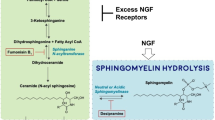
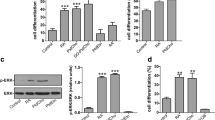
Abstract
One of the characteristics of ceramide-mediated biology is the variety of biological outcomes observed in response to its intracellular accumulation. The molecular mechanisms that govern the cell “decision-making” in response to ceramide remain largely unclear. In this perspective, the study of neural models has begun to provide important insight into the understanding of these mechanisms that regulate differentiation and cell death. Indeed, differentiation and cell death are among the most common effects elicited by ceramide in most cell types and in neural cells, too. Therefore, the lessons we may learn from the study of ceramide regulation of neurobiology would also shed light on the regulation of ceramide-mediated biology in other cellular models. Since increasing evidence links aberrant metabolism of ceramide to different pathologies, the understanding of the mechanisms underlying these events may represent the key to the design of novel therapeutic approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Taniwaki, T., Yamada, T., Asahara, H., Ohyagi, Y., and Kira, J. 1999. Ceramide induces apoptosis to immature cerebellar granule cells in culture. Neurochem. Res. 24:685-690.
Monti, B., Zanghellini, P., and Contestabile, A. 2001. Characterization of ceramide-induced apoptotic death in cerebellar granule cells in culture. Neurochem. Int. 39:11-18.
Hartfield, P. J., Mayne, G. C., and Murray, A. W. 1997. Ceramide induces apoptosis in PC12 cells. FEBS Lett. 401:148-152.
Willaime, S., Vanhoutte, P., Caboche, J., Lemaigre-Dubreuil, Y., Mariani, J., and Brugg, B. 2001. Ceramide-induced apoptosis in cortical neurons is mediated by an increase in p38 phosphorylation and not by the decrease in ERK phosphorylation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 13:2037-2046.
Larocca, J. N., Farooq, M., and Norton, W. T. 1997. Induction of oligodendrocyte apoptosis by C2-ceramide. Neurochem. Res. 22:529-534.
Colombaioni, L., Frago, L. M., Varela-Nieto, I., Pesi, R., and Garcia-Gil, M. 2002. Serum deprivation increases ceramide levels and induces apoptosis in undifferentiated HN9.10e cells. Neurochem. Int. 40:327-336.
Riboni, L., Prinetti, A., Bassi, R., Caminiti, A., and Tettamanti, G. 1995. A mediator role of ceramide in the regulation of neuroblastoma Neuro2a cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 270:26868-26875.
Brann, A. B., Scott, R., Neuberger, Y., Abulafia, D., Boldin, S., Fainzilber, M., and Futerman, A. H. 1999. Ceramide signaling downstream of the p75 neurotrophin receptor mediates the effects of nerve growth factor on outgrowth of cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 19:8199-8206.
Dobrowsky, R. T., Werner, M. H., Castellino, A. M., Chao, M. V., and Hannun, Y. A. 1994. Activation of the sphingomyelin cycle through the low-affinity neurotrophin receptor. Science, 265:1596-1599.
Yoshimura, S., Banno, Y., Nakashima, S., Takenaka, K., Sakai, H., Nishimura, Y., Sakai, N., Shimizu, S., Eguchi, Y., Tsujimoto, Y., and Nozawa, Y. 1998. Ceramide formation leads to caspase-3 activation during hypoxic PC12 cell death. Inhibitory effects of Bcl-2 on ceramide formation and caspase-3 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 273:6921-6927.
Saito, M., Guidotti, A., Berg, M. J., and Marks, N. 1998. The semisynthetic glycosphingolipid LIGA20 potently protects neurons against apoptosis. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 845:253-262.
Casaccia-Bonnefil, P., Aibel, L., and Chao, M. V. 1996. Central glial and neuronal populations display differential sensitivity to ceramide-dependent cell death. J. Neurosci. Res. 43:382-389.
Ito, A. and Horigome, K. 1995. Ceramide prevents neuronal programmed cell death induced by nerve growth factor deprivation. J. Neurochem. 65:463-466.
