Abstract
Background
Skin-sparing mastectomy (SSM) followed by immediate reconstruction has been advocated as an effective treatment option for patients with early-stage breast carcinoma. It minimizes deformity and improves cosmesis through preservation of the natural skin envelope of the breast. The purpose of this study was to evaluate postoperative morbidity, patients' satisfaction, and oncological safety for SSM and immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) with a latissimus dorsi (LD) myocutaneous flap and/or breast prosthesis in patients with operable breast cancer.
Methods
Twenty-one consecutive patients with operable breast cancer undergoing 25 SSM and immediate reconstruction with an LD flap plus implant (n = 14) or implant alone (n = 11) were retrospectively studied (from 2001 through 2005). The median patients' age was 44 years (range, 30–68). Patient satisfaction with the outcome of surgery was assessed using a detailed questionnaire including a linear visual analogue scale ranging from 0 (not satisfied) to 10 (most satisfied). Eight of 20 (40%) patients required adjuvant chemotherapy, and only 2 patients required post-mastectomy radiation. Reconstruction of the nipple–areola complex was performed in 7 patients (33%) using the trefoil local flap technique. Contralateral procedures to achieve symmetry were performed in 6 (28%) patients (5 augmentations and 1 reduction mammoplasty).
Results
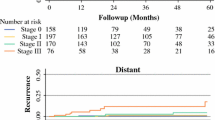
Histological analysis showed pure ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) in 4 patients and invasive carcinoma (+/− DCIS) in 20 cases, of which 5 (25%) were node positive. One prophylactic mastectomy in a BRCA-2 carrier was negative for malignancy. Tumor size ranged from 5 to 90 mm. The surgical margins were clear in all cases. There was no delay in time to commencement of adjuvant therapies. After a mean follow-up period of 13.5 months (range, 5–46 months), none of the patients developed locoregional recurrence. Only 1 patient (5%) developed systemic recurrence (bony metastases). Overall survival was 100%. The incidence of flap necrosis/loss, implant loss, wound infection, or hematoma requiring surgical evacuation was 0%, 0%, 0%, and 0%, respectively. Capsule formation requiring capsulotomy was observed in 3 of 21 patients (14%). The median patient satisfaction score was 10 (range, 6–10).
Conclusion
SSM and IBR for operable breast cancer is associated with a high level of patient satisfaction and low morbidity. The procedure seems to be oncologically safe, even in patients with high-risk (T3 or node-positive) carcinoma. The latter needs to be confirmed with greater numbers of patients and longer follow-up.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
RM Simmons TL Adamovich (2003) ArticleTitleSkin-sparing mastectomy Surg Clin N Am 83 885–899 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0039-6109(03)00035-5 Occurrence Handle12875600
SE Singletary GL Robb (2003) ArticleTitleOncologic safety of skin-sparing mastectomy Ann Surg Oncol 10 95–97 Occurrence Handle12620899
GH Cunnick K Mokbel (2004) ArticleTitleSkin-sparing mastectomy Am J Surg 188 IssueID1 78–84 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.amjsurg.2004.02.004 Occurrence Handle15219490
CM Ho CK Mak Y Lau WY Cheung MC Chan WK Hung (2003) ArticleTitleSkin involvement in invasive breast carcinoma: safety of skin-sparing mastectomy Ann Surg Oncol 10 102–107 Occurrence Handle12620902
RD Foster LJ Esserman JP Anthony et al. (2002) ArticleTitleSkin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction: a prospective cohort study for the treatment of advanced stages of breast carcinoma Ann Surg Oncol 9 IssueID5 462–466 Occurrence Handle10.1245/aso.2002.9.5.462 Occurrence Handle12052757
H Medina-Franco LO Vasconez RJ Fix et al. (2002) ArticleTitleFactors associated with local recurrence after skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction for invasive breast cancer Ann Surg 235 814–819 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000658-200206000-00008 Occurrence Handle12035037
K Mokbel (2003) ArticleTitleTowards optimal management of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast Eur J Surg Oncol 29 191–197 Occurrence Handle12633565
AJ Spiegel CE Butler (2003) ArticleTitleRecurrence following treatment of ductal carcinoma in situ with skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction Plast Reconstr Surg 111 706–711 Occurrence Handle12560691
IT Rubio N Mirza AA Sahin et al. (2000) ArticleTitleRole of specimen radiography in patients treated with skin-sparing mastectomy for ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast Ann Surg Oncol 7 544–548 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10434-000-0544-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FmtVSisQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10947024
GW Carlson J Bostwick SuffixIII TN Styblo et al. (1998) ArticleTitleSkin sparing mastectomy, oncologic and reconstructive considerations Ann Surg 225 570–578
DA Hudson (2004) ArticleTitleFactors determining shape and symmetry in immediate breast reconstruction Ann Plast Surg 52 IssueID1 15–21 Occurrence Handle14676693
SJ Kronowitz KK Hunt HM Kuerer et al. (2004) ArticleTitleDelayed-immediate breast reconstruction Plast Reconstr Surg 113 IssueID6 1617–1628 Occurrence Handle15114121
GR Evans MA Schusterman SS Kroll et al. (1995) ArticleTitleReconstruction and the radiated breast: is there a role for implants? Plast Reconstr Surg 96 1111–1115 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymD3MfpvVU%3D Occurrence Handle7568487
PG Cordeiro AL Pusic JJ Disa et al. (2004) ArticleTitleIrradiation after immediate tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction: outcomes, complications, aesthetic results, and satisfaction among 156 patients Plast Reconstr Surg 113 877–881 Occurrence Handle15108879
K Benediktsson L Perbeck (1999) ArticleTitleThe influence of radiotherapy on skin circulation of the breast after subcutaneous mastectomy and immediate reconstruction Br J Plast Surg 52 360–364 Occurrence Handle10.1054/bjps.1999.3116 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2FosFKqug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10618978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Salhab, M., Sarakbi, W., Joseph, A. et al. Skin-sparing mastectomy and immediate breast reconstruction: patient satisfaction and clinical outcome. Int J Clin Oncol 11, 51–54 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-005-0538-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-005-0538-1