Abstract
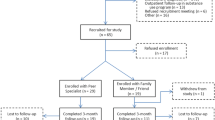
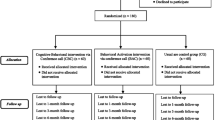
To determine if a telephone support behavioral intervention improves depressive symptoms among HIV positive outpatients, we enrolled 177 persons with Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) scores scores of ≥10. Participants were randomized to receive up to 12 scheduled psycho-educational calls over 6 months or to an assessment-only control condition. Co-enrolled informal caregivers of HIV patients received the same telephone intervention in parallel. Among the 160 (90.4%) participants who were re-interviewed at 6 months, 56% were male, and 41% were Caucasian, with a mean baseline BDI score of 22.7. Overall, participants’ mean BDI scores improved 5.3 points from baseline, but intervention group differences on depression outcomes including 50% or greater reduction in BDI scores and depression remission were not statistically significant. In the full cohort, men were significantly more likely to improve than women. We conclude that a psycho-educational telephone support intervention did not reduce depressive symptoms for HIV patients more than an assessment-only control condition.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck, A. T., Steer, R. A., & Garbin, M. G. (1988). Psychometric properties of the Beck Depression Inventory: Twenty-five years of evaluation. Clinical Psychology Review, 8, 7–100.
Bing, E. G., Burnham, M. A., Longshore, D., Fleishman, J. A., Sherbourne, C. D., London, A. S., Turner, B. J., Eggan, F., Beckman, R., Vitiello, B., Morton, S. C., Orlando, M., Bozzette, S. A., Ortiz-Barron, L., & Shapiro, M. (2001). Psychiatric disorders and drug use among human immunodeficiency virus-infected adults in the United States. Archives of General Psychiatry, 58, 721–728.
Carrieri, M. P., Hesney, M. A., Spire, B., Loundou, A., Sobel, A., Lepeu, G., Moatti, J. P., & MANIF Study Group. (2003). Failure to maintain adherence to HAART in a cohort of French HIV positive injecting drug users. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 10, 1–14.
Cisela, J. A., & Roberts, J. E. (2001). Meta-analysis of the relationship between HIV infection and risk of depressive disorders. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 158, 725–730.
Cook, J. A., Grey, D., Burke, J., Cohen, M. H., Gutman, A. C., Richardson, J. L., Wilson, T. E., Young, M. A., & Hessol, N. A. (2004). Depressive symptoms and AIDS-related mortality among a multisite cohort of HIV positive women. American Journal of Public Health, 94, 1133–1140.
Cuijpers, P. (1997). Bibliotherapy in unipolar depression: A meta analysis. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 28, 139–147.
Elliot, A. J., Uldall, K. K., Bergam, K., Russo, J., Claypoole, K., & Roy-Byrne, P. P. (1998). Randomized, placebo controlled trial of paroxetine versus imipramine in depressed HIV positive outpatients. American Journal of Psychiatry, 155, 367–372.
Epstein, N., Ryan, C., Bishop, D., Miller, I., & Keitner, G. (2003). The McMaster model: A view of health family functioning, In F. Walsh (Ed.) Normal family processes: Growing diversity and complexity, 3rd ed. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Herman, D. S., Bishop, D., Anthony, J., Chase, W., Trisvan, E., Lopez, R., & Stein, M. D. Feasibility of a telephone intervention for HIV patients and their informal caregivers. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings (in press).
Ickovics, J. R., Hamburger, M. E., Vlahov, D., Schoenbaum, E. E., Schuman, P., Boland, R. J., Moore, J., & HIV Epidemiology Research Study Group. (2001). Mortality, CD4 cell count decline, and depressive symptoms among HIV seropositive women: Longitudinal analysis from the HIV epidemiology research study. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 285, 1466–1474.
Irving, G., Bor, R., & Catalan, J. (1995). Psychological distress among gay men supporting a lover or partner with AIDS: A pilot study. AIDS Care, 7(5), 605–617.
Janoff-Bulman, R. (1989). Assumptive worlds and the stress of traumatic events: Applications of the schema construct. Social Cognition, 7(2), 113–136.
Jones, B. S., Brody, D., Roper, M., & Narrow, W. E. (2003). Prevalance of mood disorders in a national sample of young American adults. Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, 38, 618–614.
Katon, W., & Schulberg, H. (1992). Epidemiology of depression in primary care. General Hospital Psychiatry, 14, 237–247.
Lazarus, R., & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, appraisal and coping. New York, NY: Springer.
Lippmann, S., James, W., & Frierson, R. (1993). AIDS and the family: Implications for counseling. AIDS Care, 5(1), 71–78.
