Abstract
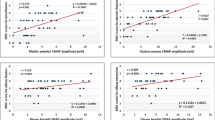
Sensory nerve function was determined in 19 patients with amyotrophie lateral sclerosis (ALS), using a battery of clinical and neurophysiological tests. This assessment was repeated on 12 patients after intervals of 6–18 months. Twelve controls were also studied. In the ALS group, only 2 patients had noticed mild sensory symptoms and none had sensory signs. Between successive studies the vibration thresholds increased, but not to a significant degree. ALS patients showed a significant fall in amplitude of the sensory nerve action potentials in the median, radial, and sural nerves (P < 0.04); sensory nerve conduction velocity did not alter. The median nerve somatosensory evoked potential N19 latency showed a highly significant increase (P < 0.008). Significant subclinical deterioration in sensory nerve function occurs in ALS, and parallels the progressive motor decline. Neuronal degeneration in ALS is not restricted to motor neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anziska BJ, Cracco RQ (1983) Short-latency somatosensory evoked potentials to median nerve stimulation in patients with diffuse neurologie disease. Neurology 33:989–993
Averback P, Crocker P (1982) Regular involvement of Clarke's nucleus in sporadic amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 39:155–156
Behnia M, Kelly JJ (1991) Role of electromyography in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 14:1236–1241
Bradley WG, Good P, Rasool CG, Adelman LS (1983) Morphometric and biochemical studies of peripheral nerves in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 14:267–277
Brownwell B, Oppenheimer DR, Hughes JT (1970) The central nervous system in motor neurone disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 33:338–357
Cascino GD, Ring SR, King PJL, Barwn RH, Chiappa KH (1988) Evoked potentials in motor system diseases. Neurology 38:231–238
Castaigne P, Cambier J, Escourolle R, Brunet P (1971) Sclerose laterale amyotrophique et lesions degeneratives des cordons posterieurs. J Neurol Sci 13:125–135
Charcot JM, Marie P (1985) Deux nouveaux cas de sclerose laterale amyotrophique suivis d'autopsies. Arch Neurol (Paris) 10:168–186
Chaudhry V, Cornblath DR, Mellits D, Freimer ML, Glass JD, Reim J, Ronnett GV, Quaskey SA, Kunci RW (1991) Inter- and intra-examiner reliability of nerve conduction measurements in normal subjects. Ann Neurol 30:841–843
Cosi V, Poloni M, Mazzini L, Callieco R (1984) Somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:857–861
Dasheiff RM, Drake ME, Brendle A, Erwin CW (1985) Abnormal somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 60:306–311
Davison C, Wechsler IS (1936) Amyotrophie lateral sclerosis with involvement of posterior column and sensory disturbances. A clinicopathologic study. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 35:229–239
Delisa JA, Machenzie K, Baron EM (1987) Manual of nerve conduction and somatosensory evoked potentials, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York
Delodovici ML, Terazzi E, Pasetti C, Pinelli P (1987) Analysis of extrinsic factors affecting pallestesic threshold (VT) of amyotrophie lateral sclerosis patients. Adv Exp Med Biol 209:125–128
Dioszeghy P, Egerhazi A, Mechler F (1987) Somatosensory evoked potentials in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 27:163–167
Dyan AD, Graveson GS, Illis LS, Robinson PK (1969) Schwann cell damage in motoneuron disease. Neurology 19:242–246
Dyck PJ, Stevens JC, Mulder DW, Espinosa RE (1975) Frequency of nerve fiber degeneration of peripheral motor and sensory neurons in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Morphometry of deep and superficial peroneal nerves. Neurology 25:781–785
Ertekin C (1967) Sensory and motor conduction in motor neurose disease. Acta Neurol Scand 43:499–512
Feller TG, Jones RE, Netsky MG (1966) Amyotrophie lateral sclerosis and sensory changes. Va Med Mon 93:328–335
Fincham RW, Van Allen MW (1964) Sensory nerve conduction in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Neurology 14:31–33
Friedman AP, Freedman D (1950) Amyohrophic lateral sclerosis. J Nerv Ment Dis 111:1–18
Ghezzi A, Mazzalovo E, Locatelli C, Zibetti A, Zaffaroni M, Montanini R (1989) Multimodality evoked potentials in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 79:353–356
Greenfield JG (1958) System degenerations of the cerebellum, brain stem, and spinal cord. In: Greenfield JG (ed) Neuropathology. Arnold, London, pp 545–548
Gubbay SS, Kahana E, Zilber N, Cooper G, Pintov S, Leibowitz Y (1985) Amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. A study of its presentation and prognosis. J Neurol 232:295–300
Hamida MB, Letaief F, Hentati F, Hamida CB (1987) Morphometric study of the sensory nerve in classical (or Charcot disease) and juvenile a myotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 78:313–329
