Abstract
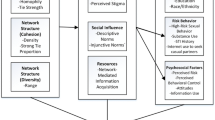
Although the Chinese government provides free-of-charge voluntary HIV counseling and testing, HIV testing rates among men who have sex with men (MSM) are reported to be extremely low. This study examines the association of structural and psychosocial factors and social network characteristics with HIV testing behaviors among “money boys” and general MSM in Shanghai. Overall, 28.5% of “money boys” and 50.5% of general MSM had never tested for HIV despite high rates of reported HIV risk behaviors. Factors associated with not testing for HIV included: not knowing of a testing site, limited HIV knowledge, low perceived HIV risk, concern about HIV testing confidentiality, being a closeted gay, not using the Internet, and having a small social network or network with few members who had tested for HIV. Future efforts to promote HIV testing should focus on outreach to general MSM, confidentiality protection, decreasing the stigma of homosexuality, and encouraging peer education and support through the Internet and social networks.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu Z, Wang Y. Introduction: China meets new AIDS challenges. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;53(Suppl 1):S1–3.
He Q, Wang Y, Lin P, Raymond HF, Li Y, Yang F, et al. High prevalence of risk behaviour concurrent with links to other high-risk populations: a potentially explosive HIV epidemic among men who have sex with men in Guangzhou, China. Sex Transm Infect. 2009;85(5):383–90.
Juan S. China to have 1.2 million HIV-positive people by 2015 [Internet]. China Daily. 2010. http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2010-12/04/content_11652055.htm.
Guo Y, Li X, Stanton B. HIV-related behavioral studies of men who have sex with men in China: a systematic review and recommendations for future research. AIDS Behav. 2011;15(3):521–34.
Wang L. HIV prevalence among populations at risk, using sentinel surveillance data from 1995 to 2009 in China. Chung-Hua Liu Hsing Ping Hsueh Tsa Chih. 2011;32(1):20.
USAID. Health policy initiative. The value of investing in MSM programs in the Asia-Pacific region [Internet]. 2007. http://www.msmasia.org/The_Value_of_Investing_in_MSM_Programs_in_the_Asia-Pacific_Region.pdf.
USAID. The value of investing in MSM programs in the Asia-Pacific region [Internet]. 2006. http://www.msmasia.org/The_Value_of_Investing_in_MSM_Programs_in_the_Asia-Pacific_Region.pdf.
State Council AIDS Working Committee Office and UN Theme Group on HIV/AIDS in China. A Joint Assessment of HIV/AIDS Prevention, Treatment and Care in China [Internet]. 2004. www.chinaaids.cn/worknet/download/2004/report2004en.pdf. Accessed 30 Dec 2011.
China Ministry of Health. China estimation report-en.pdf [Internet]. 2011. http://www.unaids.org.cn/download/2009%20China%20Estimation%20Report-En.pdf. Accessed 3 Aug 2011.
Lau JT, Lin C, Hao C, Wu X, Gu J. Public health challenges of the emerging HIV epidemic among men who have sex with men in China. Public Health. 2011;125(5):260–5.
Ma X, Zhang Q, He X, Sun W, Yue H, Chen S, et al. Trends in prevalence of HIV, syphilis, hepatitis C, hepatitis B, and sexual risk behavior among men who have sex with men. Results of 3 consecutive respondent-driven sampling surveys in Beijing, 2004 through 2006. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;45(5):581–7.
Han M, Feng LG, Jiang Y, Shen S, Ling H, Ding XB, et al. Surveillance on HIV-1 incidence among men who have sex with men in Chongqing, China, 2006–2008. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2009;30(9):878–81.
Ouyang L, Feng LG, Ding XB, Zhao JK, Xu J, Han M, et al. A respondent-driven sampling survey on HIV and risk factors among men who have sex with men in Chongqing. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2009;30(10):1001–4.
Feng Y, Wu Z, Detels R, Qin G, Liu L, Wang X, et al. HIV/STD prevalence among men who have sex with men in Chengdu, China and associated risk factors for HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;53(Suppl 1):S74–80.
Yang H, Hao C, Huan X, Yan H, Guan W, Xu X, et al. HIV incidence and associated factors in a cohort of men who have sex with men in Nanjing, China. Sex Transm Dis. 2010;37(4):208–13.
Xu JJ, Zhang M, Brown K, Reilly K, Wang H, Hu Q, et al. Syphilis and HIV seroconversion among a 12-month prospective cohort of men who have sex with men in Shenyang, China. Sex Transm Dis. 2010;37(7):432–9.
