Abstract
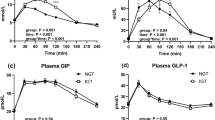
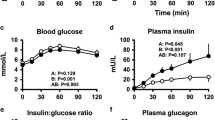
Plasma glucose, insulin, glucagon and growth hormone responses to both oral glucose and iv arginine were evaluated in 15 heroin addicts and 15 control subjects matched for age, sex and weight. The heroin users had an exaggerated rise in plasma glucose concentrations following oral sugar, which persisted until the end of the study (102 ± 5 mg/dl in addicts vs 72 ± 3 mg/dl in controls at 240 min, p <0.01) and significantly lower insulin responses (insulin peak 28 ± 4 μU/ml in addicts vs 67 ± 8 μU/ml in controls, p < 0.01). The inhibitory effect of glucose on glucagon concentrations was less evident in addicts than in controls. The responses of plasma glucose, insulin and glucagon to arginine were not significantly different between addicts and controls, while the growth hormone rise was significantly greater in addicts. These results demonstrate that heroin users have impaired insulin secretion to oral glucose but not to arginine and suggest that: a) the impaired insulin secretion in heroin addicts is not dependent on beta-cell exhaustion, and b) a selective inhibition of glucose-induced insulin secretion is operative in these subjects, as it happens in patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Passariello N., Giugliano D., Quatraro A., Consoli G., Sgambato S., Torella R., D’Onofrio F. Glucose tolerance and hormonal responses in heroin addicts. A possible role for endogenous opiates in the pathogenesis of noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Metabolism 32: 1163, 1983.
Robertson R.P., Porte D. Jr. The glucose receptor: a defective mechanism in diabetes mellitus distinct from the beta-adrenergic receptor. J. Clin. Invest. 52: 870, 1973.
Palmer J.P., Benson J.W., Walter R.M., Ensinck J.W. Arginine-stimulated acute phase of insulin and glucagon secretion in diabetic subjects. J. Clin. Invest. 58: 565, 1976.
Leslie R.D.G., Pyke D.A., Stubbs W.A. Sensitivity to enkephalins as a cause of noninsulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet 1: 341, 1979.
Giugliano D. Morphine, opioid peptides and pancreatic islet function. Diabetes Care 7: 92, 1984.
Red J.L., Ghodse A.H. Oral glucose tolerance and hormonal response in heroin-dependent males. Br. Med. J. 2: 582, 1973.
Vescovi P.P., Pezzarossa A., Caccavari R., Valenti G., Butturini U. Glucose tolerance in opiate addicts. Diabetologia 23: 459, 1982.
Radosevich P.M., Williams P.E., Brooks Lacy D., McRae J.R., Steiner K.E., Cherrington A.D., Lacy W.W., Abumrad N.N. Effects of morphine on glucose homeostasis in the conscious dog. J. Clin. Invest. 74: 1473, 1984.
Feldman M., Kiser R.S., Unger R.H., Li C.H. Beta-endorphin and the endocrine pancreas. Studies in healthy and diabetic human beings. N. Engl. J. Med. 308: 349, 1983.
Giugliano D., Salvatore T., Cozzolino D., Ceriello A., Torella R., D’Onofrio F. Hyperglycemia and obesity as determinants of glucose, insulin and glucagon responses to beta-endorphin in human diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. in press (?).
Giugliano D. Secrezione insulinica nel diabete noninsulino-dipendente. Gior. Ital. Diabetol. 5: 347, 1985.
Ceriello A., Giugliano D., Dello Russo P., Sgambato S., D’Onofrio F. Increased glycosylated hemoglobin A1 in opiate addicts: evidence for hyperglycemic effect of morphine. Diabetologia 22: 379, 1982.
Ceriello A., Dello Russo P., Curcio F., Rossano P. Increased glycosylated proteins in opiate addicts. Diabetes Care 7: 104, 1984.
Ceriello A., Dello Russo P., Niola O., Schimizzi S., Capezzuto C. Fibrinogen levels in opiate addicts. Thromb. Haemostas. 50: 759, 1983.
Dello Russo P., Ceriello A., Passariello N., Giugliano D. Hemoglobin A1 in addicts. Ann. Intern. Med. 96: 536, 1982.
Ceriello A., Dello Russo P., Curcio F., Petringa D., D’lppolito S., Varriale M. Morphine, diabetes and lipid metabolism. Arch. Intern. Med. 143: 1070, 1983.
Ceriello A., Dello Russo P., Curcio F., Tirelli A., Giugliano D. Depressed antithrombin III biological activity in opiate addicts. J. Clin. Pathol. 37: 1040, 1984.
Ceriello A., Dello Russo P., Zuccotti C., Florio A., Nazzaro S., Pietrantuono C., Rosato G.B. Decreased antithrombin III activity in diabetes may be due to non-enzymatic glycosylation. A preliminary report. Thromb. Haemostas. 50: 633, 1983.
Jeanrenaud X., Maeder E., Del Pozo E., Felber J.P. Effect on an enkephalin analogue (FK 33–824) on glucose tolerance in man. Acta Endocrinol. (Kbh.) 104: 85, 1983.
Reid R.L., Sandler J.A., Yen S.S.C. Beta-endorphin stimulates the secretion of insulin and glucagon in diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 33: 197, 1984.
Giugliano D., Quatraro A., Consoli G., Ceriello A., Torella R., D’Onofrio F. Inhibitory effect of enkephalin upon insulin secretion in healthy subjects and in non-insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. Metabolism (in press).
Giugliano D., Ceriello A., Quatraro A., D’Onofrio F. Endogenous opiates, heroin addiction and non insulin-dependent diabetes. Lancet 2: 769, 1985.
Bruni J.F., Watkins W.B., Yen S.S.C. Beta-endorphin in the human pancreas. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 49: 646, 1979.
Giugliano D., Ceriello A., Di Pinto P., Saccomanno F., Gentile S., Cacciapuoti F. Impaired insulin secretion in human diabetes mellitus. The effect of naloxone-induced opiate receptor blockade. Diabetes 31: 367, 1982.
Radosevich P.M., Williams P.E., McRae J.R., Lacy W.W., Orth D.N., Abumrad N.N. Beta-endorphin inhibits glucose production in the conscious dog. J. Clin. Invest. 73: 1237, 1984.
Sullivan S.N., Lamki L., Corcoran P. Inhibition of gastric emptying by enkephalin analogue. Lancet 2: 86, 1981.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Passariello, N., Giugliano, D., Ceriello, A. et al. Impaired insulin response to glucose but not to arginine in heroin addicts. J Endocrinol Invest 9, 353–357 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346942
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03346942