Abstract
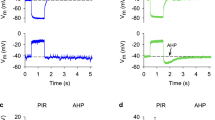
The effect of menthol on voltage-dependent Ca currents was investigated in cultured dorsal root ganglion cells from chick and rat embryos. Bath application of menthol (0.1–1 mM) had different effects on the various Ca currents present in these neurons. Below −20 mV, the low threshold Ca currents were reduced in amplitude in a dose-dependent manner by menthol with little changes of their activation kinetics. In contrast to this, the time course of inactivation of the high-threshold Ca currents, activated above −20 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV, was drastically accelerated by external menthol. The action of menthol was unchanged with more positive holding potentials (−50 mV). Thus, a proposed third type of Ca current with transient activation and complete deactivation below −50 mV was either not present or not affected by menthol. Menthol exerted its action only when applied from the outside. Its effect was completely reversible within 15–20 min of wash-out. Our findings are consistent with the idea that menthol acts on two types of Ca channels coexisting on the membrane of cultured sensory neurons. Menthol blocks currents through the low voltage-activated Ca channel, and facilitates inactivation gating of the classical high voltage-activated Ca channel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong CM, Matteson DR (1985) Two distinct populations of calcium channels in a clonal line of pituitary cell. Science 227:65–67
Barde Y, Edgar D, Thoenen H (1980) Sensory neurons in culture: changing requirements for survival factors during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1199–1203
Bean BP (1985) Two kinds of calcium channels in canine atrial cells. J Gen Physiol 86:1–30
Bevington PR (1969) Data reduction and error analysis for the physical sciences. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 336
Boll W, Lux HD (1985) Action of organic antagonist on neuronal calcium currents. Neurosci Lett 56:335–339
Bossu JL, Feltz A, Thomann JM (1985) Depolarization elicits two distinct calcium currents in vertebrate sensory neurons. Pflügers Arch 403:360–368
Brown AM, Lux HD, Wilson DL (1984) Activation and inactivation of single calcium channels in snail neurons. J Gen Physiol 83:751–769
Byerly L, Hagiwara S (1982) Calcium currents in internally perfused nerve cell bodies ofLimmea stagnalis. J Physiol (Lond) 322:503–528
Carbone E, Lux HD (1984a) A low voltage-activated calcium conductance in embryonic chick sensory neurons. Biophys J 46:413–418
Carbone E, Lux HD (1984b) A low voltage-activated fully inactivating calcium channel in vertebrate sensory neurons. Nature (Lond) 310:501–503
Carbone E, Lux HD (1986a) Low and high voltage-activated Ca channels in vertebrate cultured neurons: properties and function. Exp Brain Res (Suppl) 14:1–8
Carbone E, Lux HD (1986b) Sodium channels in cultured chick dorsal root ganglion neurons. Eur Biophs J 13:259–271
Carbone E, Lux HD (1987) Kinetics and selectivity of a low voltageactivated Ca2+ current in chick and rat sensory neurons. J Physiol (Lond) (in press)
Carbone E, Morad M, Lux HD (1987) External Ni2+ selectively blocks the low-threshold Ca2+ current of chick sensory neurons. Pflügers Arch 408 (Suppl) R60
Deitmer JW (1984) Evidence for two voltage-dependent calcium currents in the membrane of the ciliataStylonychia. J Physiol 355:137–159
DeRiemer SA, Sakamann B (1986) Two calcium currents in normal rat anterior pituitary identified by a plaque assay. Exp Brain Res (Suppl) 14:139–154
Fedulova SA, Kostyuk PG, Veselovsky NS (1985) Two types of calcium channels in the somatic membrane of new-born rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Physiol (Lond) 359:431–446
Fenwick EM, Marty A, Neher E (1982) Sodium and calcium channels in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol (Lond) 331:599–635
Fox AP, Krasne S (1984) Two calcium currents inNeanthes arena ceodentatus egg cell membranes. J Physiol (Lond) 356:491–505
Grisham CM, Barnett RE (1973) The effect of long chain alcohols on membrane lipids and the (Na++K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta 311:417–422
Hagiwara S, Byerly L (1981) Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci 4:69–125
Hagiwara N, Irisawa H, Kameyama M (1987) Transient-type calcium current contributes to the pace-maker potential. J Physiol (Lond) (in press)
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakamann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Haydon DA, Hendry BM, Levison SR, Requena J (1977) Anesthesia by the n-alkanes. A comparative study of nerve impulse blockage and the properties of black lipid bilayer membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 470:17–34
Hille BJ (1984) Ionic channels of excitable membranes. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA
Kostyuk PG, Veselovsky NS, Tsyndrenko AY (1981a) Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. I. Sodium currents. Neuroscience 6:2423–2430
Kostyuk PG, Veselovsky NS, Fedulova SA (1981b) Ionic currents in the somatic membrane of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. II. Calcium currents. Neuroscience 6:2431–2437
Llinas R, Jahnsen H (1982) Electrophosiology of mammalian thalamic neurons in vitro. Nature (Lond)297:406–408
Llinas R, Yarom Y (1981) Properties and distribution of ionic conductances generating electroresponsiveness of mammalian inferior olivary neurones in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 315:569–584
Llinas R, Yarom Y (1986) Specific blockage of the low-threshold calcium channel by high molecular weight alcohols. Neurosciences (Abstract) 12:174
Lux HD, Carbone E, Davies N (1987) Monovalent cation currents through low-and high-threshold Ca2+ channels in chick sensory neurons. Pflügers Arch 408 (Suppl):R60
Marchetti C, Carbone E, Lux HD (1986) Effects of dopamine and noradrenaline on Ca channels of cultured sensory and sympathetic neurons of chick. Pflügers Arch 406:104–111
McCleskey EW, Fox AP, Feldman D, Olivera BM, Tsien RW, Yoshikami D (1986) The peptide toxin ωCgTX blocks particular types of neuronal Ca channels (Abstract). Biophys J 49:431a
Nowycky MC, Fox AP, Tsien RW (1984) Multiple types of calcium channel in dorsal root ganglion cell distinguished by sensitivity to cadmium and single channel properties (Abstract). Soc Neurosci 10:526
Nowycky MC, Fox AP, Tsien RW (1985) Three types of neuronal calcium channels with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature 316:440–443
Swandulla D, Carbone E, Schäfer K, Lux HD (1985) Menthol modulates Ca inactivation in neurons. Pflügers Arch 405 (Suppl):R39
Swandulla D, Schäfer K, Lux HD (1986) Ca channel current inactivation is selectively modulated by menthol. Neurosci Lett 68:23–28
Yaari Y, Hamon B, Lux HD (1987) Development of two distinct types of calcium channels incultured mammalian hippocampal neurons. Science (USA) (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Swandulla, D., Carbone, E., Schäfer, K. et al. Effect of menthol on two types of Ca currents in cultured sensory neurons of vertebrates. Pflugers Arch. 409, 52–59 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584749
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00584749