Markowitz, J. C., Klerman, G. L., Clougherty, K. F., Spielman, L. A., Jacobsberg, L. B., Fishman, B., Frances, A. J., Kocsis, J. H., & Perry, S. W. 3rd (1995). Individual psychotherapies for depressed HIV positive patients. American Journal of Psychiatry, 152, 1504–1509.
Markowitz, J. C., Kocsis, J. H., Fishman, B., Spielman, L. A., Jocabsberg, L. B., Frances, A. J., Klerman, G. L., & Perry, S. W. (1998). Treatment of depressive symptoms in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients. Archives of General Psychiatry, 55, 452–457.
Masiak, R., Austin, J., & Heck, L. (1996). Health outcomes of two telephone interventions for patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 39, 1391–1399.
McKay, J., Lynch, K., Shepard, D., Ratichek, S., Morrison, R., Koppenhaver, J., & Pettinati, H. M. (2002a). The effectiveness of telephone-based continuing care in the clinical management of alcohol and cocaine use disorders. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72(6), 967–979.
McKay, M. M., Harrison, M. E., Gonzales, J., Kim, L., & Quintana, E. (2002b). Multiple family groups for urban children with conduct difficulties and their families. Psychiatric Services, 53, 1467–1468.
Mohr, D. C., Hart, S. L., Julian, L., Catledge, C., Honos-Webb, L., Vella, L., & Tasch, E. T. (2005). Telephone-administered psychotherapy for depression. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 1007–1014.
Osgood-Hynes, D. J., Greist, J., Marks, I., Baer, L., Heneman, S., Wenzel, K., Manzo, P. A., Parkin, J. R., Spierings, C. J., Dottl, S. L., & Vitse, H. M. (1998). Self-administered psychotherapy for depression using a telephone-accessed computer system plus booklets: An open US-UK study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 59(7), 358–365.
Pakenham, K. (2001). Application of a stress and coping model to caregiving in multiple sclerosis. Psychology Health and Medicine, 6(1), 13–27.
Pakenham, K., Dadds, M., & Lennon, H. (2002). The efficacy of a psychosocial intervention for HIV/AIDS caregiving dyads and individual caregivers: A controlled treatment outcome study. AIDS Care, 14(6), 731–750.
Pakenham, K., Dadds, M., & Terry, D. (1995). Carers’ burden and adjustment to HIV. AIDS Care, 7(2), 189–203.
Pirraglia, P., Bishop, D., Herman, D., Trisvan, E., Lopez, R., Torgerson, C., Van Hof, A. M., Anderson, B. J., Miller, I., & Stein, M. D. (2005). Caregiver burden and depression among informal caregivers of HIV infected individuals. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 20(6), 510–514.
Rabkin, J. G., Rabkin, R., Harrison, W., & Wagner, G. (1994). Effects of imipramine on mood and enumerative measures of immune status in depressed patients with HIV illness. American Journal of Psychiatry, 151, 516–523.
Rabkin, J. G., Wagner, G. J., & Rabkin, R. (1999). Fluoxetine treatment for depression in patients with HIV and AIDS: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. American Journal of Psychiatry, 156, 101–107.
Savetsky, J. B., Sullivan, L. M., Clarke, J., Stein, M. D., & Samet, J. H. (2001). Evaluation of depressive symptoms in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients entering primary care. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 189, 76–83.
Simoni, J. M., Frick, P. A., Pantalone, A. B., & Turner, B. J. (2003). Antiretroviral adherence interventions: A review of current literature and ongoing studies. Topics in HIV Medicine, 11, 185–198.
Stein, M., Herman, D., Solomon, D., Anthony, J., Anderson, B., Ramsey, S., & Miller, I. W. (2004). Adherence to treatment of depression in active injection drug users: The Minerva study. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 26(2), 87–93.
Vitiello, B., Burnam, A. M., Bing, E. G., Beckman, R., & Shapiro, M. F. (2003). Use of psychotropic medications among HIV infected patients in the United States. American Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 547–555.
Ware, J. E. Jr., & Sherbourne, C. D. (1992) The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care, 30(6), 473–483.
Wight, R. G., Aneshensel, C. S., & Leblanc, A. J. (2003). Stress buffering effects of family supports in AIDS caregiving. AIDS Care, 15, 595–613.
Zisook, S., Peterkin, J., Groggin, K. J., Sledge, P., Atkinson, J. H., & Grant, I. (1998). Treatment of major depression in HIV seropositive men. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 59, 217–224.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded in part by National Institute of Health grants MH62719 and MH63051.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stein, M.D., Herman, D.S., Bishop, D. et al. A Telephone-Based Intervention for Depression in HIV Patients: Negative Results from a Randomized Clinical Trial. AIDS Behav 11, 15–23 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-006-9131-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10461-006-9131-5