Abstract
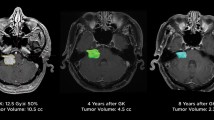
Radiosurgery (RS) is a noninvasive, ambulatory special neurosurgical procedure for the treatment of vestibular schwannoma (VS). We treated 123 patients with unilateral schwannomas between 1994 and 2000 at the gamma knife (GK) center in Munich using a primary stereotactic procedure. These patients were followed up until June 2004 in respect to audiological, neurological, neurootological and radiological features before and after radiosurgical intervention. The actual tumor control rate of 8.2 years (mean) after GK surgery for all patients and a single treatment was calculated to be 96.7%. The impairment of hearing was on average 18% after GK, ranking from 0% gain of hearing loss up to 90%. Facial nerve function, graded according to the House–Brackmann scale, deteriorated in none of the patients; 5.8% reported a trigeminal neuralgia. Tinnitus developed in 4.1% of the patients after RS; 13.3% had vertigo for the first time after the treatment, age apparently being a predisposing factor. Radiosurgical treatment for VS is an alternative to microsurgery (MS). It is associated with a lower rate of facial and trigeminal neuropathy, postoperative complications and hospital stay. The hearing preservation rate is equivalent to MS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews DW, Suarez O, Goldman HW, Downes MB, Bednarz G, Corn BW, Werner-Wasik M, Rosenstock J, Curran WJ Jr (2001) Stereotactic radiosurgery and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for the treatment of acoustic schwannomas: comparative observations of 125 patients treated at one institution. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50:1265–1278
Boenninghaus HG, Röser D (1973) New tables for the determination of percentile loss of speech hearing. Z Laryngol Rhinol Otol 52:153–161
Chang SD, Poen J, Hancock SL, Martin DP, Adler JR Jr (1998) Acute hearing loss following fractionated stereotactic radiosurgery for acoustic neuroma. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 89:321–325
Coker NJ (2003) The radiosurgical option: too many unanswered questions. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:906–907
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Pollock BE, Lunsford LD (1996) Evolution in technique for vestibular schwannoma radiosurgery and effect on outcome. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 36:275–280
Foote RL, Coffey RJ, Swanson JW, Harner SG, Beatty CW, Kline RW, Stevens LN, Hu TC (1995) Stereotactic radiosurgery using the gamma knife for acoustic neuromas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 32:1153–1160
House WF, Brackmann DE (1985) Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 93:184–185
Karpinos M, Teh BS, Zeck O, Carpenter LS, Phan C, Mai W, Lu HH, Chiu JK, Butler EB, Gormley WB, Woo SY (2002) Treatment of acoustic neuroma: stereotactic radiosurgery vs. microsurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 54:1410–1421
Koos WT, Matula Ch, Levy D, Kitz K (1995) Microsurgery versus radiosurgery in the treatment of small acoustic neurinomas. Acta Neurochir Suppl 63:73–80
Leksell DG (1987) Stereotactic radiosurgery: present status and future trends. Neurol Res 9:60–68
Mack A, Czempiel H, Kreiner HJ, Durr G, Wowra B (2002) Quality assurance in stereotactic space. A system test for verifying the accuracy of aim in radiosurgery. Med Phys 29:561–568
Petit JH, Hudes RS, Chen TT, Eisenberg HM, Simard JM, Chin LS (2001) Reduced-dose radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas. Neurosurgery 49:1299–1307
Pollock BE, Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Bissonette DJ, Kelsey SF, Jannetta PJ (1995) Outcome analysis of acoustic neuroma management: a comparison of microsurgery and stereotactic radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 36:215–224
Pollock BE, Lunsford LD, Noren G (1998) Vestibular schwannoma management in the next century: a radiosurgical perspective. Neurosurgery 43:475–481
Unger F, Walch C, Papaefthymiou G, Trummer M, Eustachhio S, Pendl G (1999) Die Radiochirurgie des Akustikusneurinoms als minimal-invasive Alternative zur Microchirurgie. HNO 47:1046–1051
Weber PC, Gantz BJ (1996) Results and complications from acoustic neuroma excision via the middle cranial fossa approach. Am J Otol 17:669–675
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hempel, J.M., Hempel, E., Wowra, B. et al. Functional outcome after gamma knife treatment in vestibular schwannoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263, 714–718 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-006-0054-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-006-0054-6