Abstract
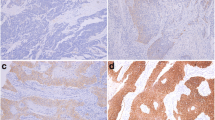
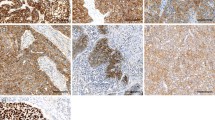
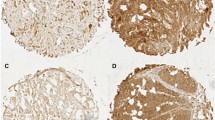
Expression of Eag1 was detected in resected esophageal squamous cell carcinomas tissues and matched tissues by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR. Positive expression of Eag1 protein was 75% (51/68), and mRNA was 73% (8/11) in primary cancer tissues. Eag1 protein positively stained in all 10 metastatic lymph nodes. Eag1 protein and mRNA were negatively expressed in all non-cancerous matched tissues. Eag1 protein was associated with depth of penetration (P = 0.023), but not associated with other clinicopathological factors. Eag1 protein positive group had a significantly shorter survival time than the negative group (P = 0.005). Survival rates at each time-point for the positive group were lower than that for the negative group (P = 0.006), and Eag1 was identified as an independent prognostic factor of long-term survival (P = 0.016). In conclusion, Eag1 was aberrantly expressed in ESCC and correlated with poor prognosis after surgery.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu JF, Wang QZ, Hou J (2004) Surgical treatment for cancer of the oesophagus, gastric cardia in Hebei. China Br J Surg 91:90–98
Latour I, Louw DF, Beedle AM, Hamid J, Sutherland GR, Zamponi GW (2004) Expression of T-type calcium channel splice variants in human glioma. Glia 48:112–119
Wang XT, Nagaba Y, Cross HS, Wrba F, Zhang L, Guggino SE (2000) The mRNA of L-type calcium channel elevated in colon cancer: protein distribution in normal and cancerous colon. Am J Pathol 157:1549–1562
Kim CJ, Cho YG, Jeong SW, Kim YS, Kim SY, Nam SW, Lee SH, Yoo NJ, Lee JY, Park WS (2004) Altered expression of KCNK9 in colorectal cancers. APMIS 112:588–594
Bustin SA, Li SR, Dorudi S (2001) Expression of the Ca2+-activated chloride channel genes CLCA1 and CLCA2 is downregulated in human colorectal cancer. DNA Cell Biol 20:331–333
Abdel-Ghany M, Cheng HC, Elble RC, Lin H, DiBiasio J, Pauli BU (2003) The interacting binding domains of the beta(4) integrin and calcium-activated chloride channels (CLCAs) in metastasis. J Biol Chem 278:49406–49416
Bennet ES, Smith BA, Harper JM (2004) Voltage-gated NaC channels confer invasive properties on human prostate cancer cells. Pflugers Arch 447:908–914
Schonherr R (2005) Clinical relevance of ion channels for diagnosis and therapy of cancer. J Membr Biol 205:175–184
Kunzelmann K (2005) Ion channels and cancer. J Membr Biol 205:159–173
Pardo LA, Contreras-Jurado C, Zientkowska M, Alves F, Stuhmer W (2005) Role of voltage-gated potassium channels in cancer. J Membr Biol 205:115–124
Wang Z (2004) Roles of KC channels in regulating tumor cell proliferation and apoptosis. Pflugers Arch 448:274–286
Patel AJ, Lazdunski M (2004) The 2P-domain KC channels: role in apoptosis and tumorigenesis. Pflugers Arch 448:261–273
Camacho J (2006) Ether à go-go potassium channels and cancer. Cancer Lett 233:1–9
Camacho J, Sanchez A, Stuhmer W, Pardo LA (2000) Cytoskeletal interactions determine the electrophysiological properties of human EAG potassium channels. Pflugers Arch 441:167–174
Pardo LA, Brüggemann A, Camacho J, Stühmer W (1998) Cell cycle-related changes in the conducting properties of r-eag K+ channels. J Cell Biol 143:767–775
Brüggemann A, Stühmer W, Pardo LA (1997) Mitosis-promoting factor-mediated suppression of a cloned delayed rectifier potassium channel expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:537–542
Occhiodoro T, Bernheim L, Liu JH, Bijlenga P, Sinnreich M, Bader CR, Fischer-Lougheed J (1998) Cloning of a human ether-a-go-go potassium channel expressed in myoblasts at the onset of fusion. FEBS Lett 434:177–182
Meyer R, Schonherr R, Gavrilova-Ruch O, Wohlrab W, Heinemann SH (1999) Identification of ether à go-go and calcium-activated potassium channels in human melanoma cells. J Membr Biol 171:107–115
Meyer R, Heinemann SH (1998) Characterization of an eag-like potassium channel in human neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol 508:49–56
Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Le Bourhis X, Roudbaraki M, Toillon RA, Delcourt P, Prevarskaya N (2001) Changes in the K+ current-density of MCF-7 cells during progression through the cell cycle: possible involvement of a h-ether. a-gogo K+ channel. Recept Channels 7:345–356
Farias LM, Ocana DB, Diaz L, Larrea F, Avila-Chavez E, Cadena A, Hinojosa LM, Lara G, Villanueva LA, Vargas C, Hernandez-Gallegos E, Camacho-Arroyo I, Duenas-Gonzalez A, Perez-Cardenas E, Pardo LA, Morales A, Taja-Chayeb L, Escamilla J, Sanchez-Pena C, Camacho J (2004) Ether à go-go potassium channels as human cervical cancer markers. Cancer Res 64:6996–7001
Patt S, Preussat K, Beetz C, Kraft R, Schrey M, Kalff R, Schonherr K, Heinemann SH (2004) Expression of ether à go-go potassium channels in human gliomas. Neurosci Lett 368:249–253
Mello de Queiroz F, Suarez-Kurtz G, Stuhmer W, Pardo LA (2006) Ether à go-go potassium channel expression in soft tissue sarcoma patients. Mol Cancer 5:42
Ding XW, Yan JJ, An P, Lü P, Luo HS (2007) Aberrant expression of ether à go-go potassium channel in colorectal cancer patients and cell lines. World J Gastroenterol 13:1257–1261
Hemmerlein B, Weseloh RM, Mello de Queiroz F, Knotgen H, Sanchez A, Rubio ME, Martin S, Schliephacke T, Jenke M, Radzun HJ, Stuhmer W, Pardo LA (2006) Overexpression of Eag1 potassium channels in clinical tumours. Mol Cancer 5:41
Pardo LA, del Camino D, Sanchez A, Alves F, Bruggemann A, Beckh S, Stuhmer W (1999) Oncogenic potential of EAG K(+) channels. EMBO J 18:5540–5547
Mega S, Miyamoto M, Ebihara Y, Takahashi R, Hase R, Li L, Shichinohe T, Kawarada Y, Uehara H, Kaneko H, Hashimoto H, Murakami Y, Itoh T, Morikawa T, Kondo S (2005) Cyclin D1, E2F1 expression levels are associated with characteristics and prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus 18:109–113
Stoecklein NH, Siegmund A, Scheunemann P, Luebke AM, Erbersdobler A, Verde PE, Eisenberger CF, Peiper M, Rehders A, Esch JS, Knoefel WT, Hosch SB (2006) Ep-CAM expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a potential therapeutic target and prognostic marker. BMC Cancer 6:165
Xue LY, Ren LQ, Luo W, Guan XJ, Zou SM, Zheng S, Bi R, Xie YQ, He ZG, Lu N (2007) Expression of Fas, Fas ligand, Fas-associated death domain protein, caspase 8 and mutant P53 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 87:150–154
Uehara H, Miyamoto M, Kato K, Cho Y, Kurokawa T, Murakami S, Fukunaga A, Ebihara Y, Kaneko H, Hashimoto H, Murakami Y, Shichinohe T, Kawarada Y, Itoh T, Okushiba S, Kondo S, Katoh H (2005) Deficiency of hMLH1 and hMSH2 expression is a poor prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol 92:109–115
Wada S, Noguchi T, Takeno S, Kawahara K (2006) PIK3CA and TFRC located in 3q are new prognostic factors in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 13:961–966
Ishiyama A, Hibi K, Koike M, Fujiwara M, Kodera Y, Ito K, Nakao A (2006) PTCH gene expression as a potential marker for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 26:195–198
Takashima N, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura M, Haruki N, Ando T, Kurehara H, Sugito N, Mori R, Fujii Y (2006) Expression and prognostic roles of PABPC1 in esophageal cancer: correlation with tumor progression and postoperative survival. Oncol Rep 15:667–671
Rosato A, Pivetta M, Parenti A, Iaderosa GA, Zoso A, Milan G, Mandruzzato S, Del Bianco P, Ruol A, Zaninotto G, Zanovello P (2006) Survivin in esophageal cancer: an accurate prognostic marker for squamous cell carcinoma but not adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 119:1717–1722
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Xiangfan Central Hospital and Wuhan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, XW., Wang, XG., Luo, HS. et al. Expression and Prognostic Roles of Eag1 in Resected Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Dig Dis Sci 53, 2039–2044 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0116-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0116-7