Abstract
Objective:
To determine the effectiveness of school-based strategies for obesity prevention and control using methods of systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods:
Peer-reviewed studies published between 1966 and October 2004 were considered for review. Studies meeting eligibility criteria were published in English, targeted children aged 3–18 in a school setting, reported weight-related outcomes, included a control measurement and had at least a 6-month follow-up period. Studies employed interventions related to nutrition, physical activity, reduction in television viewing or combinations thereof. Weight related data were analyzed using RevMan software.
Results:
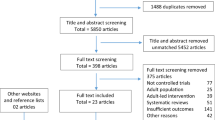
Sixty-four studies were considered for inclusion. Fourteen did not meet inclusion criteria; 29 were excluded due to poor methodological quality. Twenty-one papers describing 19 studies were included in the systematic review and 8 of these were included in the meta-analysis. Nutrition and physical activity interventions resulted in significant reductions in body weight compared with control ((standardized mean difference, SMD=−0.29, 95% confidence interval (CI)=−0.45 to −0.14), random effects model). Parental or family involvement of nutrition and physical activity interventions also induced weight reduction ((SMD=−0.20, 95%CI=−0.41 to 0.00), random effects model).
Conclusion:
Combination nutrition and physical activity interventions are effective at achieving weight reduction in school settings. Several promising strategies for addressing obesity in the school setting are suggested, and warrant replication and further testing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Flegal KM . Epidemiologic trends in overweight and obesity. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2003; 32: 741–760.
Ogden CL, Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Johnson CL . Prevalence and trends in overweight among US children and adolescents, 1999–2000. JAMA 2002; 288: 1728–1732.
Falkner B, Michel S . Obesity and other risk factors in children. Ethn Dis 1999; 9: 284–289.
Richards GE, Cavallo A, Meyer III WJ, Prince MJ, Peters EJ, Stuart CA et al. Obesity, acanthosis nigricans, insulin resistance, and hyperandrogenemia: pediatric perspective and natural history. J Pediatr 1985; 107: 893–897.
Manson J, Nathan DM, Krolewski AS, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Hennekens CH . A prospective study of exercise and incidence of diabetes among US male physicians. JAMA 1992; 268: 63–67.
Colditz GA, Willett WC, Rotnitzky A, Manson JE . Weight gain as a risk factor for clinical diabetes mellitus in women [see comments]. Ann Intern Med 1995; 122: 481–486.
Rames LK, Clarke WR, Connor WE, Reiter MA, Lauer RM . Normal blood pressure and the evaluation of sustained blood pressure elevation in childhood: the Muscatine study. Pediatrics 1978; 61: 245–251.
Figueroa-Colon R, Franklin FA, Lee JY, Aldridge R, Alexander L . Prevalence of obesity with increased blood pressure in elementary school-aged children. South Med J 1997; 90: 806–813.
Retnakaran R, Hanley AJ, Connelly PW, Harris SB, Zinman B . Elevated C-reactive protein in Native Canadian children: an ominous early complication of childhood obesity. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006; 8: 483–491.
Reilly JJ, Methven E, McDowell ZC, Hacking B, Alexander D, Stewart L et al. Health consequences of obesity. Arch Dis Child 2003; 88: 748–752.
Friesen CA, Roberts CC . Cholelithiasis. Clinical characteristics in children. Case analysis and literature review. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1989; 28: 294–298.
Tominaga K, Kurata JH, Chen YK, Fujimoto E, Miyagawa S, Abe I et al. Prevalence of fatty liver in Japanese children and relationship to obesity. An epidemiological ultrasonographic survey. Dig Dis Sci 1995; 40: 2002–2009.
Tazawa Y, Noguchi H, Nishinomiya F, Takada G . Serum alanine aminotransferase activity in obese children. Acta Paediatr 1997; 86: 238–241.
Schwimmer JB, Burwinkle TM, Varni JW . Health-related quality of life of severely obese children and adolescents. JAMA 2003; 289: 1851–1853.
Hill AJ, Draper E, Stack J . A weight on children's minds: body shape dissatisfactions at 9-years old. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1994; 18: 383–389.
French S, Jeffery R, Klesges L, Forster J . Weight concerns and change in smoking behavior over two years in working population. Am J Public Health 1995; 85: 720–722.
Robinson T, Haydel F, Killen J . Are overweight children unhappy? Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 2000; 154: 931–935.
Latner JD, Schwartz MB . Weight Bias in a Child's World. In: Brownell KD, Puhl RM, Schwartz MB, Rudd L (eds). Weight Bias: Nature, Consequences and Remedies, The Guilford Press: NY, NY, pp 54–67.
