Abstract
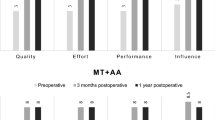
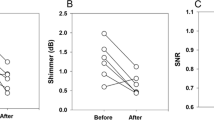
Medialization thyroplasty (MT) is the most widely used laryngeal framework phonosurgical procedure for managing glottic incompetence secondary to unilateral vocal fold paralysis (UVFP). The aim of the study was to evaluate the functional outcomes of MT in 32 UVFP patients, comparing multidimensional perceptual and instrumental measures of voice before and after surgery, and to evaluate how close to normal that postoperative voice measure became. Video laryngostroboscopy (VLS), auditory perceptive evaluation of voice, the patients’ self-evaluation of hoarseness on the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and calculation of the Voice Handicap Index (VHI), analysis of objective acoustic voice parameters, quantitative assessment of phonetograms and measurement of maximum phonation time were conducted. Vocal function was evaluated before the surgery and for the period from 1 month to 3 years (Mo 1.0 month; Me 2.0 months) after MT. VLS confirmed remarkable medialization of the paralyzed vocal fold. As a consequence, hoarseness and breathiness were found to be significantly decreased after MT. Pitch and intensity range and phonetogram area were significantly increased. A significant decrease of jitter, shimmer and normalized noise energy reflected improvement of the stability of acoustic signal and a more efficient pattern of phonation. Thus, the perceptual and acoustic voice parameters studied showed statistically significant differences (P<0.001) between preoperative and postoperative voices, and these objective measurements of voice changes provided accurate and documentary evidence of the results of surgical treatment. A high degree of patient satisfaction with the MT was confirmed by a significant decrease of VHI and hoarseness on VAS. Thus, results of the present investigation confirm the functionality and effectiveness of MT in patient voice rehabilitation with UVFP. However, the means of acoustic voice parameters measured in the study did not reach normal limits, probably because of the remaining underlying condition of UVFP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benninger MS, Crumley RL, Ford CN, Gould WJ, Hanson DG, Ossoff RH, Sataloff RT (1994) Evaluation and treatment of unilateral paralysed vocal fold. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 111:497–508
Billante CR, Clary J, Childs P, Netterville JL (2002) Voice gains following thyroplasty may improve over time. Clin Otolaryngol 27:1–6
Dejonckere PH, Bradley P, Clemente P, Cornut G, Crevier-Buchman L, Friedrich G, Heyning PV.D, Remacle M, Woisard V (2001) A basic protocol for functional assessment of voice pathology, especially for investigating the efficacy of (phonosurgical) treatments and evaluating new assessment techniques. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 258:77–82
Friedrich G (1999) Titanium vocal fold medializing implant: introducing a novel implant system for external vocal fold medialization. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108:79–86
Friedrich G, de Jong FICRS, Mahieu HF, Benninger MS, Isshiki N (2001) Laryngeal framework surgery: a proposal for classification and nomenclature by the Phonosurgery Committee of the European Laryngological Society. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 258:389–396
Gray SD, Barkmeier J, Jones D, Titze I, Druker D (1992) Vocal evaluation of thyroplastic surgery in the treatment of unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Laryngoscope 102:415–421
Hajioff D, Rattenbury H, Carrie S, Carding P, Wilson J (2000) The effect of Isshiki type 1 thyroplasy on quality of life and vocal performance. Clin Otolaryngol 25:418–422
Harries ML, Morriso M (1995) Short-term results of laryngeal framework surgery-thyroplasty type I: a pilot study. J Otolaryngol 24:281–287
Hogikyan ND, Wodchis WP, Terrell JE, Bradford CR, Esclamado RM (2000) Voice-related quality of life (V-RQOL) following type I thyroplast for unilateral vocal fold paralysis. J Voice 14:378–386
Isshiki N (1989) Phonosurgery. theory and practice. Springer, New York Heidelberg Berlin
Jacobson BH, Jonhson A, Grywalski C, Silbergleit A (1997) The Voice Handicap Index (VHI): development and validation. Am J Speech-Lang Path 6:66–69
Lu FL, Casiano RR, Lundy DS, Xue JW (1998) Vocal evaluation of thyroplasty type I in the treatment of nonparalytic glottic incompetence. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 107:113–119
Omori K, Kacker A, Slavit DH, Blaugrund SM (1996) Quantitative videostroboscopic measurement of glottal gap and vocal function: an analysis of thyroplasty type I. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 105:280–285
Plant RL, Hillel AD, Waugh PF (1997) Analysis of voice changes after thyroplasty using linear predictive coding. Laryngoscope 107:703–709
Rao SS, Gupta AK, Raghunatham M, Mann SBS (2003) To study voice quality after thyroplasty type 1 in patients with symptomatic unilateral vocal cord paralysis. Am J Otolaryngol 24:361–365
Rosing HJ, Dikkers FG (1995) Thyroplasty to improve the voice patients with a unilateral vocal fold paralysis. Clin Otolaryngol 20:124–126
Schneider B, Denk DM, Bigenzahn W (2003) Functional results after external vocal fold medialization thyroplasty with the titanium vocal fold medialization implant. Laryngoscope 113:628–634
Shutte HK, Seidner W (1983) Recommendations by the Union of European Phoniatricians (UEP): Standardizing voice area measurement/phonetography. Folia Phoniatr 35:286–288
Thompson DM, Maragos NE, Edward BW (1995) The study of vocal fold vibratory patterns in patients with unilateral vocal fold paralysis before and after type I thyroplasty with or without arytenoid adduction. Laryngoscope 105:481–486
Shiffman S, Reinolds MI, Young FW (1981) Introduction to multidimensional scaling: theory, methods and applications. New York, pp.227–236
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was presented at the 4th Congress of the European Laryngological Society, Brussels, 5–7 September 2002.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uloza, V., Pribuisiene, R. & Saferis, V. Multidimensional assessment of functional outcomes of medialization thyroplasty. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262, 616–621 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-004-0755-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-004-0755-7