Abstract
Purpose
To determine to what extent intensive care unit environment affects family and patient satisfaction.
Methods
A before–after study was performed in one university hospital in The Netherlands, 2 months before and 2 months after the migration of an intensive care unit (ICU) with multiple beds on a ward to a newly built ICU with all single rooms. Family and patient satisfaction were determined by two surveys: family satisfaction with care in the ICU and patient satisfaction with care in the ICU, respectively.
Results
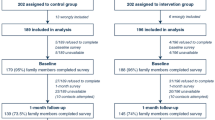
From 387 of 617 (63 %) discharged patients at least one survey (patient and/or family) was returned. Both family and patients were more satisfied with their overall ICU experience in the new ICU as compared with the old ICU. Mean scores for family satisfaction increased from 69.5 [standard deviation (SD) 16.6] to 74.1 (SD 15.2) for old and new ICU, respectively (p = 0.02). For patients, satisfaction rates increased from 63.6 (SD 18.9) to 69.6 (SD 18.3) for old and new ICU, respectively (p = 0.02). The largest differences on single items of the surveys were noted on environmental aspects.
Conclusions
This is the first study to quantify the effect of ICU environment on family and patient satisfaction. Family and patient satisfaction with ICU experience increased by 6 % in the new ICU environment with noise-reduced, single rooms with daylight, adapted colouring and improved family facilities.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartley J, Streifel AJ (2010) Design of the environment of care for safety of patients and personnel: does form follow function or vice versa in the intensive care unit? Crit Care Med 38:S388–S398. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181e6d0c1
Zborowsky T, Hellmich LB (2011) Impact of place on people and process: the integration of research on the built environment in the planning and design of critical care areas. Crit Care Nurs Q 34:268–281. doi:10.1097/CNQ.0b013e31822c3831
Bazuin D, Cardon K (2011) Creating healing intensive care unit environments: physical and psychological considerations in designing critical care areas. Crit Care Nurs Q 34:259–267. doi:10.1097/CNQ.0b013e31822b8f76
Wall RJ, Engelberg RA, Downey L, Heyland DK, Curtis JR (2007) Refinement, scoring, and validation of the family satisfaction in the intensive care unit (FS-ICU) survey. Crit Care Med 35:271–279. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000251122.15053.50
Kryworuchko J, Heyland DK (2009) Using family satisfaction data to improve the processes of care in ICU. Intensive Care Med 35:2015–2017. doi:10.1007/s00134-009-1612-3
Stricker KH, Kimberger O, Brunner L, Rothen HU (2011) Patient satisfaction with care in the intensive care unit: can we rely on proxies? Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 55:149–156. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2010.02293.x
Heyland DK, Tranmer JE (2001) Measuring family satisfaction with care in the intensive care unit: the development of a questionnaire and preliminary results. J Crit Care 16:142–149. doi:10.1053/jcrc.2001.30163
Wall RJ, Curtis JR, Cooke CR, Engelberg RA (2007) Family satisfaction in the ICU: differences between families of survivors and nonsurvivors. Chest 132:1425–1433. doi:10.1378/chest.07-0419
Henrich NJ, Dodek P, Heyland D, Cook D, Rocker G, Kutsogiannis D, Dale C, Fowler R, Ayas N (2011) Qualitative analysis of an intensive care unit family satisfaction survey. Crit Care Med 39:1000–1005. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31820a92fb
Heyland DK, Rocker GM, Dodek PM, Kutsogiannis DJ, Konopad E, Cook DJ, Peters S, Tranmer JE, O’Callaghan CJ (2002) Family satisfaction with care in the intensive care unit: results of a multiple center study. Crit Care Med 30:1413–1418
Stricker KH, Kimberger O, Schmidlin K, Zwahlen M, Mohr U, Rothen HU (2009) Family satisfaction in the intensive care unit: what makes the difference? Intensive Care Med 35:2051–2059. doi:10.1007/s00134-009-1611-4
Simini B (1999) Patients’ perceptions of intensive care. Lancet 354:571–572. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(99)02728-2
Clark PA (2007) Intensive care patients’ evaluations of the informed consent process. Dimens Crit Care Nurs 26:207–226. doi:10.1097/01.DCC.0000286826.57603.6a
Regaira ME, Sola IM, Goni VR, Del Barrio LM, Margall Coscojuela MA, siain Erro MC (2010) Care quality in intensive care evaluated by the patients using a service quality scale (SERVQUAL). Enferm Intensiva 21:3–10. doi:10.1016/j.enfi.2009.10.001
Hunziker S, McHugh W, Sarnoff-Lee B, Cannistraro S, Ngo L, Marcantonio E, Howell MD (2012) Predictors and correlates of dissatisfaction with intensive care. Crit Care Med 40:1554–1561. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182451c70
Osborn TR, Curtis JR, Nielsen EL, Back AL, Shannon SE, Engelberg RA (2012) Identifying elements of ICU care that families report as important but unsatisfactory: decision-making, control and ICU atmosphere. Chest 142:1185–1192. doi:10.1378/chest.11-3277
Trochelman K, Albert N, Spence J, Murray T, Slifcak E (2012) Patients and their families weigh in on evidence-based hospital design. Crit Care Nurse 32:e1–e10. doi:10.4037/ccn2012785
Kesecioglu J, Schneider MM, van der Kooi AW, Bion J (2012) Structure and function: planning a new ICU to optimize patient care. Curr Opin Crit Care 18:688–692. doi:10.1097/MCC.0b013e328358d4bd
Stichler JF (2001) Creating healing environments in critical care units. Crit Care Nurs Q 24:1–20
Thompson DR, Hamilton DK, Cadenhead CD, Swoboda SM, Schwindel SM, Anderson DC, Schmitz EV, St Andre AC, Axon DC, Harrell JW, Harvey MA, Howard A, Kaufman DC, Petersen C (2012) Guidelines for intensive care unit design. Crit Care Med 40:1586–1600. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182413bb2
