Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to compare the intraocular pressure (IOP) results measured by the iCare rebound tonometer with those obtained by the Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT) over a wide range of IOP values. Furthermore, the comfort level of the iCare measurement was evaluated.
Method
The study included 75 eyes of 75 patients. The patients were divided into three groups (7–15 mmHg n = 25, 16–22 mmHg n = 25, 23–60 mmHg n = 25). The measurements were taken by two independent observers in a masked fashion. All patients were asked about discomfort during the iCare measurement. To establish the agreement between the two devices, a Bland-Altman analysis was performed.
Results
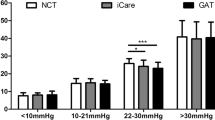
Overall, the 95% confidence interval of the differences between the two devices was −8.67 to 10.25 mmHg and in 62.7%, the iCare measurement was within ±3 mmHg of the GAT measurements. The distribution of the differences in IOP was similar, from 7–22 mmHg. In the higher IOP range (23–60 mmHg), however, the deviation was almost twice as large. The measurement with the iCare tonometer was well tolerated; 100% of the patients denied any discomfort.
Conclusions
The iCare tonometer is a mobile alternative to GAT in a low to moderate IOP range, but our findings show a greater deviation than previously reported. In high IOP values, measurements with the iCare tonometer do not correlate well with GAT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS) : 7 (2000) The relationship between control of intraocular pressure and visual field deterioration. The AGIS Investigators. Am J Ophthalmol 130(4):429–440
Internationaler Standard für Augentonometer ISO 8612 (2001) Beuth-Verlag GmbH, Berlin
Bechrakis E (1966) On spontaneous decrease of pressure in applanation tonometry. Ophthalmologica 151(5):604–614
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Brusini P, Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M, Tosoni C, Parisi L (2006) Comparison of ICare tonometer with Goldmann applanation tonometer in glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma 15(3):213–217
Chapman CR, Casey KL, Dubner R, Foley KM, Gracely RH, Reading AE (1985) Pain measurement: an overview. Pain 22(1):1–31
Davies LN, Bartlett H, Mallen EA, Wolffsohn JS (2006) Clinical evaluation of rebound tonometer. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 84(2):206–209
Dekking HM, Coster HD (1967) Dynamic tonometry. Ophthalmologica 154(1):59–74
Fernandes P, Diaz-Rey JA, Queiros A, Gonzalez-Meijome JM, Jorge J (2005) Comparison of the ICare rebound tonometer with the Goldmann tonometer in a normal population. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25(5):436–440
Goldmann H, Schmidt T (1957) About applanation tonometry. Ophthalmologica 134(4):221–242
Heijl A, Leske MC, Bengtsson B, Hyman L, Bengtsson B, Hussein M (2002) Reduction of intraocular pressure and glaucoma progression: results from the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Arch Ophthalmol 120(10):1268–1279
Iliev ME, Goldblum D, Katsoulis K, Amstutz C, Frueh B (2006) Comparison of rebound tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry and correlation with central corneal thickness. Br J Ophthalmol 90(7):833–835
Kohlhaas M, Boehm AG, Spoerl E, Pursten A, Grein HJ, Pillunat LE (2006) Effect of central corneal thickness, corneal curvature, and axial length on applanation tonometry. Arch Ophthalmol 124(4):471–476
Kontiola A, Puska P (2004) Measuring intraocular pressure with the Pulsair 3000 and Rebound tonometers in elderly patients without an anesthetic. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242(1):3–7
Kontiola AI (2000) A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 78(2):142–145
Kontiola AI (2003) Developing impact tonometers for clinical use and glaucoma research. Finland: Department of Ophthalmology, University of Helsinki
Kontiola AI, Goldblum D, Mittag T, Danias J (2001) The induction/impact tonometer: a new instrument to measure intraocular pressure in the rat. Exp Eye Res 73(6):781–785
Krakau CE, Wilke K (1971) On repeated tonometry. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 49(4):611–614
Obbink J (1931) Onderzoek naar het verband tusschen inwendigen oogdruk en ballistische reacties. Thesis, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Parker VA, Herrtage J, Sarkies NJ (2001) Clinical comparison of the Keeler Pulsair 3000 with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Br J Ophthalmol 85(11):1303–1304
Phelps CD, Phelps GK (1976) Measurement of intraocular pressure: a study of its reproducibility. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol 198(1):39–43
Sandhu SS, Chattopadhyay S, Birch MK, Ray-Chaudhuri N (2005) Frequency of goldmann applanation tonometer calibration error checks. J Glaucoma 14(3):215–218
Schreiber W, Vorwerk CK, Langenbucher A, Behrens-Baumann W, Viestenz A (2007) A comparison of rebound tonometry (ICare) with TonoPenXL and Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ophthalmologe 104:299–304
van der Jagt LH, Jansonius NM (2005) Three portable tonometers, the TGDc-01, the ICARE and the Tonopen XL, compared with each other and with Goldmann applanation tonometry*. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 25(5):429–435
Wessels IF, Oh Y (1990) Tonometer utilization, accuracy, and calibration under field conditions. Arch Ophthalmol 108(12):1709–1712
Acknowledgements
For the study the iCare rebound tonometer was provided by PESCHKE GmbH, Nürnberg, Germany. This was the only source of funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munkwitz, S., Elkarmouty, A., Hoffmann, E.M. et al. Comparison of the iCare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer over a wide IOP range. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246, 875–879 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-007-0758-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-007-0758-3