De Chaves, E. I. P., Bussière, M., Vance, D. E., Campenot, R. B., and Vance, J. E. 1997. Elevation of ceramide within distal neurites inhibits neurite growth in cultured rat sympathetic neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 272:3028-3035.
Xie, H. and Johnson, G. V. 1997. Ceramide selectively decreases tau levels in differentiated PC12 cells through modulation of calpain I. J. Neurochem. 69:1020-1030.
Mitoma, J., Ito, M., Furuya, S., and Hirabayashi, Y. 1998. Bipotential roles of ceramide in the growth of hippocampal neurons: Promotion of cell survival and dendritic outgrowth in dose-and developmental stage-dependent manners. J. Neurosci. Res. 51:712-722.
Brann, A. B., Tcherpakov, M., Williams, I. M., Futerman, A. H., and Fainzilber, M. 2002. NGF-induced p75-mediated death of cultured hippocampal neurons is age-dependent and transduced through ceramide generated by neutral sphingomyelinase. J. Biol. Chem. 3:3.
Prinetti, A., Chigorno, V., Prioni, S., Loberto, N., Marano, N., Tettamanti, G., and Sonnino, S. 2001. Changes in the lipid turnover, composition, and organization, as sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains, in rat cerebellar granule cells developing in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 276:21136-21145.
Irie, F. and Hirabayashi, Y. 1998. Application of exogenous ceramide to cultured rat spinal motoneurons promotes survival or death by regulation of apoptosis depending on its concentrations. J. Neurosci. Res. 54:475-485.
Schwarz, A. and Futerman, A. H. 1997. Distinct roles for ceramide and glucosylceramide at different stages of neuronal growth. J. Neurosci. 17:2929-2938.
Goodman, Y. and Mattson, M. P. 1996. Ceramide protects hippocampal neurons against excitotoxic and oxidative insults, and amyloid beta-peptide toxicity. J. Neurochem. 66:869-872.
Campenot, R. B., Walji, A. H., and Draker, D. D. 1991. Effects of sphingosine, staurosporine, and phorbol ester on neurites of rat sympathetic neurons growing in compartmented cultures. J. Neurosci. 11:1126-1139.
de Chaves, E. P., Bussiere, M., MacInnis, B., Vance, D. E., Campenot, R. B., and Vance, J. E. 2001. Ceramide inhibits axonal growth and nerve growth factor uptake without compromising the viability of sympathetic neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 276:36207-36214.
Birbes, H., El Bawab, S., Hannun, Y. A., and Obeid, L. M. 2001. Selective hydrolysis of a mitochondrial pool of sphingomyelin induces apoptosis. FASEB J. 15:2669-2679.
Riboni, L., Bassi, R., Prinetti, A., Viani, P., and Tettamanti, G. 1999. Predominance of the acylation route in the metabolic processing of exogenous sphingosine in neural and extraneural cells in culture. Biochem. J. 338:147-151.
Riboni, L., Viani, P., Bassi, R., Giussani, P., and Tettamanti, G. 2000. Cultured granule cells and astrocytes from cerebellum differ in metabolizing sphingosine. J. Neurochem. 75:503-510.
Sugiura, M., Kono, K., Liu, H., Shimizugawa, T., Minekura, H., Spiegel, S., and Kohama, T. 2002. Ceramide kinase, a novel lipid kinase. Molecular cloning and functional characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 277:23291-23300.
Sato, K., Tomura, H., Igarashi, Y., Ui, M., and Okajima, F. 1997. Exogenous sphingosine 1-phosphate induces neurite retraction possibly through a cell surface receptor in PC12 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 240:329-334.
Van Brocklyn, J. R., Tu, Z., Edsall, L. C., Schmidt, R. R., and Spiegel, S. 1999. Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced cell rounding and neurite retraction are mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor H218. J. Biol. Chem. 274:4626-4632.
Moore, A. N., Kampfl, A. W., Zhao, X., Hayes, R. L., and Dash, P. K. 1999. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces apoptosis of cultured hippocampal neurons that requires protein phosphatases and activator protein-1 complexes. Neuroscience, 94:405-415.
