Abstract
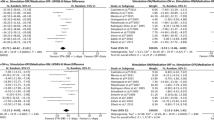
Until recent years there has been no evidence from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on the efficacy of deep brain stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson’s disease (PD). This review and meta-analysis of RCTs describes the efficacy of DBS in improving motor signs, functionality and quality of life of PD patients. Several electronic databases were consulted up to April 2013. RCTs that compared DBS plus medication versus medication (alone or plus sham DBS) in PD patients were included. Outcome measures were motor function, waking time on good functioning without troublesome dyskinesias, levodopa-equivalent dose reduction, medication-induced complications, activities of daily living, health-related quality of life, and neurocognitive and psychiatric effects. Six RCTs (n = 1,184) that compared DBS plus medication versus medication alone were included. The results show that DBS significantly improves patients’ symptoms, functionality and quality of life. Effects sizes are intense for the reduction of motor signs and improvement of functionality in the off-medication phase, in addition to the reduction of the required medication dose and its associated complications. Moderate effects were observed in the case of motor signs and time in good functionality in the on-medication phase, in addition to the quality of life. Although the number of RCTs obtained is small, the total sample size is relatively large, confirming the efficacy of DBS in the control of motor signs and improvement of patients’ functionality and quality of life. More controlled research is required on the neurocognitive and psychiatric effects of DBS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
LP: Lilisbeth Perestelo-Pérez; AR: Amado Rivero-Santana.
LP: Lilisbeth Perestelo-Pérez; AR: Amado Rivero-Santana; JPR: Jeanette Pérez-Ramos; PS: Pedro Serrano-Pérez; JP: Josefina Panetta.
References
Follett KA (2000) The surgical treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Ann Rev Med 51:135–147
Rezai AR, Kopell BH, Gross RE et al (2006) Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: surgical issues. Mov Disord 21:197–218
Rodriguez RL, Fernandez HH, Haq I, Okun MS (2007) Pearls in patient selection for deep brain stimulation. Neurologist 13:253–260
Benabid AL (2003) Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13:696–706
Pillon B, Ardouin C, Damier P et al (2000) Neuropsychological changes between “off” and “on” STN or GPi stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 55:411–418
Lagrange E, Krack P, Moro E et al (2002) Bilateral subthalamic nucleus stimulation improves health-related quality of life in PD. Neurology 59:1976–1978
Tavella A, Bergamasco B, Bosticco E et al (2002) Deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease: long-term follow-up. Neurol Sci 23:S111–S112
Weaver F, Follett K, Hur K, Ippolito D, Stern M (2005) Deep brain stimulation in Parkinson disease: a metaanalysis of patient outcomes. J Neurosurg 103:956–967
Kleiner-Fisman G, Herzog J, Fisman DN et al (2006) Subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation: summary and meta-analysis of outcomes. Mov Disord 21:S290–S304
Andrade P, Carrillo-Ruiz JD, Jiménez F (2009) A systematic review of the efficacy of globus pallidus stimulation in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Clin Neurosci 16:877–881
Sharma A, Szeto K, Desilets AR (2012) Efficacy and safety of deep brain stimulation as an adjunct to pharmacotherapy for the treatment of Parkinson disease. Ann Pharmacother 46:248–254
Parsons TD, Rogers SA, Braaten AJ, Woods SP, Tröster AI (2006) Cognitive sequelae of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 5:578–588
Appleby BS, Duggan PS, Regenberg A, Rabins PV (2007) Psychiatric and neuropsychiatric adverse events associated with deep brain stimulation: a meta-analysis of 10 years’ experience. Mov Disord 22:1722–1728
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman D, The PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Ann Int Med 151:264–269
DerSimonian R, Laird N (1986) Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trial 7:177–188
Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P et al (2006) A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 355:896–908
Witt K, Daniels C, Reiff J et al (2008) Neuropsychological and psychiatric changes after deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: a randomised, multicentre study. Lancet Neurol 7:605–614
Schüpbach WMM, Maltête D, Houeto JL et al (2007) Neurosurgery at an earlier stage of Parkinson disease: a randomized, controlled trial. Neurology 68:267–271
Weaver FM, Follett K, Stern M et al (2009) Bilateral deep brain stimulation vs best medical therapy for patients with advanced Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 301:63–73