Heads T, Pollock M, Robertson A, Sutherland WHF, Allpress S (1991) Sensory nerve patholgoy in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 82:316–320
Heidrich R, Krause H, Koch K (1982) Empfindungs- und Sensibilitätsstörungen bei amyotropher Lateralsklerose. Psychiatr Neurol Med Psychol (Leipz) 34:107–110
Hirano A, Kurland LT, Sayre GP (1967) Familial amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 16:232–243
Holmes G (1990) The pathology of amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Rev Neurol Psychiatry 7:693–725
Jamal GA, Weir AI, Hansen S, Ballantyne JP (1985) Sensory involvement in motor neuron disease: further evidence form automated thermal threshold determination. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 48:906–910
Kawamura Y, Dyck PJ, Shimono M, Okazaki H, Tateishi J, Doi H (1981) Morphometric comparison of the vulnerabiltiy of peripheral motor and sensory neurons in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 40:667–675
Lawyer T Jr, Netsky MG (1953) Amyotrophie lateral sclerosis: a clinicoanatomic study of 53 cases. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 69:171–192
Leigh PN (1991) Amyotrophie lateral sclerosis and other motor neurone diseases. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg 4:586–596
Li T, Alberman E, Swash M (1988) Comparison of sporadic and familial disease amongst 580 cases of motor neuron disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:778–784
Luthy F, Martin F (1947) Beobachtungen über zwei Fälle von amyotrophischer Lateralsklerose mit besonderer Berücksichtigung der mitbeteiligten sensiblen Systeme. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 25:694–697
Martyn CN (1987) Neurological clues from environmental neurotoxins. BMJ 295:346–347
Matheson JK, Harrington HJ, Hallett M (1986) Abnormalities of multimodality evoked potentials in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 43:338–340
Mulder DW, Bushek W, Spring E, Karnes J, Dyck PJ (1983) Motor neuron disease (ALS): evaluation of dection thresholds of cutaneous sensation. Neurology 33:1625–1627
Page RW, Moskowitz RW, Nash RE, Roessmann U (1977) Lower motor neuron disease with spinocerebellar degeneration. Ann Neurol 2:524–527
Poole EW (1957) Ischaemic and post-ischaemic paraesthesiae in motor neurone disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatrty 20:225–227
Radtke RA, Erwin A, Erwin CW (1986) Abnormal sensory evoked potentials in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Neurology 36:796–801
Shahani B, Russell WR (1969) Motor neurone disease. An abnormality of nerve metabolism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 32:1–5
Shefner JM, Tyler R, Krarup C (1991) Abnormalities in the sensory action potential in patients with amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 14:1242–1246
Swash M, Scholtz CL, Vowles G, Ingram DA (1988) Selective and asymmetric vulnerability of corticospinal and spinocerebellar tracts in motor neuron disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:785–789
Tashiro K (1984) Sensory disturbances in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis (in Japanese). Rinsho Shinkeigaku 24:1250–1253
Toghi H, Tsukagoshi H, Toyokura Y (1977) Quantitative changes of sural nerves in varions neurological diseases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 38:95–101
Walton J (1985)Motor-neurone disease. In: Walton J (ed) Brain's disases of the nervous system, 9th edn. Oxford Medical Publications Oxford, pp 370–379
Wechsler IS, Brock S, Weil A (1929) Amyotrophie lateral sclerosis with objective and subjective (neuritic) sensory disturbances. A clinical and pathologie report. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 21:299–310
Wechsler IS, Sapirstein MR, Stein A (1944) Primary and symptomatic amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. A clinical study of 81 cases. Am J Med Sci 208:70–81
Williams C, Kozlowski MA, Hinton DR, Miller CA (1990) Degeneration of spinocerebellar neurons in amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 27:215–225
World Federation Neurology (1990) Criteria for diagnosis of amyotrophie lateral sclerosis. World Neurol 5:12
Yamada T, Bosch PE, Kimura J (1984) Somatosensory evoked potentials in motor neuron disease (Abstract). Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 58:54P
Zanette G, Polo, Gasperini M, Berolasi L, Grandis D (1990) Far-field and cortical somatosensory evoked potentials in motor neuron disease. Muscle Nerve 13:47–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregory, R., Mills, K. & Donaghy, M. Progressive sensory nerve dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a prospective clinical and neurophysiological study. J Neurol 240, 309–314 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00838169
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00838169