Edsall, L. C., Pirianov, G. G., and Spiegel, S. 1997. Involvement of sphingosine 1-phosphate in nerve growth factor-mediated neuronal survival and differentiation. J. Neurosci. 17: 6952-6960.
Edsall, L. C., Cuvillier, O., Twitty, S., Spiegel, S., and Milstien, S. 2001. Sphingosine kinase expression regulates apoptosis and caspase activation in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 76:1573-1584.
Bieberich, E., MacKinnon, S., Silva, J., and Yu, R. K. 2001. Regulation of apoptosis during neuronal differentiation by ceramide and b-series complex gangliosides. J. Biol. Chem. 276:44396-44404.
Korkotian, E., Schwarz, A., Pelled, D., Schwarzmann, G., Segal, M., and Futerman, A. H. 1999. Elevation of intracellular glucosylceramide levels results in an increase in endoplasmic reticulum density and in functional calcium stores in cultured neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 274:21673-21678.
Bajjalieh, S. M., Martin, T. F., and Floor, E. 1989. Synaptic vesicle ceramide kinase. A calcium-stimulated lipid kinase that co-purifies with brain synaptic vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 264:14354-14360.
Shinghal, R. Scheller, R. H., and Bajjalieh, S. M. 1993. Ceramide 1-phosphate phosphatase activity in brain. J. Neurochem. 61:2279-2285.
Condorelli, F., Sortino, M. A., Stella, A. M., and Canonico, P. L. 2000. Relative contribution of different receptor subtypes in the response of neuroblastoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Neurochem. 75:1172-1179.
Hida, H., Nagano, S., Takeda, M., and Soliven, B. 1999. Regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by sphingolipid products in oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. 19:7458-7467.
Brann, A. B., Tcherpakov, M., Williams, I. M., Futerman, A. H., and Fainzilber, M. 2002. Nerve growth factor-induced p75-mediated death of cultured hippocampal neurons is age-dependent and transduced through ceramide generated by neutral sphingomyelinase. J. Biol. Chem. 277:9812-9818.
Yoshimura, S., Banno, Y., Nakashima, S., Hayashi, K., Yamakawa, H., Sawada, M., Sakai, N., and Nozawa, Y. 1999. Inhibition of neutral sphingomyelinase activation and ceramide formation by glutathione in hypoxic PC12 cell death. J. Neurochem. 73:675-683.
Blazquez, C., Galve-Roperh, I., and Guzman, M. 2000. De novo-synthesized ceramide signals apoptosis in astrocytes via extracellular signal-regulated kinase. FASEB J. 14:2315-2322.
Herget, T., Esdar, C., Oehrlein, S. A., Heinrich, M., Schutze, S., Maelicke, A., and van Echten-Deckert, G. 2000. Production of ceramides causes apoptosis during early neural differentiation in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 275:30344-30354.
Esdar, C., Milasta, S., Maelicke, A., and Herget, T. 2001. Differentiation-associated apoptosis of neural stem cells is effected by Bcl-2 overexpression: Impact on cell lineage determination. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 80:539-553.
Gomez Del Pulgar, T., Velasco, G., Sanchez, C., Haro, A., and Guzman, M. 2002. De novo-synthesized ceramide is involved in cannabinoid-induced apoptosis. Biochem. J. 363:183-188.
MacPhee, I. and Barker, P. A. 1999. Extended ceramide exposure activates the trkA receptor by increasing receptor homodimer formation. J. Neurochem. 72:1423-1430.
Pelled, D., Raveh, T., Riebeling, C., Fridkin, M., Berissi, H., Futerman, A. H., and Kimchi, A. 2002. Death-associated protein (DAP) kinase plays a central role in ceramide-induced apoptosis in cultured hippocampal neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 277:1957-1961.
Ramos, B., Salido, G. M., Campo, M. L., and Claro, E. 2000. Inhibition of phosphatidylcholine synthesis precedes apoptosis induced by C2-ceramide: Protection by exogenous phosphatidylcholine. Neuroreport 11:3103-3108.