Williams A, Gill S, Varma T et al (2010) Deep brain stimulation plus best medical therapy versus best medical therapy alone for advanced Parkinson’s disease (PD SURG trial): a randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol 9:581–591
Okun MS, Gallo BV, Mandybur G et al (2012) Subthalamic deep brain stimulation with a constant-current device in Parkinson’s disease: an open-label randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 11:140–149
Schuepbach WMM, Rau J, Knudsen K et al (2013) Neurostimulation for Parkinson’s disease with early motor complications. N Engl J Med 368:610–622
Schüpbach WM, Chastan N, Welter ML et al (2005) Stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease: a 5 year follow up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1640–1644
Kleiner-Fisman G, Fisman DN, Sime E, Saint-Cyr JA, Lozano AM, Lang AE (2003) Long-term follow up of bilateral deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in patients with advanced Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 99:489–495
Follett KA, Weaver FM, Stern M et al (2010) Pallidal versus subthalamic deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 362:2077–2091
Burkhard PR, Vingerhoets FJ, Berney A, Bogousslavsky J, Villemure JG, Ghika J (2004) Suicide after successful deep brain stimulation for movement disorders. Neurology 63:2170–2172
Soulas T, Gurruchaga JM, Palfi S, Cesaro P, Nguyen JP, Fénelon G (2008) Attempted and completed suicides after subthalamic nucleus stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:952–954
Voon V, Krack P, Lang AE et al (2008) A multicentre study on suicide outcomes following subthalamic stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Brain 131:2720–2728
Weintraub D, Duda JE, Carlson K et al (2013) Suicide ideation and behaviours after STN and GPi DBS surgery for Parkinson’s disease: results from a randomised, controlled trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84:1113–1118
Tsai ST, Hung HY, Hsieh TC, Lin SH, Lin SZ, Chen SY (2013) Long-term outcome of young onset Parkinson’s disease after subthalamic stimulation—a cross-sectional study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115:2082–2087
St George RJ, Nutt JG, Burchiel KJ, Horak FB (2010) A meta-regression of the long-term effects of deep brain stimulation on balance and gait in PD. Neurology 75:1292–1299
Robertson LT, St George RJ, Carlson-Kuhta P, Hogarth P, Burchiel KJ, Horak FB (2011) Site of deep brain stimulation and jaw velocity in Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 115:985–994
Weaver FM, Follett KA, Stern M et al (2012) Randomized trial of deep brain stimulation for Parkinson disease: thirty-six-month outcomes. Neurology 79:55–65
St George RJ, Carlson-Kuhta P, Burchiel KJ, Hogarth P, Frank N, Horak FB (2012) The effects of subthalamic and pallidal deep brain stimulation on postural responses in patients with Parkinson disease. J Neurosurg 116:1347–1356
Odekerken VJ, van Laar T, Staal MJ et al (2013) Subthalamic nucleus versus globus pallidus bilateral deep brain stimulation for advanced Parkinson’s disease (NSTAPS study): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 12:37–44
Temel Y, Wilbrink P, Duits A et al (2007) Single electrode and multiple electrode guided electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus in advanced Parkinson’s disease. Neurosurgery 61:346–355
Temel Y, Prinsenberg T, Visser-Vandewalle V (2008) Imaging of the subthalamic nucleus for deep brain stimulation: a systematic review. Neuromodulation 11:8–12
Farris S, Giroux M (2013) Retrospective review of factors leading to dissatisfaction with subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation during long-term management. Surg Neurol Int 4:69
Angeli A, Mencacci NE, Duran R et al (2013) Genotype and phenotype in Parkinson’s disease: lessons in heterogeneity from deep brain stimulation. Mov Disord 28:1370–1375
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank to Leticia Cuellar for her technical assistance with the search strategies and to Mª Carmen Bujalance for her assistance with the literature retrieval. The authors would also like to thank Jason Willis-Lee for his copyediting support. This study was funded by Spanish Health Ministry (Ministerio de Sanidad, Servicios Sociales e Igualdad).
Conflicts of interest
All authors stated that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Ethical standard
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perestelo-Pérez, L., Rivero-Santana, A., Pérez-Ramos, J. et al. Deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Neurol 261, 2051–2060 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7254-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7254-6