Abstract
Background
Although buprenorphine therapy has proved to be successful in opioid maintenance treatments, the drug is also widely abused in many countries by intravenous injection or sniffing (“snorting”). In Finland, buprenorphine is the most important abused opioid causing fatal poisonings.
Purpose
To evaluate the drug and alcohol findings as well as the cause and manner of death in all buprenorphine-related post-mortem cases for the age group 14–44 years in Finland from 2000 to 2008.
Method
This was a retrospective analysis of data on opioid-associated deaths in the Finnish comprehensive postmortem toxicology database based on medico-legal autopsies, case background information and laboratory analyses.
Results
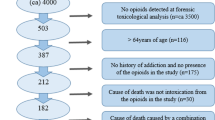
Buprenorphine was found in 29% of all 1,363 opioid-positive cases, and buprenorphine poisoning was the cause of death in 182 cases out of 391 buprenorphine-positive cases (47%). In these fatal poisonings, the blood buprenorphine/norbuprenorphine concentration ratio was significantly higher than in cases with other causes of death. The manner of death in buprenorphine poisonings that were almost exclusively accidental differed significantly from other buprenorphine-related cases, which also involved diseases and suicides. Death was immediate in 10% of fatal buprenorphine poisonings, was delayed, during sleep, in 52%, and followed an unknown course of events in 38%. In immediate poisonings, the median blood buprenorphine concentration (3.0 μg/l) was significantly higher than that in delayed poisonings (1.2 μg/l). In most buprenorphine poisonings (92%), no opioids other than buprenorphine were involved, but benzodiazepines and alcohol were found in 82 and 58% of cases, respectively. The median concentrations of opioids and benzodiazepines in buprenorphine poisonings were in the therapeutic range. Only one fatal poisoning was found in which neither alcohol nor drugs other than buprenorphine were found.
Conclusion
A fatal buprenorphine poisoning is typically accidental, and the average victim is a 27-year-old male addict. Circumstantial and environmental factors seem to be crucial in determining the outcome of the poisoning.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jasinski DR, Pevnick JS, Griffith JD (1978) Human pharmacology and abuse potential of the analgesic buprenorphine: a potential agent for treating narcotic addiction. Arch Gen Psychiatry 35:501–516
Lewis JW (1973) Ring C-bridged derivatives of thebaine and oripavine. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 8:123–136
Cowan A, Doxey JC, Harry EJ (1977) The animal pharmacology of buprenorphine, an oripavine analgesic agent. Br J Pharmacol 60:547–554
Cowan A, Lewis JW, Macfarlane IR (1977) Agonist and antagonist properties of buprenorphine, a new antinociceptive agent. Br J Pharmacol 60:537–545
Martin WR, Eades CG, Thompson JA, Huppler RE, Gilbert PE (1976) The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 197:517–532
Negus SS, Dykstra LA (1988) Kappa antagonist properties of buprenorphine in the shock titration procedure. Eur J Pharmacol 156:77–86
Leander JD (1988) Buprenorphine is a potent kappa-opioid receptor antagonist in pigeons and mice. Eur J Pharmacol 151:457–461
Mello NK, Mendelson JH (1980) Buprenorphine suppresses heroin use by heroin addicts. Science 207:657–659
Brewster D, Humphrey MJ, McLeavy MA (1981) Biliary excretion, metabolism and enterohepatic circulation of buprenorphine. Xenobiotica 11:189–196
Cone EJ, Gorodetzky CW, Yousefnejad D, Buchwald WF, Johnson RE (1984) The metabolism and excretion of buprenorphine in humans. Drug Metab Dispos 12:577–581
Ohtani M, Kotaki H, Sawada Y, Iga T (1995) Comparative analysis of buprenorphine- and norbuprenorphine-induced analgesic effects based on pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 272:505–510
Kobayashi K, Yamamoto T, Chiba K, Tani M, Shimada N, Ishizaki T, Kuroiwa Y (1998) Human buprenorphine N-dealkylation is catalyzed by cytochrome P450 3A4. Drug Metab Dispos 26:818–821
Elkader A, Sproule B (2005) Buprenorphine: Clinical pharmacokinetics in the treatment of opioid dependence. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:661–680
Steentoft A, Teige B, Holmgren P, Vuori E, Kristinsson J, Hansen AC, Ceder G, Wethe G, Rollmann D (2006) Fatal poisoning in Nordic drug addicts in 2002. Forensic Sci Int 160:148–156
European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) (2009) Drug situation—Finland 2009. National Report to the EMCDDA. EMCDDA, Lisbon
Simonsen KW, Normann PT, Ceder G, Vuori E, Thordardottir S, Thelander G, Hansen AC, Teige B, Rollmann D (2011) Fatal poisoning in drug addicts in the Nordic countries in 2007. Forensic Sci Int 207:170–176
Aalto M, Visapää J, Halme JT, Fabritius C, Salaspuro M (2011) Effectiveness of buprenorphine maintenance treatment as compared to a syringe exchange program among buprenorphine misusing opioid-dependent patients. Nord J Psychiatry 65:238–243
Lintzeris N, Nielsen S (2009) Benzodiazepines, methadone and buprenorphine: interactions and clinical management. Am J Addiction 19:59–72
White JM, Irvine RJ (1999) Mechanisms of fatal opioid overdose. Addiction 94:961–972
Gerostamoulos J, Staikos V, Drummer OH (2001) Heroin-related deaths in Victoria: a review of cases for 1997 and 1998. Drug Alcohol Depend 61:123–127