Hong FC, Zhou H, Cai YM, Pan P, Feng TJ, Liu XL, et al. Prevalence of syphilis and HIV infections among men who have sex with men from different settings in Shenzhen, China: implications for HIV/STD surveillance. Sex Transm Infect. 2009;85(1):42–4.
Liu H, Liu H, Cai Y, Rhodes AG, Hong F. Money boys, HIV risks, and the associations between norms and safer sex: a respondent-driven sampling study in Shenzhen, China. AIDS Behav. 2009;13(4):652–62.
Ruan S, Yang H, Zhu Y, Wang M, Ma Y, Zhao J, et al. Rising HIV prevalence among married and unmarried among men who have sex with men: Jinan, China. AIDS Behav. 2009;13(4):671–6.
Guo H, Wei J-F, Yang H, Huan X, Tsui SK-W, Zhang C. Rapidly increasing prevalence of HIV and syphilis and HIV-1 subtype characterization among men who have sex with men in Jiangsu, China. Am Sex Transm Dis Assoc. 2009;36(2):120–5.
Choi KH, Ning Z, Gregorich SE, Pan QC. The influence of social and sexual networks in the spread of HIV and syphilis among men who have sex with men in Shanghai, China. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2007;45(1):77–84.
Choi KH, Diehl E, Guo Y, Qu S, Mandel J. High HIV risk but inadequate prevention services for men in China who have sex with men: an ethnographic study. AIDS Behav. 2002;6(3):255–66.
Choi KH, Gibson DR, Han L, Guo Y. High levels of unprotected sex with men and women among men who have sex with men: a potential bridge of HIV transmission in Beijing, China. AIDS Educ Prev. 2004;16(1):19–30.
Choi KH, Liu H, Guo Y, Han L, Mandel JS, Rutherford GW. Emerging HIV-1 epidemic in China in men who have sex with men. Lancet. 2003;361(9375):2125–6.
He N, Wong FY, Huang ZJ, Thompson EE, Fu C. Substance use and HIV risks among male heterosexual and “money boy” migrants in Shanghai, China. AIDS Care. 2007;19(1):109–15.
Liu S, Wang K, Yao S, Guo X, Liu Y, Wang B. Knowledge and risk behaviors related to HIV/AIDS, and their association with information resource among men who have sex with men in Heilongjiang province, China. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:250.
Cai WD, Zhao J, Zhao JK, Raymond HF, Feng YJ, Liu J, et al. HIV prevalence and related risk factors among male sex workers in Shenzhen, China: results from a time-location sampling survey. Sex Transm Infect. 2010;86(1):15–20.
Wong FY, Huang ZJ, Wang W, He N, Marzzurco J, Frangos S, et al. STIs and HIV among men having sex with men in China: a ticking time bomb? AIDS Educ Prev. 2009;21(5):430–46.
Wei C, Ruan S, Zhao J, Yang H, Zhu Y, Raymond HF. Which Chinese men who have sex with men miss out on HIV testing? Sex Transm Infect. 2011;87(3):225–8.
Marks G, Crepaz N, Senterfitt JW, Janssen RS. Meta-analysis of high-risk sexual behavior in persons aware and unaware they are infected with HIV in the United States: implications for HIV prevention programs. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;39(4):446–53.
Marseille E, Hofmann PB, Kahn JG. HIV prevention before HAART in sub-Saharan Africa. Lancet. 2002;359(9320):1851–6.
Shen J, Yu DB. Governmental policies on HIV infection in China. Cell Res. 2005;15(11–12):903–7.
Choi KH, Lui H, Guo Y, Han L, Mandel JS. Lack of HIV testing and awareness of HIV infection among men who have sex with men, Beijing, China. AIDS Educ Prev. 2006;18(1):33–43.
Wong FY, Huang ZJ, He N, Smith BD, Ding Y, Fu C, et al. HIV risks among gay- and non-gay-identified migrant money boys in Shanghai, China. AIDS Care. 2008;20(2):170–80.
Wong FY, Huang ZJ, He N, Young D, O’Conor CA, Ding Y, et al. Migration and illicit drug use among two types of male migrants in Shanghai, China. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2010;42(1):1–9.
RDS Inc. RDS analysis tool, V.5.6, user manual. Ithaca: RDS Inc.; 2006.
Ramirez-Valles J, Heckathorn DD, Vazquez R, Diaz RM, Campbell RT. From networks to populations: the development and application of respondent-driven sampling among IDUs and Latino gay men. AIDS Behav. 2005;9(4):387–402.