North American Association for the Study of Obesity. NAASO Scientific Meeting: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2005.
Doak CM, Visscher TL, Renders CM, Seidell JC . The prevention of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: a review of interventions and programmes. Obes Rev 2006; 7: 111–136.
Glenny AM, O’Meara S, Melville A, Sheldon TA, Wilson C . The treatment and prevention of obesity: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1997; 21: 715–737.
Summerbell CD, Waters E, Edmunds LD, Kelly S, Brown T, Campbell KJ . Interventions for preventing obesity in children. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005; 20: CD001871.
Snethen JA, Broome ME, Cashin SE . Effective weight loss for overweight children: a meta-analysis of intervention studies. J Pediatr Nurs 2006; 21: 45–56.
Flynn MA, McNeil DA, Maloff B, Mutasingwa D, Wu M, Ford C et al. Reducing obesity and related chronic disease risk in children and youth: a synthesis of evidence with ‘best practice’ recommendations. Obes Rev 2006; 7 (Suppl 1): 7–66.
Katz DL, O’Connell M, Yeh MC, Nawaz H, Njike V, Anderson LM et al. Public health strategies for preventing and controlling overweight and obesity in school and worksite settings: a report on recommendations of the Task Force on Community Preventive Services. MMWR Recomm Rep 2005; 54 (RR-10): 1–12.
Sharma M . School-based interventions for childhood and adolescent obesity. Obes Rev 2006; 7: 261–269.
Story M . School-based approaches for preventing and treating obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999; 23 (Suppl 2): S43–S51.
Cole K, Waldrop J, D’Auria J, Garner H . An integrative research review: effective school-based childhood overweight interventions. J Spec Pediatr Nurs 2006; 11: 166–177.
Dietz WH, Gortmaker SL . Preventing obesity in children and adolescents. Annu Rev Public Health 2001; 22: 337–353.
Veugelers PJ, Fitzgerald AL . Effectiveness of school programs in preventing childhood obesity: a multilevel comparison. Am J Public Health 2005; 95: 432–435.
Budd GM, Volpe SL . School-based obesity prevention: research, challenges, and recommendations. J Sch Health 2006; 76: 485–495.
Muller MJ, Danielzik S, Pust S . School- and family-based interventions to prevent overweight in children. Proc Nutr Soc 2005; 64: 249–254.
Ells LJ, Campbell K, Lidstone J, Kelly S, Lang R, Summerbell C . Prevention of childhood obesity. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 19: 441–454.
Flodmark CE, Ohlsson T, Ryden O, Sveger T . Prevention of progression to severe obesity in a group of obese schoolchildren treated with family therapy. Pediatrics 1993; 91: 880–884.
Hardeman W, Griffin S, Johnston M, Kinmonth AL, Wareham NJ . Interventions to prevent weight gain: a systematic review of psychological models and behaviour change methods. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000; 24: 131–143.
Zaza S, Wright-DeAguero LK, Briss PA, Truman BI, Hopkins DP, Hennessy MH et al. Data collection instrument and procedure for systematic reviews in the Guide to Community Preventive Services. Task Force on Community Preventive Services. Am J Prev Med 2000; 18 (1 Suppl): 44–74.
Walter HJ, Hofman A, Vaughan RD, Wynder EL . Modification of risk factors for coronary heart disease. Five-year results of a school-based intervention trial. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: 1093–1100.
Tamir D, Feurstein A, Brunner S, Halfon ST, Reshef A, Palti H . Primary prevention of cardiovascular diseases in childhood: changes in serum total cholesterol, high density lipoprotein, and body mass index after 2 years of intervention in Jerusalem schoolchildren age 7–9 years. Prev Med 1990; 19: 22–30.
Lionis C, Kafatos A, Vlachonikolis J, Vakaki M, Tzortzi M, Petraki A . The effects of a health education intervention program among Cretan adolescents. Prev Med 1991; 20: 685–699.
Skybo TA, Ryan-Wenger N . A school-based intervention to teach third grade children about the prevention of heart disease. Pediatr Nurs 2002; 28: 223–229, 35.
Grey M, Berry D, Davidson M, Galasso P, Gustafson E, Melkus G . Preliminary testing of a program to prevent type 2 diabetes among high-risk youth. J Sch Health 2004; 74: 10–15.
Warren JM, Henry CJ, Simonite V . Low glycemic index breakfasts and reduced food intake in preadolescent children. Pediatrics 2003; 112: e414.