Caplehorn JR, Drummer OH (2002) Fatal methadone toxicity: signs and circumstances, and the role of benzodiazepines. Aust NZ J Publ Heal 26:358–362
Faroqui MH, Cole M, Curran J (1983) Buprenorphine, benzodiazepines and respiratory depression. Anaesthesia 38:1002–1003
Papworth DP (1983) High dose buprenorphine for postoperative analgesia. Anaesthesia 38:163
Tracqui A, Kintz P, Ludes B (1998) Buprenorphine-related deaths among drug addicts in France: a report on 20 fatalities. J Anal Toxicol 22:430–434
Reynaud M, Petit G, Potard D, Courty P (1998) Six deaths linked to concomitant use of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines. Addiction 93:1385–1392
Kintz P (2001) Deaths involving buprenorphine: a compendium of French cases. Forensic Sci Int 121:65–69
Kintz P (2002) A new series of 13 buprenorphine-related deaths. Clin Biochem 35:513–516
Pirnay S, Borron SW, Giudicelli CP, Tourneau J, Baud FJ, Ricordel I (2004) A critical review of the causes of death among post-mortem toxicological investigations: analysis of 34 buprenorphine-associated and 35 methadone-associated deaths. Addiction 99:978–988
Lai SH, Yao YJ, Lo DST (2006) A survey of buprenorphine related deaths in Singapore. Forensic Sci Int 162:80–86
Ferrant O, Papin F, Clin B, Lacroix C, Saussereau E, Remoué J, Goullé J (2011) Fatal poisoning due to snorting buprenorphine and alcohol consumption. Forensic Sci Int 204:e8–e11
Nielsen S, Taylor DA (2005) The effect of buprenorphine and benzodiazepines on respiration in the rat. Drug Alcohol Depend 79:95–101
Lintzeris N, Mitchell TB, Bond AJ, Nestor L, Strang J (2007) Pharmacodynamics of diazepam co-administered with methadone or buprenorphine under high dose conditions in opioid dependent patients. Drug Alcohol Depend 91:187–194
Lunetta P, Lounamaa A, Sihvonen S (2007) Surveillance of injury-related deaths: medicolegal autopsy rates and trends in Finland. Inj Prev 13:282–284
Launiainen T, Vuori E, Ojanperä I (2009) Prevalence of adverse drug combinations in a large post-mortem toxicology database. Int J Legal Med 123:109–115
Baselt RC (2008) Disposition of toxic drugs and chemicals in man. Biomedical Publications, Foster City
Druid H, Holmgren P (1997) A compilation of fatal and control concentrations of drugs in postmortem femoral blood. J Forensic Sci 42:79–87
Gergov M, Nokua P, Vuori E, Ojanperä I (2009) Simultaneous screening and quantification of 25 opioid drugs in post-mortem blood and urine by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci Int 186:36–43
Pelander A, Ojanperä I, Sistonen J, Rasanen I, Vuori E (2003) Screening for basic drugs in 2-mL urine samples by dual-plate overpressured layer chromatography and comparison with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 27:226–232
Pelander A, Ojanperä I, Laks S, Rasanen I, Vuori E (2003) Toxicological screening with formula-based metabolite identification by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 75:5710–5718
Ojanperä S, Pelander A, Pelzing M, Krebs I, Vuori E, Ojanperä I (2006) Isotopic pattern and accurate mass determination in urine drug screening by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Sp 20:1161–1167
Ojanperä I, Rasanen I, Vuori E (1991) Automated quantitative screening for acidic and neutral drugs in whole blood by dual-column capillary gas chromatography. J Anal Toxicol 15:204–208
Rasanen I, Ojanpera I, Vuori E (2000) Quantitative screening for benzodiazepines in blood by dual-column gas chromatography and comparison of the results with urine immunoassay. J Anal Toxicol 24:46–53
Rasanen I, Kontinen I, Nokua J, Ojanperä I, Vuori E (2003) Precise gas chromatography with retention time locking in comprehensive toxicological screening for drugs in blood. J Chromatogr B 788:243–250
Bullingham RES, McQuay HJ, Moore RA, Bennett MRD (1980) Buprenorphine kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 28:667–672
Seldén T, Roman M, Druid H, Kronstrand R (2011) LC–MS–MS analysis of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine in whole blood from suspected drug users. Forensic Sci Int 209:113–119
Pelissier-Alicot A, Sastre C, Baillif-Couniou V, Gaulier J, Kintz P, Kuhlmann E, Perich P, Bartoli C, Piercecchi-Marti M, Leonetti G (2010) Buprenorphine-related deaths: unusual forensic situations. Int J Legal Med 124:647–651
Larance B, Degenhardt L, O'Brien S, Lintzeris N, Winstock A, Mattick RP, Bell J, Ali R (2011) Prescribers' perceptions of the diversion and injection of medication by opioid substitution treatment patients. Drug Alcohol Rev. doi:10.1111/j.1465-3362.2010.00274.x
Heikman PK, Ojanperä IA (2009) Inadequate dose of opioid-agonist medication is related to misuse of benzodiazepine. Addict Disord Their Treatment 8:145–153
Nielsen S, Dietze P, Lee N, Dunlop A, Taylor D (2007) Concurrent buprenorphine and benzodiazepines use and self-reported opioid toxicity in opioid substitution treatment. Addiction 102:616–622
Acknowledgements
Margareeta Häkkinen received a research grant for this study from the Finnish Foundation for Alcohol Studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Häkkinen, M., Launiainen, T., Vuori, E. et al. Benzodiazepines and alcohol are associated with cases of fatal buprenorphine poisoning. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 68, 301–309 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-011-1122-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-011-1122-4