Kuroki, J., Hirokawa, M., Kitabayashi, A., Lee, M., Horiuchi, T., Kawabata, Y., and Miura, A. B. 1996. Cell-permeable ceramide inhibits the growth of B lymphoma Raji cells lacking TNF-alpha-receptors by inducing G0/G1 arrest but not apoptosis: A new model for dissecting cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Leukemia 10:1950-1958.
Alesse, E., Zazzeroni, F., Angelucci, A., Giannini, G., Di Marcotullio, L., and Gulino, A. 1998. The growth arrest and downregulation of c-myc transcription induced by ceramide are related events dependent on p21 induction, Rb underphosphorylation and E2F sequestering. Cell Death Differ. 5:381-389.
Lee, J. Y., Bielawska, A. E., and Obeid, L. M. 2000. Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activity by ceramide. Exp. Cell Res. 261:303-311.
Lane, S. C., Jolly, R. D., Schmechel, D. E., Alroy, J., and Boustany, R. M. 1996. Apoptosis as the mechanism of neurodegeneration in Batten's disease. J. Neurochem. 67:677-683.
Puranam, K., Qian, W. H., Nikbakht, K., Venable, M., Obeid, L., Hannun, Y., and Boustany, R. M. 1997. Upregulation of Bcl-2 and elevation of ceramide in Batten disease. Neuropediatrics 28:37-41.
Puranam, K. L., Guo, W. X., Qian, W. H., Nikbakht, K., and Boustany, R. M. 1999. CLN3 defines a novel antiapoptotic pathway operative in neurodegeneration and mediated by ceramide. Mol. Genet. Metab. 66:294-308.
Rylova, S. N., Amalfitano, A., Persaud-Sawin, D. A., Guo, W. X., Chang, J., Jansen, P. J., Proia, A. D., and Boustany, R. M. 2002. The CLN3 gene is a novel molecular target for cancer drug discovery. Cancer Res. 62:801-808.
Cho, S., Dawson, P. E., and Dawson, G. 2001. Role of palmitoyl-protein thioesterase in cell death: Implications for infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 5 (Suppl A):53-55.
Cho, S., Dawson, P. E., and Dawson, G. 2000. Antisense palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 (PPT1) treatment inhibits PPT1 activity and increases cell death in LA-N-5 neuroblastoma cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 62:234-240.
Bejaoui, K., Wu, C., Scheffler, M. D., Haan, G., Ashby, P., Wu, L., de Jong, P., and Brown, R. H., Jr. 2001. SPTLC1 is mutated in hereditary sensory neuropathy, type 1. Nat. Genet. 27:261-262.
Dawkins, J. L., Hulme, D. J., Brahmbhatt, S. B., Auer-Grumbach, M., and Nicholson, G. A. 2001. Mutations in SPTLC1, encoding serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit-1, cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type I. Nat. Genet. 27:309-312.
Gable, K., Han, G., Monaghan, E., Bacikova, D., Natarajan, M., Williams, R., and Dunn, T. M. 2002. Mutations in the yeast LCB1 and LCB2 genes, including those corresponding to the hereditary sensory neuropathy type I mutations, dominantly inactivate serine palmitoyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 277:10194-10200.
Toman, R. E., Spiegel, S., and Faden, A. I. 2000. Role of ceramide in neuronal cell death and differentiation. J. Neurotrauma 17:891-898.
Yu, Z. F., Nikolova-Karakashian, M., Zhou, D., Cheng, G., Schuchman, E. H., and Mattson, M. P. 2000. Pivotal role for acidic sphingomyelinase in cerebral ischemia-induced ceramide and cytokine production, and neuronal apoptosis. J. Mol. Neurosci. 15:85-97.
Herr, I., Martin-Villalba, A., Kurz, E., Roncaioli, P., Schenkel, J., Cifone, M. G., and Debatin, K. M. 1999. FK506 prevents stroke-induced generation of ceramide and apoptosis signaling. Brain Res. 826:210-219.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luberto, C., Kraveka, J.M. & Hannun, Y.A. Ceramide Regulation of Apoptosis versus Differentiation: A Walk on a Fine Line. Lessons from Neurobiology. Neurochem Res 27, 609–617 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020267831851
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020267831851