Lohman T, Thompson J, Going S, Himes JH, Caballero B, Norman J et al. Indices of changes in adiposity in American Indian children. Preventive Medicine 2003; 37: S91–S96.
Kain J, Uauy R, Albala C, Vio F, Cerda R, Leyton B . School-based obesity prevention in Chilean primary school children: methodology and evaluation of a controlled study. Int J Obes 2004; 28: 483–493.
Sallis JF, McKenzie TL, Alcaraz JE, Kolody B, Hovell MF, Nader PR . Project SPARK. Effects of physical education on adiposity in children. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1993; 699: 127–136.
Nader PR, Stone EJ, Lytle LA, Perry CL, Osganian SK, Kelder S et al. Three-year maintenance of improved diet and physical activity: the CATCH cohort. Child and Adolescent Trial for Cardiovascular Health. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999; 153: 695–704.
Sahota P, Rudolf MJ, Dixey R, Hill AJ, Barth JH, Cade J . Randomised controlled trial of primary school based intervention to reduce risk factors for obesity. BMJ 2001; 323: 1029.
Sallis JF, McKenzie TL, Conway TL, Elder JP, Prochaska JJ, Brown M et al. Environmental interventions for eating and physical activity: a randomized controlled trial in middle schools. Am J Prev Med 2003; 24: 209–217.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M, Hannan PJ, Rex J . New moves: a school-based obesity prevention program for adolescent girls. Prevent Med 2003; 37: 41–51.
Gortmaker S, Cheung L, Peterson K, Chomitz G, Cradle J, Dart H et al. Impact of a school-based interdisciplinary intervention on diet and physical activity among urban primary school children: eat well and keep moving. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999; 153: 975–983.
Mo-suwan L, Pongprapai S, Junjana C, Puetpaiboon A . Effects of a controlled trial of a school-based exercise program on the obesity indexes of preschool children. Am J Clin Nutr 1998; 68: 1006–1011.
Gortmaker SL, Peterson K, Wiecha J, Sobol AM, Dixit S, Fox MK et al. Reducing obesity via a school-based interdisciplinary intervention among youth: Planet Health. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1999; 153: 409–418.
Burke V, Milligan RA, Thompson C, Taggart AC, Dunbar DL, Spencer MJ et al. A controlled trial of health promotion programs in 11-year-olds using physical activity ‘enrichment’ for higher risk children. J Pediatr 1998; 132: 840–848.
Microsoft. RevMan for Windows, 4.2 edn. Oxford, England.
Robinson TN . Reducing children's television viewing to prevent obesity: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1999; 282: 1561–1567.
James J, Thomas P, Cavan D, Kerr D . Preventing childhood obesity by reducing consumption of carbonated drinks: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2004; 328: 1236–1237.
American Dietetic Association. Position of the American Dietetic Association. JADA 2006; 106: 925–945.
Dietz WH, Gortmaker SL . Do we fatten our children at the television set? Obesity and television viewing in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 1985; 75: 807–812.
Aktas A . The effects of television food advertisement on children's food purchasing requests. Pediatric Int 2006; 48: 138–145.
Stice E, Shaw H, Marti CN . A meta-analytic review of obesity prevention programs for children and adolescents: the skinny on interventions that work. Psychol Bull 2006; 132: 667–691.
Connor SM . Food-related advertising on preschool television: building brand recognition in young viewers. Pediatrics 2006; 118: 1478–1485.
No Child Left Behind Act of 2001. 2002.
Daly BP, Burke R, Hare I, Mills C, Owens C, Moore E et al. Enhancing No Child Left Behind-School mental health connections. J Sch Health 2006; 76: 446–451.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katz, D., O'Connell, M., Njike, V. et al. Strategies for the prevention and control of obesity in the school setting: systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes 32, 1780–1789 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.158
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2008.158
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A systematic review of school-based weight-related interventions in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries
Systematic Reviews (2024)
-
The Impact of Typical School Provision of Physical Education, Physical Activity and Sports on Adolescent Physical Health: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis
Adolescent Research Review (2024)
-
Effects of nutrition intervention strategies in the primary prevention of overweight and obesity in school settings: a protocol for a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Systematic Reviews (2021)
-
School-based gardening, cooking and nutrition intervention increased vegetable intake but did not reduce BMI: Texas sprouts - a cluster randomized controlled trial
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity (2021)
-
Rationale and design of a type 2 diabetes prevention intervention for at-risk mothers and children at a Federally Qualified Healthcare Center: EPIC El Rio Families Study Protocol
BMC Public Health (2021)