Valentin A, Ferdinande P (2011) Recommendations on basic requirements for intensive care units: structural and organizational aspects. Intensive Care Med 37:1575–1587. doi:10.1007/s00134-011-2300-7
Dehmel C, Braune SA, Kreymann G, Baehr M, Langebrake C, Hilgarth H, Nierhaus A, Dartsch DC, Kluge S (2011) Do centrally pre-prepared solutions achieve more reliable drug concentrations than solutions prepared on the ward? Intensive Care Med 37:1311–1316. doi:10.1007/s00134-011-2230-4
Canadian researchers at the end of life network (CARENET) (2006) Family satisfaction in the intensive care unit (FS-ICU) survey. http://www.thecarenet.ca/docs/fss/FS_ICU_34.pdf. Accessed 10 November 2009
Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB (2000) Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine 25:3186–3191
Guillemin F, Bombardier C, Beaton D (1993) Cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality of life measures: literature review and proposed guidelines. J Clin Epidemiol 46:1417–1432
Stricker KH, Niemann S, Bugnon S, Wurz J, Rohrer O, Rothen HU (2007) Family satisfaction in the intensive care unit: cross-cultural adaptation of a questionnaire. J Crit Care 22:204–211. doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2006.12.008
Polit DF, Beck CT (2012) Nursing research: generating and assessing evidence for nursing practice. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Bland JM, Altman DG (1997) Cronbach’s alpha. BMJ 314:572. doi:10.1136/bmj.314.7080.572
Crow R, Gage H, Hampson S, Hart J, Kimber A, Storey L, Thomas H (2002) The measurement of satisfaction with healthcare: implications for practice from a systematic review of the literature. Health Technol Assess 6:1–244
Nguyen Thi PL, Briancon S, Empereur F, Guillemin F (2002) Factors determining inpatient satisfaction with care. Soc Sci Med 54:493–504
Soufi G, Belayachi J, Himmich S, Ahid S, Soufi M, Zekraoui A, Abouqal R (2010) Patient satisfaction in an acute medicine department in Morocco. BMC Health Serv Res 10:149. doi:10.1186/1472-6963-10-149
Schwarzkopf D, Behrend S, Skupin H, Westermann I, Riedemann NC, Pfeifer R, Gunther A, Witte OW, Reinhart K, Hartog CS (2013) Family satisfaction in the intensive care unit: a quantitative and qualitative analysis. Intensive Care Med. doi: 10.1007/s00134-013-2862-7
Davidson JE, Powers K, Hedayat KM, Tieszen M, Kon AA, Shepard E, Spuhler V, Todres ID, Levy M, Barr J, Ghandi R, Hirsch G, Armstrong D (2007) Clinical practice guidelines for support of the family in the patient-centered intensive care unit: American College of Critical Care Medicine task force 2004–2005. Crit Care Med 35:605–622. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000254067
Jastremski CA, Harvey M (1998) Making changes to improve the intensive care unit experience for patients and their families. New Horiz 6:99–109
Davidson JE (2011) The family experience with intensive care unit care: more than mere satisfaction. Crit Care Med 39:1207–1208. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e318211f90a
Zaal IJ, Spruyt CF, Peelen LM, van Eijk MM, Wientjes R, Schneider MM, Kesecioglu J, Slooter AJ (2012) Intensive care unit environment may affect the course of delirium. Intensive Care Med. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2726-6
Shahheidari M, Homer C (2012) Impact of the design of neonatal intensive care units on neonates, staff, and families: a systematic literature review. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs 26:260–266. doi:10.1097/JPN.0b013e318261ca1d
Dodek PM, Wong H, Heyland DK, Cook DJ, Rocker GM, Kutsogiannis DJ, Dale C, Fowler R, Robinson S, Ayas NT (2012) The relationship between organizational culture and family satisfaction in critical care. Crit Care Med 40:1506–1512. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e318241e368
Saal D, Nuebling M, Husemann Y, Heidegger T (2005) Effect of timing on the response to postal questionnaires concerning satisfaction with anaesthesia care. Br J Anaesth 94:206–210. doi:10.1093/bja/aei024
Bjertnaes OA (2012) The association between survey timing and patient-reported experiences with hospitals: results of a national postal survey. BMC Med Res Methodol 12:13. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-12-13
Kross EK, Engelberg RA, Shannon SE, Curtis JR (2009) Potential for response bias in family surveys about end-of-life care in the ICU. Chest 136:1496–1502. doi:10.1378/chest.09-0589
Tanja-Dijkstra K, Pieterse ME (2011) The psychological effects of the physical healthcare environment on healthcare personnel. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006210
Harden J, Falahee M, Bickes J, Schafenacker A, Walker J, Mood D, Northouse L (2009) Factors associated with prostate cancer patients’ and their spouses’ satisfaction with a family-based intervention. Cancer Nurs 32:482–492. doi:10.1097/NCC.0b013e3181b311e9
Okamura H, Fukui S, Nagasaka Y, Koike M, Uchitomi Y (2003) Psychoeducational intervention for patients with primary breast cancer and patient satisfaction with information: an exploratory analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat 80:331–338
Chan RJ, Webster J, Marquart L (2011) Information interventions for orienting patients and their carers to cancer care facilities. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008273
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all patients and their families for filling in the surveys, and Marie-Louise Luiking for the back-translation of the FS-ICU.
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jongerden, I.P., Slooter, A.J., Peelen, L.M. et al. Effect of intensive care environment on family and patient satisfaction: a before–after study. Intensive Care Med 39, 1626–1634 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-013-2966-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-013-2966-0