Malekinejad M, Johnston LG, Kendall C, Kerr LR, Rifkin MR, Rutherford GW. Using respondent-driven sampling methodology for HIV biological and behavioral surveillance in international settings: a systematic review. AIDS Behav. 2008;12(4 Suppl):S105–30.
He N, Wong FY, Huang ZJ, Ding Y, Fu C, Smith BD, et al. HIV risks among two types of male migrants in Shanghai, China: money boys vs. general male migrants. AIDS. 2007;21(Suppl 8):S73–9.
Huang ZJ, Wong FY, De Leon JM, Park RJ. Self-reported HIV testing behaviors among a sample of southeast Asians in an urban setting in the United States. AIDS Educ Prev. 2008;20(1):65–77.
Do TD, Hudes ES, Proctor K, Han CS, Choi KH. HIV testing trends and correlates among young Asian and Pacific Islander men who have sex with men in two U.S. cities. AIDS Educ Prev. 2006;18(1):44–55.
Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: a self report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas. 1977;1:385–401.
Hendrick S, Hendrick C. Multidimensionality of sexual attitudes. J Sex Res. 1987;23:502–26.
Zane N, Yeh M. The use of culturally-based variables in assessment: studies on loss of face. In: Asian American mental health: assessment theories and methods. New York, NY: Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers; 2002. p. 123–38.
Mohr J, Fassinger R. Measuring dimensions of lesbian and gay male experience. Meas Eval Couns Dev. 2000;33:66–90.
Russell D, Cutrona CE, Rose J, Yurko K. Social and emotional loneliness: an examination of Weiss’s typology of loneliness. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1984;46(6):1313–21.
Iguchi MY, Ober AJ, Berry SH, Fain T, Heckathorn DD, Gorbach PM, et al. Simultaneous recruitment of drug users and men who have sex with men in the United States and Russia using respondent-driven sampling: sampling methods and implications. J Urban Health. 2009;86(Suppl 1):5–31.
Heckathorn D. Deriving valid population estimates from chain-referral samples of hidden populations. Soc Probl. 2002;49:11–34.
SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT 9.2 user’s guide. Cary: SAS Institute Inc.; 2010.
Borgatti S. A brief guide to using NETDRAW [Internet]. 2009. http://www.analytictech.com/Netdraw/netdraw.htm.
Heckathorn D. Respondent driven sampling [Internet]. 2011. http://www.respondentdrivensampling.org/. Accessed 14 Dec 2011.
Liu H, Liu H, Cai Y, Rhodes AG, Hong F. Money boys, HIV risks, and the associations between norms and safer sex: a respondent-driven sampling study in Shenzhen, China. AIDS Behav. 2009;13:652–62.
Sheridan S, Phimphachanh C, Chanlivong N, et al. HIV prevalence and risk behaviour among men who have sex with men in Vientane Capital, Lao People’s Democratic Republic. AIDS. 2009;23(3):409–14.
呂麗萍反同志 央視批「要反省」 | 港陸傳真 | 娛樂追星 | 聯合新聞網 [Internet]. World News. 2011. http://udn.com/NEWS/ENTERTAINMENT/ENT8/6444368.shtml. Accessed 3 Aug 2011.
Zou H, Wu Z, Yu J, Li M, Ablimit M, Li F, et al. Sexual risk behaviors and HIV infection among men who have sex with men who use the internet in Beijing and Urumqi, China. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2010;53(Suppl 1):S81–7.
Rosser BR, Oakes JM, Konstan J, Hooper S, Horvath KJ, Danilenko GP, et al. Reducing HIV risk behavior of men who have sex with men through persuasive computing: results of the Men’s INTernet Study-II. AIDS. 2010;24(13):2099–107.
Coleman E, Horvath KJ, Miner M, Ross MW, Oakes M, Rosser BR. Compulsive sexual behavior and risk for unsafe sex among internet using men who have sex with men. Arch Sex Behav. 2010;39(5):1045–53.
Mansergh G, Koblin BA, McKirnan DJ, Hudson SM, Flores SA, Wiegand RE, et al. An intervention to reduce HIV risk behavior of substance-using men who have sex with men: a two-group randomized trial with a nonrandomized third group. PLoS Med. 2010;7(8):e1000329.
Acknowledgments
Preparation of this article was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01HD046354; PI: Wong) and the Emory Center for AIDS Research (P30 AI050409; Nehl and Wong).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z.J., He, N., Nehl, E.J. et al. Social Network and Other Correlates of HIV Testing: Findings from Male Sex Workers and Other MSM in Shanghai, China. AIDS Behav 16, 858–871 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-011-0119-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-011-0119-4