Abstract
Objective
To collect epidemiological data of peripheral facial palsy, and especially to chart the incidence and clinical characteristics of Lyme associated facial palsy.
Material and methods
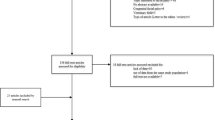
We included consecutive adult patients presenting with peripheral facial palsy in Vest–Agder County from January 1997 to December 1998. The facial palsy was graded according to the House and Brackman facial function scoring system,and cerebrospinal fluid and serum samples were examined for Borrelia burgdorferi antibodies and virus antibodies. Final outcome was evaluated by follow up visits or telephone interview.
Results
Sixty nine patients were included and followed until complete recovery, or for 5 years. Ten per cent were caused by Lyme disease, 17% by virus infection, 4% by other causes and 68% were classified as Bell’s palsy. All patients with Lyme facial palsy had additional neurological symptoms, and 87% reported constitutional complaints. The overall final outcome was good with complete recovery in 77%, slight sequelae in 20% and moderate sequelae in 3%. No patients experienced severe sequelae. Two of 28 patients examined with neurography had absent compound muscle action potentials in orbicularis oculi. Both made good recovery with only slight sequelae.
Conclusions
Peripheral facial palsy is a common disorder with a favourable prognosis. Lyme disease seems to be an infrequent cause of facial palsy in patients without constitutional symptoms or additional neurological findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowlands S, Hooper R, Hughes R, Burney P (2002) The epidemiology and treatment of Bell’s palsy in the UK. Eur J Neurol 9:63–67
Gilbert SC (2002) Bell’s palsy and herpesviruses. Herpes 9:70–73
Grogan PM, Gronseth GS (2001) Practice parameter: Steroids, acyclovir, and surgery for Bell’s palsy (an evidencebased review): report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 56:830–836
Peitersen E (2002) Bell’s palsy: the spontaneous course of 2,500 peripheral facial nerve palsies of different etiologies. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl:4–30
Ljostad U, Mygland A, Skarpaas T (2003) Neuroborreliosis in Vest-Agder. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 123:610–613
Smith IM, Murray JA, Cull RE, Slattery J (1992) A comparison of facial grading systems. Clin Otolaryngol 17:303–307
Hyden D, Roberg M, Forsberg P, Fridell E, Fryden A, Linde A, Odkvist L (1993) Acute “idiopathic” peripheral facial palsy: clinical, serological, and cerebrospinal fluid findings and effects of corticosteroids. Am J Otolaryngol 14:179–186
Peltomaa M, Pyykko I, Seppala I, Viljanen M (2002) Lyme borreliosis and facial paralysis–a prospective analysis of risk factors and outcome. Am J Otolaryngol 23:125–132
Kohler A, Chofflon M, Sztajzel R, Magistris MR (1999) Cerebrospinal fluid in acute peripheral facial palsy. J Neurol 246:165–169
Lotric-Furlan S, Cimperman J, Maraspin V, Ruzic-Sabljic E, Logar M, Jurca T, Strle F (1999) Lyme borreliosis and peripheral facial palsy. Wien Klin Wochenschr 111:970–975
Engervall K, Carlsson-Nordlander B, Hederstedt B, Berggren D, Bjerkhoel A, Carlborg A, Grenner J, Hanner P, Hogmo A, Isholt RM (1995) Borreliosis as a cause of peripheral facial palsy: a multi-center study. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 57:202–206
Halperin JJ, Logigian EL, Finkel MF, Pearl RA (1996) Practice parameters for the diagnosis of patients with nervous system Lyme borreliosis (Lyme disease).Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 46:619–627
Halperin JJ (2003) Facial nerve palsy associated with lyme disease. Muscle Nerve 28:516–517
Smouha EE, Coyle PK, Shukri S (1997) Facial nerve palsy in Lyme disease: evaluation of clinical diagnostic criteria. Am J Otol 18:257–261
Tysnes OB, Hofstad H, Jacobsen H (1992) Peripheral facial paresis as a symptom of Borrelia burgdorferi infection. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 112:50–51
Kuiper H, Devriese PP, de Jongh BM, Vos K, Dankert J (1992) Absence of Lyme borreliosis among patients with presumed Bell’s palsy. Arch Neurol 49:940–943
Roberg M, Ernerudh J, Forsberg P, Fridell E, Fryden A, Hyden D, Linde A, Odkvist L (1991) Acute peripheral facial palsy: CSF findings and etiology. Acta Neurol Scand 83:55–60
Redaelli de Zinis LO, Gamba P, Balzanelli C (2003) Acute otitis media and facial nerve paralysis in adults. Otol Neurotol 24:113–117
Olsen PZ (1975) Prediction of recovery in Bell’s palsy. Acta Neurol Scand 61 (Suppl):1–121
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ljøstad, U., Økstad, S., Topstad, T. et al. Acute peripheral facial palsy in adults. J Neurol 252, 672–676 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0715-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0715-1