Journal of Cardiology, 102(5), 573–577.
Dixen, U., Vang Larsen, M., Ravn, L., Parner, J., & Jensen, G. B. (2008). Signal-averaged P wave duration and the long-term risk of permanent atrial fibrillation. Scandinavian Cardiovascular Journal, 42(1), 31–37.
de Bayes, L. A., Platonov, P., Cosio, F. G., Cygankiewicz, I., Pastore, C., Baranowski, R., et al. (2012). Interatrial blocks. A separate entity from left atrial enlargement: a consensus report. Journal of Electrocardiology, 45(5), 445–451.
Berruezo, A., Tamborero, D., Mont, L., Benito, B., Tolosana, J. M., Sitges, M., et al. (2007). Pre-procedural predictors of atrial fibrillation recurrence after circumferential pulmonary vein ablation. European Heart Journal, 28(7), 836–841.
den Uijl, D. W., Delgado, V., Bertini, M., Tops, L. F., Trines, S. A., van de Veire, N. R., et al. (2011). Impact of left atrial fibrosis and left atrial size on the outcome of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. Heart, 97(22), 1847–1851.
Sohns, C., Sohns, J. M., Vollmann, D., Luthje, L., Bergau, L., Dorenkamp, M., et al. (2013). Left atrial volumetry from routine diagnostic work up prior to pulmonary vein ablation is a good predictor of freedom from atrial fibrillation. European Heart Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging, 14(7), 684–691.
den Uijl, D. W., Tops, L. F., Delgado, V., Schuijf, J. D., Kroft, L. J. M., de Roos, A., et al. (2011). Effect of pulmonary vein anatomy and left atrial dimensions on outcome of circumferential radiofrequency catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. The American Journal of Cardiology, 107(2), 243–249.
Parikh, S. S., Jons, C., McNitt, S., Daubert, J. P., Schwarz, K. Q., & Hall, B. (2010). Predictive capability of left atrial size measured by CT, TEE, and TTE for recurrence of atrial fibrillation following radiofrequency catheter ablation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 33(5), 532–540.
Blanche, C., Tran, N., Rigamonti, F., Burri, H., & Zimmermann, M. (2013). Value of P-wave signal averaging to predict atrial fibrillation recurrences after pulmonary vein isolation. Europace, 15(2), 198–204.
Okumura, Y., Watanabe, I., Ohkubo, K., Ashino, S., Kofune, M., Hashimoto, K., et al. (2007). Prediction of the efficacy of pulmonary vein isolation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation by the signal-averaged P-wave duration. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 30(3), 304–313.
Ogawa, M., Kumagai, K., Vakulenko, M., Yasuda, T., Siegerman, C., Garfinkel, A., et al. (2007). Reduction of P-wave duration and successful pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18(9), 931–938.
Baranchuk, A., Pang, H., Seaborn, G., Yazdan-Ashoori, P., Redfearn, D. P., Simpson, C. S., et al. (2013). Reverse atrial electrical remodelling induced by continuous positive airway pressure in patients with severe obstructive sleep apnoea. Journal of Interventional Cardiac Electrophysiology, 36(3), 247–253.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an unrestricted grant provided by the Clinical Teachers’ Association of Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caldwell, J., Koppikar, S., Barake, W. et al. Prolonged P-wave duration is associated with atrial fibrillation recurrence after successful pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 39, 131–138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-013-9851-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-013-9851-1